Charting The Cosmos: A Guide To Exoplanet Maps
Charting the Cosmos: A Guide to Exoplanet Maps
Related Articles: Charting the Cosmos: A Guide to Exoplanet Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Charting the Cosmos: A Guide to Exoplanet Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Cosmos: A Guide to Exoplanet Maps
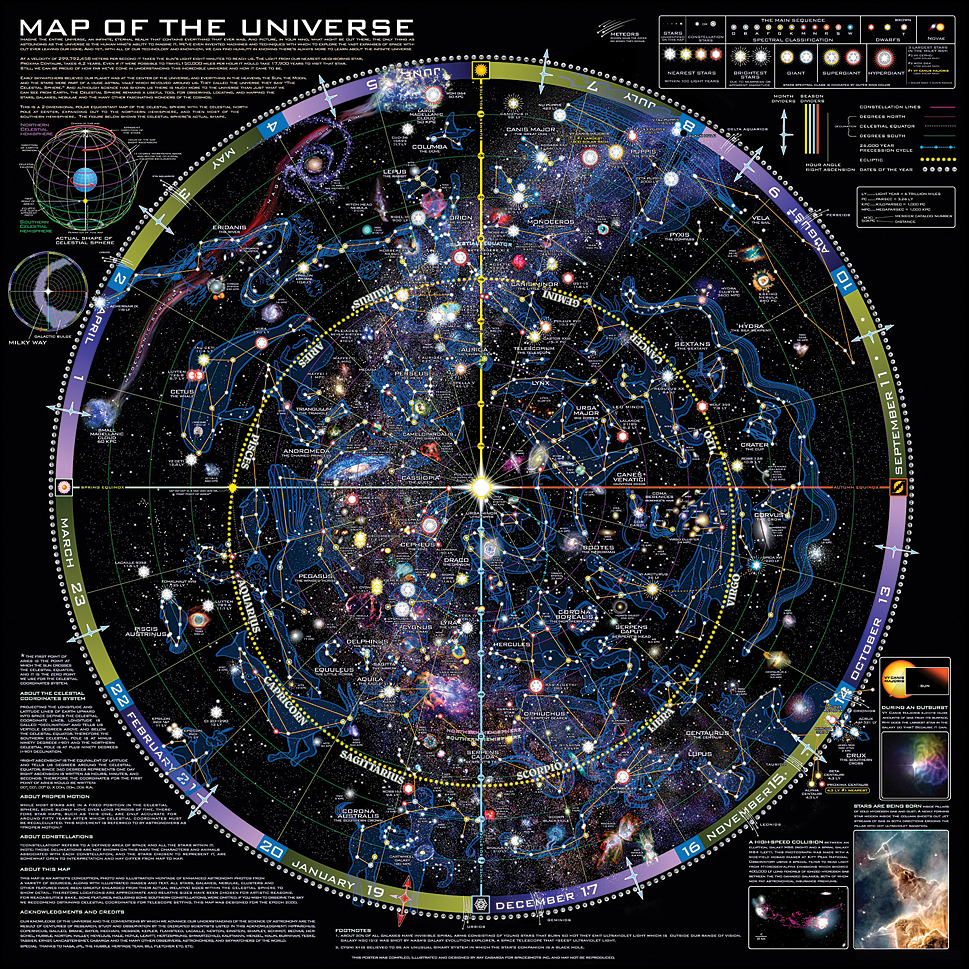
The universe, vast and enigmatic, harbors countless celestial bodies beyond our own solar system. Among these, exoplanets – planets orbiting stars other than our Sun – hold a special fascination. As our understanding of these distant worlds grows, so too does the need for a comprehensive and visual representation of their locations and characteristics. Enter the exoplanet map, a powerful tool that helps us navigate the cosmic landscape and unravel the mysteries of planetary systems beyond our own.
The Genesis of Exoplanet Maps
The quest to find exoplanets began decades ago, fueled by the pioneering work of astronomers like Aleksander Wolszczan and Dale Frail, who discovered the first confirmed exoplanets around a pulsar in 1992. Since then, advancements in technology, particularly in space-based telescopes like Kepler and TESS, have led to an explosion in exoplanet discoveries. This influx of data necessitates a structured approach to organizing and visualizing the vast amount of information gathered.
