A Journey Through Time: Exploring The Map Of Mexico In 1830
A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of Mexico in 1830
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of Mexico in 1830
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of Mexico in 1830. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of Mexico in 1830
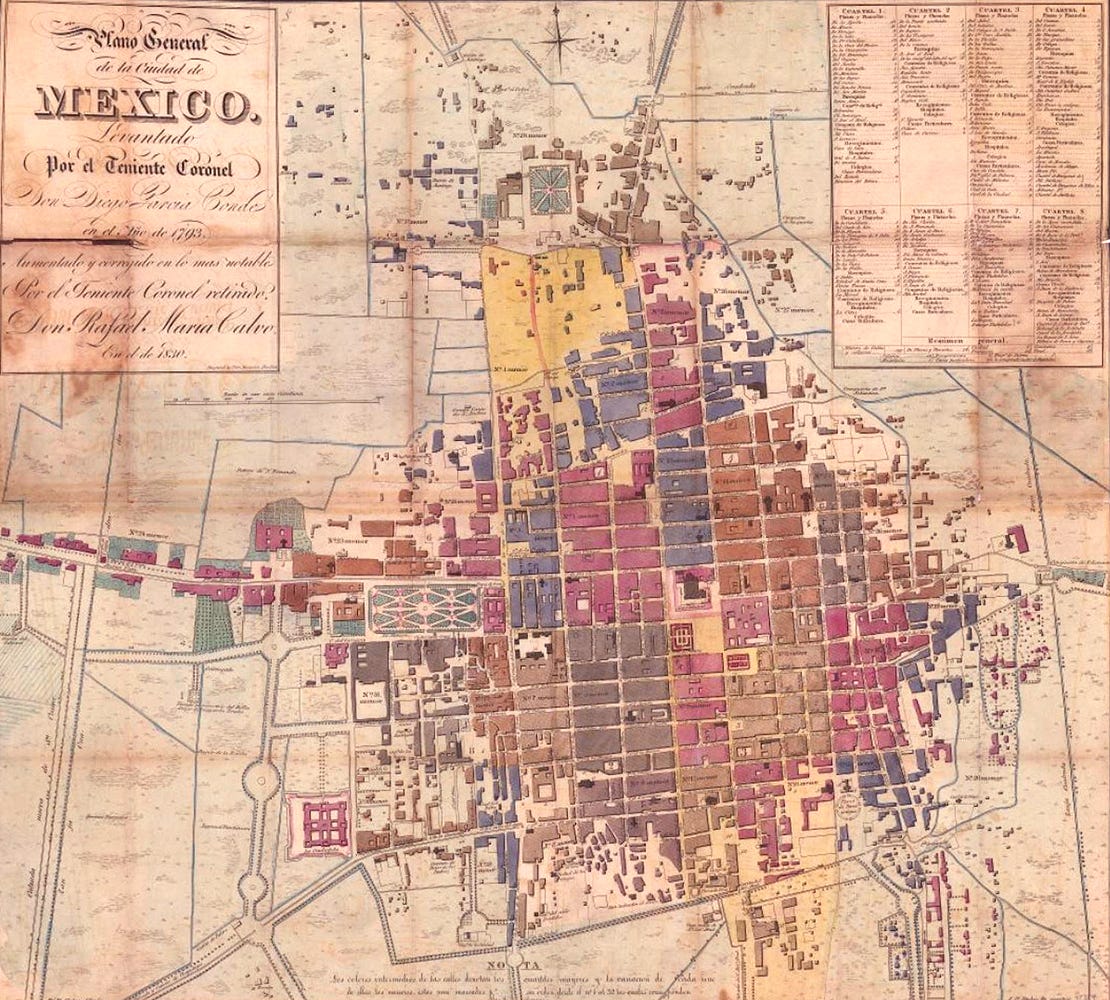
The year 1830 marks a pivotal moment in Mexican history, a period of political turmoil and territorial evolution. This era is vividly captured in maps, historical artifacts that offer a unique lens into the past, revealing not only geographical boundaries but also the complexities of a nation in flux. Examining the map of Mexico in 1830 provides a fascinating glimpse into the nation’s nascent identity, its evolving political landscape, and the seeds of future conflicts.