Exoplanet maps serve as the visual backbone for this endeavor. They provide a graphical representation of exoplanet locations, distances from their host stars, orbital periods, and other key characteristics. These maps, often interactive and dynamic, offer a unique perspective on the diversity and distribution of exoplanets within our galaxy and beyond.
Types of Exoplanet Maps
Exoplanet maps come in various forms, each tailored to highlight specific aspects of exoplanet data:
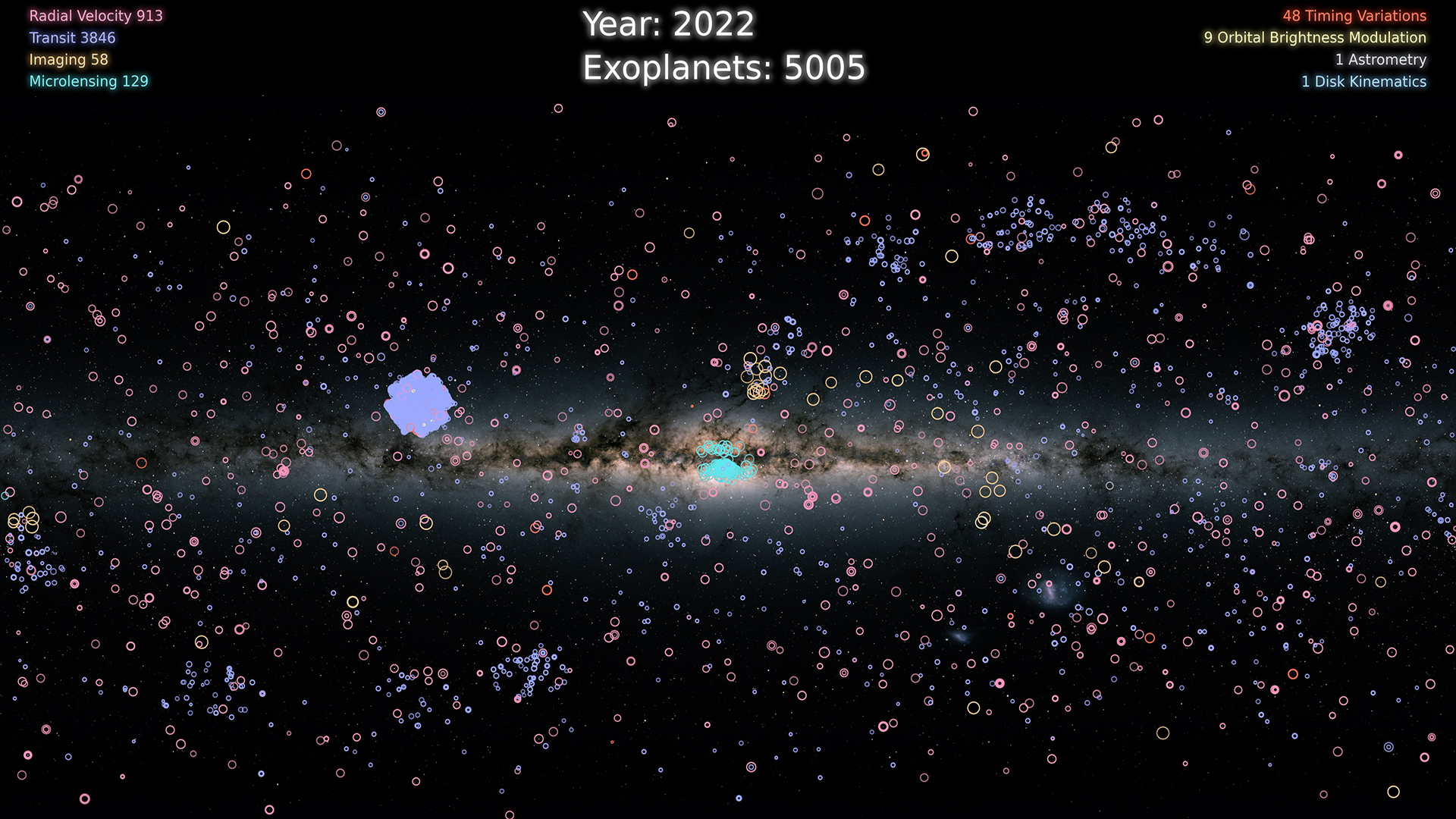
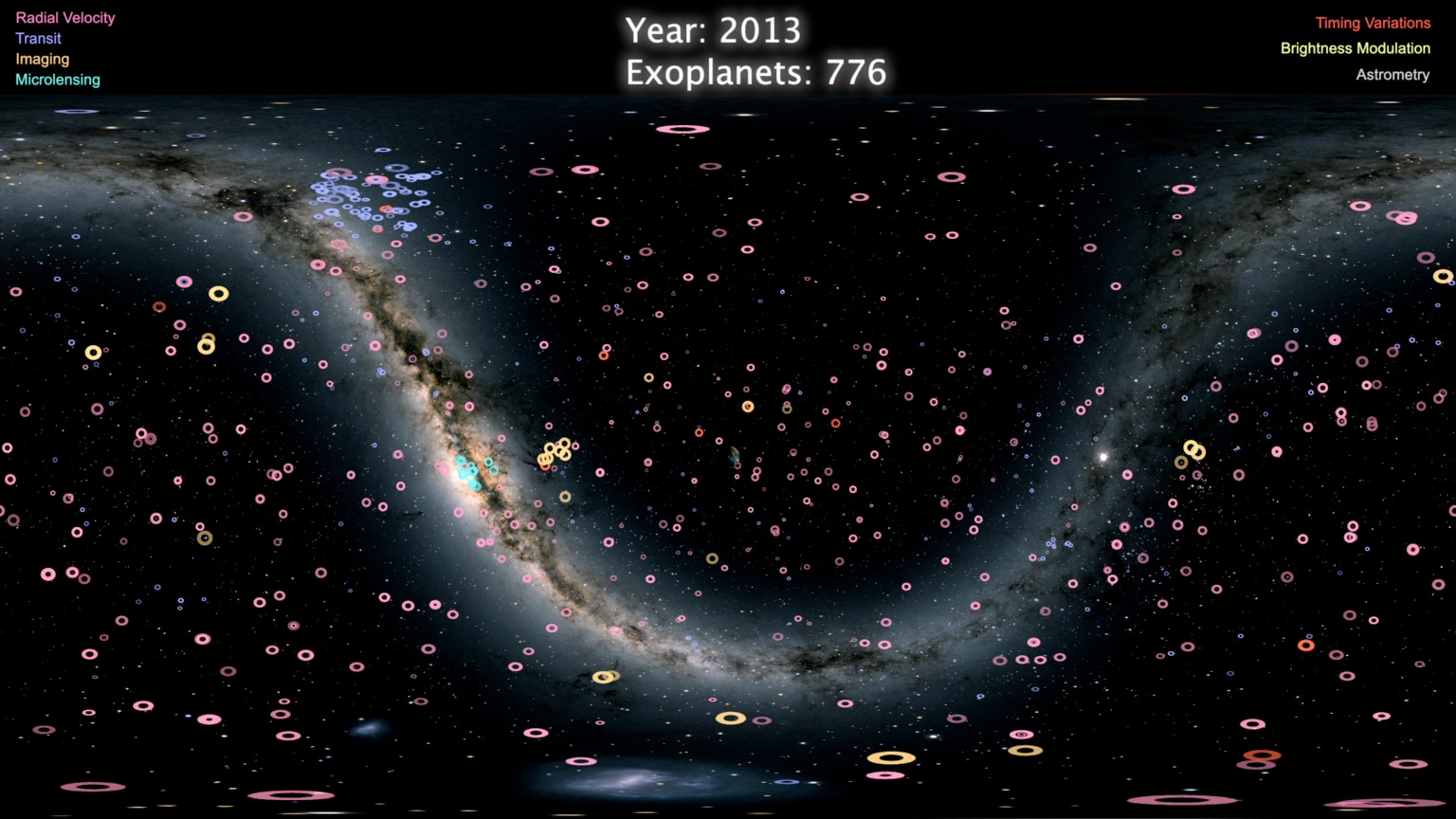
- Spatial Distribution Maps: These maps depict the locations of exoplanets within the Milky Way galaxy, often using color coding to represent different characteristics like size, mass, or orbital period. This type of map helps visualize the overall distribution of exoplanets and identify potential regions of high exoplanet density.
- Orbital Parameter Maps: These maps focus on the orbital properties of exoplanets, showcasing their distances from their host stars, orbital periods, and eccentricities. This type of map is crucial for understanding the dynamics of planetary systems and identifying potential habitable zones.