A Nation in Transition:
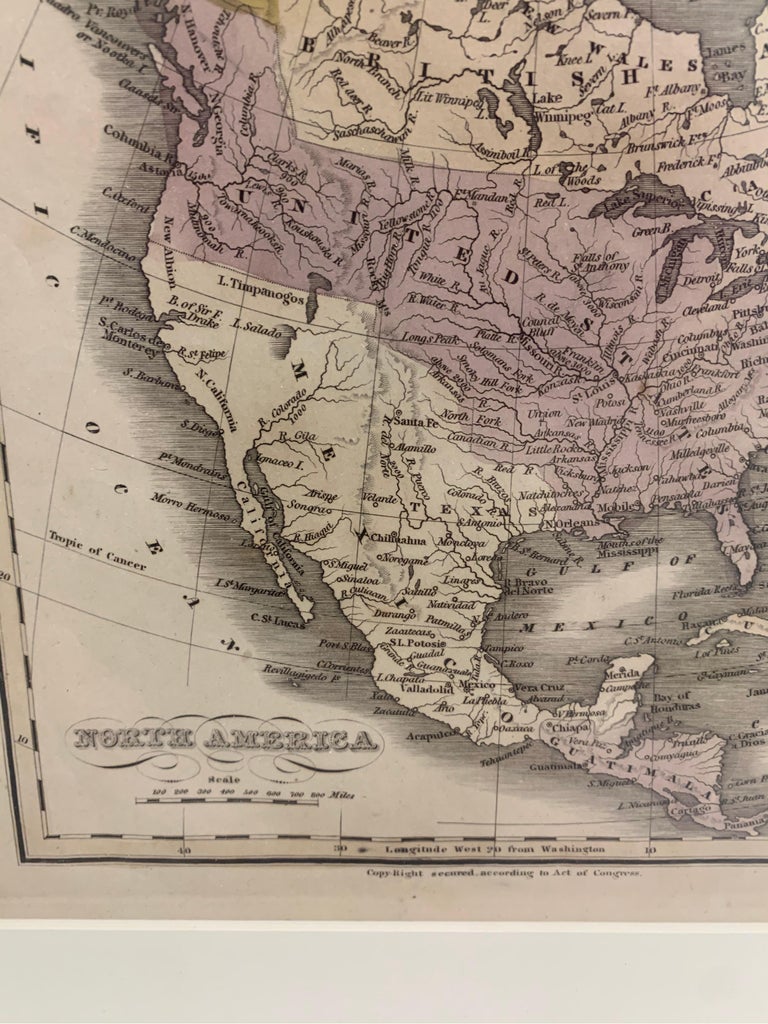
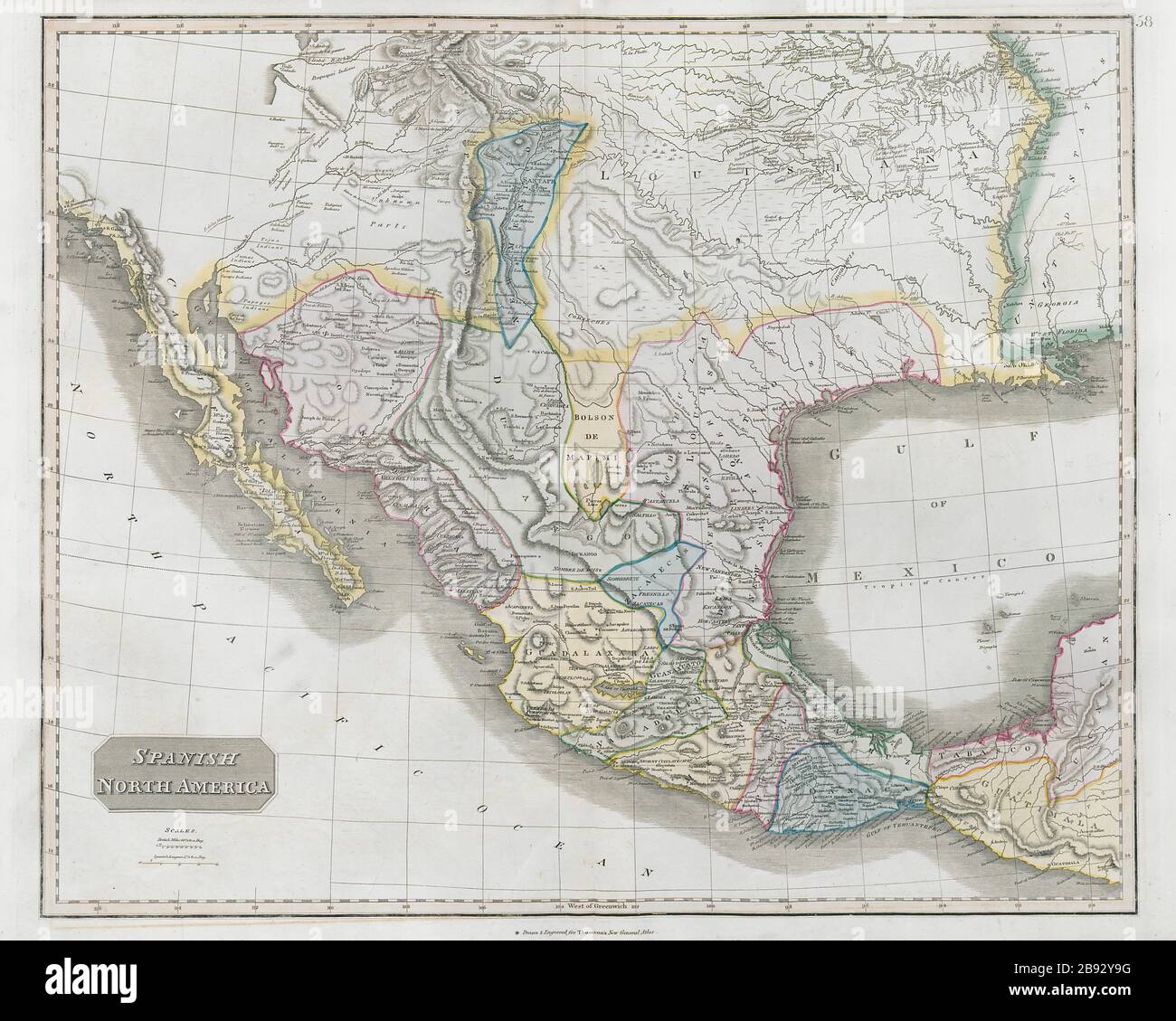
The map of Mexico in 1830 reveals a country vastly different from its modern counterpart. The vast territory encompassed present-day Mexico, Texas, California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, and parts of Oklahoma and Kansas. This expansive territory was the product of Mexico’s independence from Spain in 1821, an event that ushered in a period of significant change. However, the newly formed nation faced internal struggles, grappling with political instability and the challenge of consolidating its vast domain.
The Texas Question:
One of the most striking features of the 1830 map is the presence of Texas as an integral part of Mexico. This region, populated by a growing number of Anglo-American settlers, had become a source of tension between the Mexican government and the burgeoning Anglo-American population. The influx of settlers, coupled with disputes over land ownership and policies, ignited a simmering conflict that would culminate in the Texas Revolution of 1836.
The Northern Frontier:
The map also reveals the vast expanse of Mexico’s northern frontier, a sparsely populated region that stretched from present-day Texas to California. This frontier was a land of immense potential, attracting settlers, traders, and explorers, but it also posed significant challenges for the Mexican government. The vast distances, the presence of indigenous communities, and the growing influence of the United States all contributed to the complexities of managing this region.