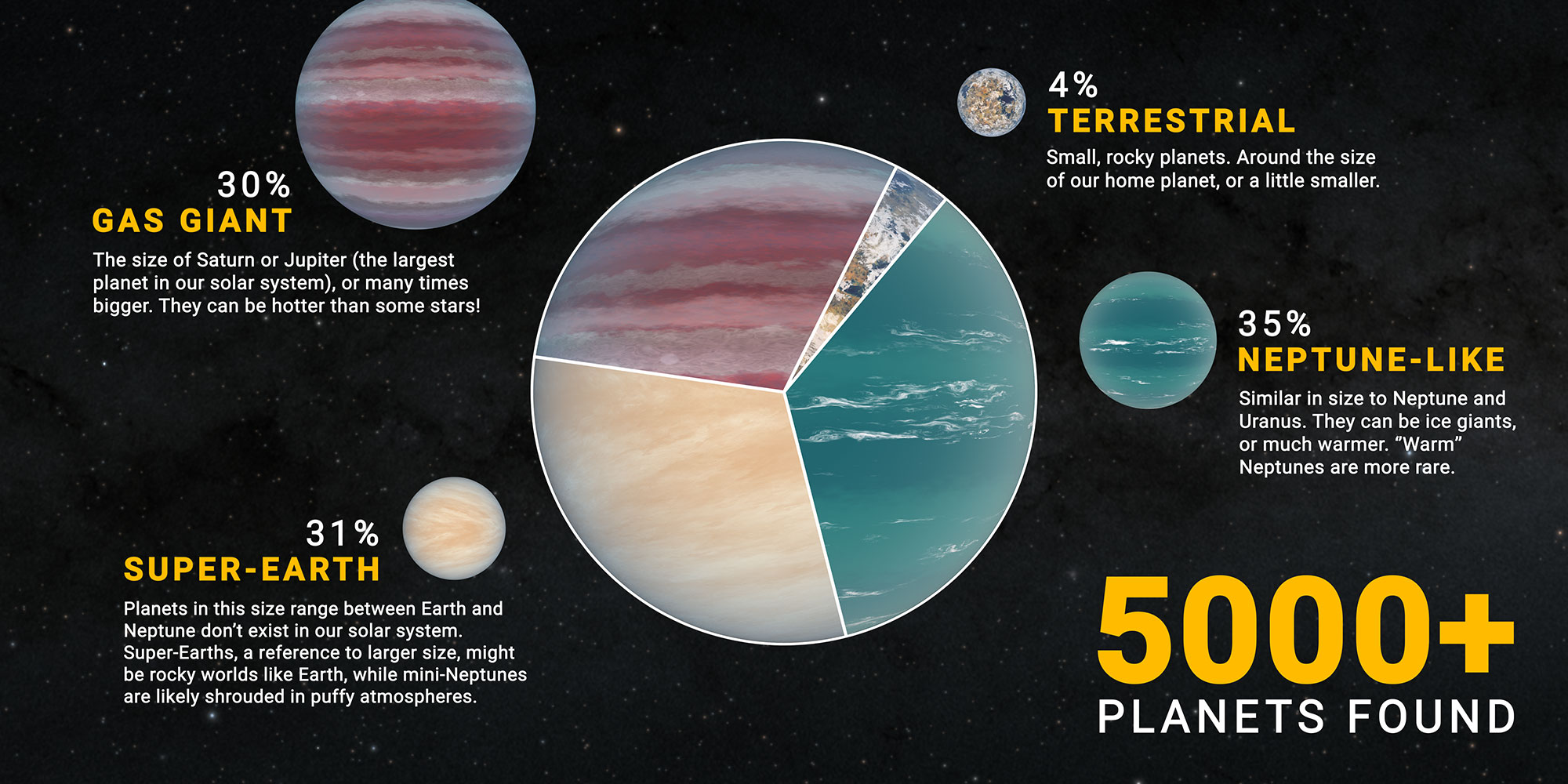
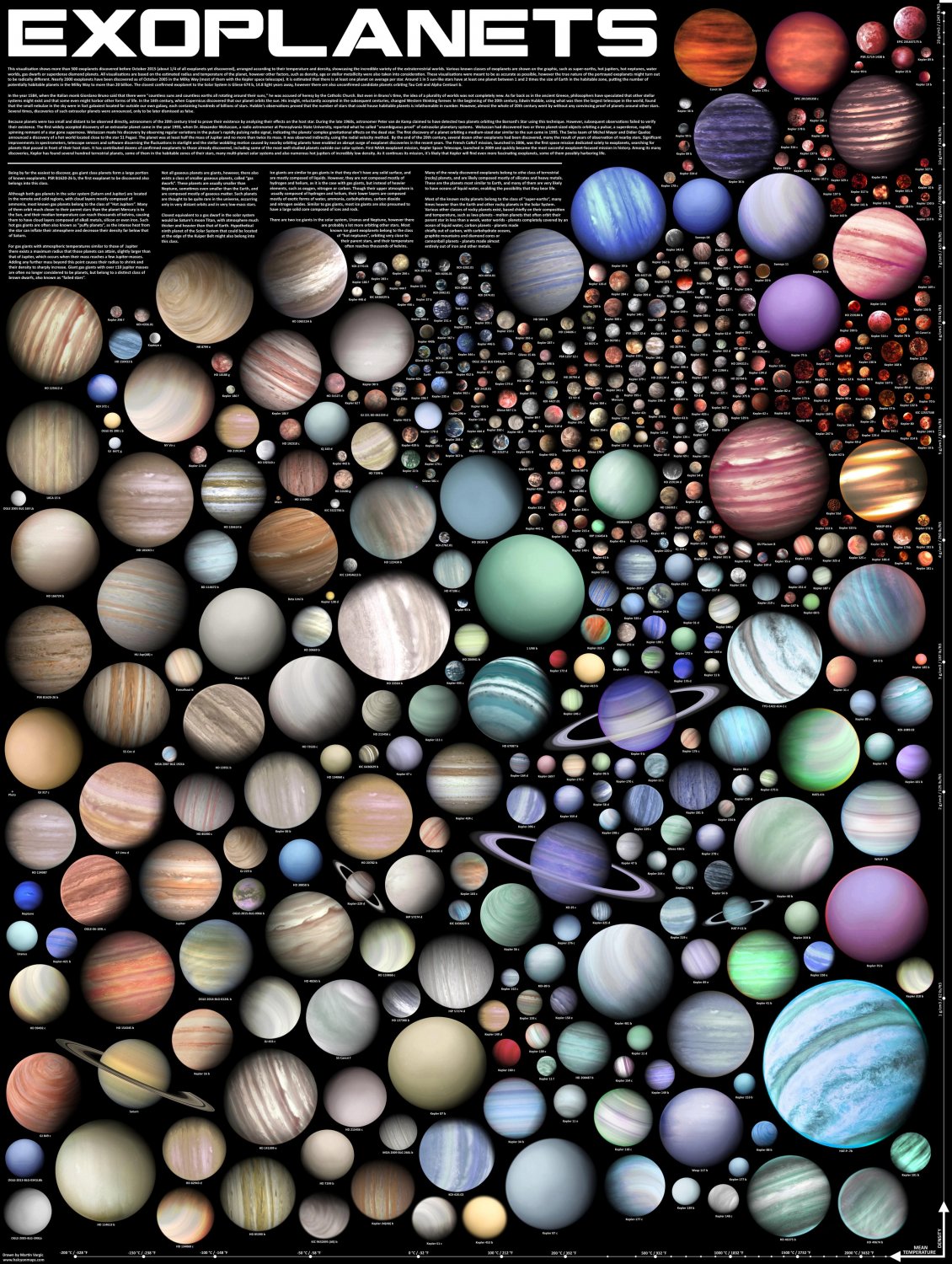
- Exoplanet Catalog Maps: These maps combine information from various sources, including observational data, theoretical models, and statistical analysis, to present a comprehensive overview of known exoplanets. They often include detailed information on each exoplanet, such as its mass, radius, temperature, and atmospheric composition.
Benefits of Exoplanet Maps
Exoplanet maps offer a wealth of benefits for researchers, educators, and the general public alike:
- Visualizing the Unseen: Exoplanets, by their very nature, are incredibly distant and often invisible to the naked eye. Exoplanet maps provide a tangible representation of these celestial bodies, allowing us to visualize their locations and properties in a clear and understandable manner.