The Rise of Regionalism:
The map of Mexico in 1830 highlights the growing regional identities within the nation. The distinct cultural and economic characteristics of different regions, from the bustling port cities of the Gulf Coast to the agricultural heartland of central Mexico, were becoming increasingly apparent. This regionalism would play a significant role in the political landscape of the 19th century, leading to conflicts over resources, power, and autonomy.
Beyond the Boundaries:
The map of Mexico in 1830 is not merely a geographical representation. It is a testament to the dynamic forces that shaped the nation’s early history. It reflects the ambitions of a newly independent nation, the challenges of territorial expansion, and the seeds of future conflicts. By studying this map, we gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of Mexican history and the profound transformations that shaped the nation we know today.
Understanding the Importance:
The map of Mexico in 1830 holds immense historical significance. It serves as a tangible reminder of the nation’s territorial evolution, the political struggles that defined its early years, and the complexities of its relationship with the United States. Studying this map allows us to:
- Visualize the territorial scope of Mexico in the 19th century: It reveals the vast expanse of the nation, encompassing regions that are now part of the United States.
- Gain insight into the political and social dynamics of the period: The map reflects the tensions between the Mexican government and the Anglo-American settlers in Texas, the challenges of managing the northern frontier, and the growing regional identities within the nation.
- Appreciate the historical context of future events: By understanding the territorial configuration of Mexico in 1830, we can better comprehend the events that led to the Texas Revolution, the Mexican-American War, and the subsequent territorial losses.
- Foster a deeper understanding of Mexican history: The map serves as a gateway to exploring the rich tapestry of Mexican history, from the struggle for independence to the challenges of nation-building.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What was the political situation in Mexico in 1830?
A: Mexico was a newly independent nation, struggling to establish a stable government and consolidate its vast territory. The country faced internal divisions, with different political factions vying for power. The presence of a growing Anglo-American population in Texas further complicated the political landscape.
Q: What were the key features of the map of Mexico in 1830?
A: The map depicted a vast territory that encompassed present-day Mexico, Texas, California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, and parts of Oklahoma and Kansas. It also highlighted the presence of Texas as an integral part of Mexico, the vast expanse of the northern frontier, and the distinct regional identities within the nation.
Q: How did the map of Mexico in 1830 reflect the nation’s relationship with the United States?
A: The map showed the growing influence of the United States on Mexico’s northern frontier. The presence of Anglo-American settlers in Texas and the expansion of American settlements in the west created tensions that would ultimately lead to conflict.
Q: What were the challenges faced by Mexico in managing its vast territory?
A: Mexico faced significant challenges in managing its vast territory, including:
- Controlling the flow of settlers: The influx of Anglo-American settlers in Texas created tensions and posed challenges for the Mexican government.
- Managing the northern frontier: The vast distances, the presence of indigenous communities, and the growing influence of the United States made it difficult to control this region.
- Establishing a stable government: Internal divisions and political instability made it challenging to consolidate power and establish a stable government.
Tips for Studying the Map of Mexico in 1830:
- Use multiple sources: Consult historical maps, texts, and primary sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the period.
- Focus on key events: Analyze the map in relation to significant events, such as the Texas Revolution, the Mexican-American War, and the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo.
- Consider the perspectives of different groups: Examine the map from the perspectives of the Mexican government, the Anglo-American settlers, and the indigenous communities.
- Draw connections between the map and other historical developments: Explore the connections between the map and other historical events, such as the rise of nationalism, the growth of regionalism, and the expansion of the United States.
Conclusion:
The map of Mexico in 1830 is more than just a static representation of geographical boundaries. It is a window into a crucial period in Mexican history, a period of transformation, conflict, and the forging of a national identity. By studying this map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of Mexican history and the enduring legacy of its past. It reminds us that maps are not merely static representations but dynamic artifacts that reveal the intricate tapestry of human history and the ever-evolving landscape of our world.




/Mexican_Cession-58b8cabe5f9b58af5c8cfa04.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of Mexico in 1830. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!