- Understanding Planetary Diversity: By mapping exoplanets, we gain insights into the incredible diversity of planetary systems beyond our own. This knowledge helps us understand the processes of planet formation and evolution, as well as the potential for life elsewhere in the universe.
- Identifying Potential Habitable Zones: Exoplanet maps can highlight regions around stars where conditions might be suitable for liquid water, a key ingredient for life as we know it. This information is crucial for the search for habitable exoplanets and the potential for finding extraterrestrial life.
- Facilitating Research and Collaboration: Exoplanet maps serve as a central repository for data and information, facilitating research and collaboration among scientists from various disciplines. They provide a common ground for sharing knowledge and fostering new discoveries.
- Inspiring Public Engagement: Exoplanet maps can captivate the imagination of the general public, fostering a deeper understanding of the universe and our place within it. They can inspire curiosity and encourage further exploration of the cosmos.
Exploring the Data: Exoplanet Map FAQs
Q: How are exoplanets detected?
A: Exoplanets are detected using a variety of methods, including:
- Radial Velocity (Doppler) Method: This method detects the wobble of a star caused by the gravitational pull of an orbiting planet.
- Transit Method: This method observes the slight dimming of a star’s light as a planet passes in front of it.
- Microlensing Method: This method uses the gravitational lensing effect of a star to magnify the light of a more distant star, revealing the presence of a planet.
- Astrometry Method: This method measures the tiny shift in a star’s position caused by the gravitational pull of an orbiting planet.
- Direct Imaging Method: This method directly captures images of exoplanets, though it is challenging due to the faintness of these objects.
Q: What is the significance of the habitable zone?
A: The habitable zone, also known as the Goldilocks zone, is the region around a star where conditions might be suitable for liquid water to exist on the surface of a planet. Liquid water is considered essential for life as we know it, making the habitable zone a prime target for the search for extraterrestrial life.
Q: How are exoplanet maps created?
A: Exoplanet maps are created using data from various sources, including:
- Observational Data: Data from telescopes like Kepler, TESS, and ground-based observatories are used to identify and characterize exoplanets.
- Theoretical Models: Models based on physical laws and principles are used to simulate the formation and evolution of planetary systems.
- Statistical Analysis: Statistical methods are used to analyze the data and identify trends and patterns in exoplanet properties.
Q: What are some of the most notable exoplanet discoveries?
A: Some of the most notable exoplanet discoveries include:
- 51 Pegasi b: The first confirmed exoplanet orbiting a Sun-like star, discovered in 1995.
- Kepler-186f: The first confirmed Earth-sized exoplanet in the habitable zone of another star, discovered in 2014.
- Proxima Centauri b: The closest known exoplanet to our solar system, discovered in 2016.
- TRAPPIST-1 system: A system of seven Earth-sized exoplanets orbiting a red dwarf star, discovered in 2017.
Q: What are the future prospects for exoplanet mapping?
A: Future advancements in technology, particularly in space-based telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope, will revolutionize our ability to detect and characterize exoplanets. These advancements will lead to the discovery of even more exoplanets, providing a wealth of data for creating more detailed and informative exoplanet maps.
Tips for Understanding Exoplanet Maps
- Familiarize Yourself with Key Terminology: Understand terms like "orbital period," "eccentricity," "stellar mass," and "habitable zone."
- Pay Attention to Scale: Exoplanet maps often use logarithmic scales to represent vast distances and sizes.
- Explore Interactive Features: Many exoplanet maps offer interactive features, allowing you to zoom in, rotate, and filter data.
- Consult Multiple Sources: Compare different exoplanet maps to get a comprehensive understanding of the data.
- Stay Updated on New Discoveries: The field of exoplanet research is constantly evolving, so stay informed about the latest discoveries.
Conclusion: Navigating the Cosmic Landscape
Exoplanet maps are essential tools for navigating the vast cosmic landscape and unraveling the mysteries of planetary systems beyond our own. They provide a visual representation of the incredible diversity of exoplanets, fostering our understanding of planetary formation, evolution, and the potential for life elsewhere in the universe. As our knowledge of exoplanets continues to expand, exoplanet maps will play an increasingly important role in guiding our exploration of the cosmos and answering fundamental questions about our place within it.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Cosmos: A Guide to Exoplanet Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!