Charting The Past: A Journey Through Old Maps Of Afghanistan
Charting the Past: A Journey Through Old Maps of Afghanistan
Related Articles: Charting the Past: A Journey Through Old Maps of Afghanistan
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Charting the Past: A Journey Through Old Maps of Afghanistan. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Past: A Journey Through Old Maps of Afghanistan
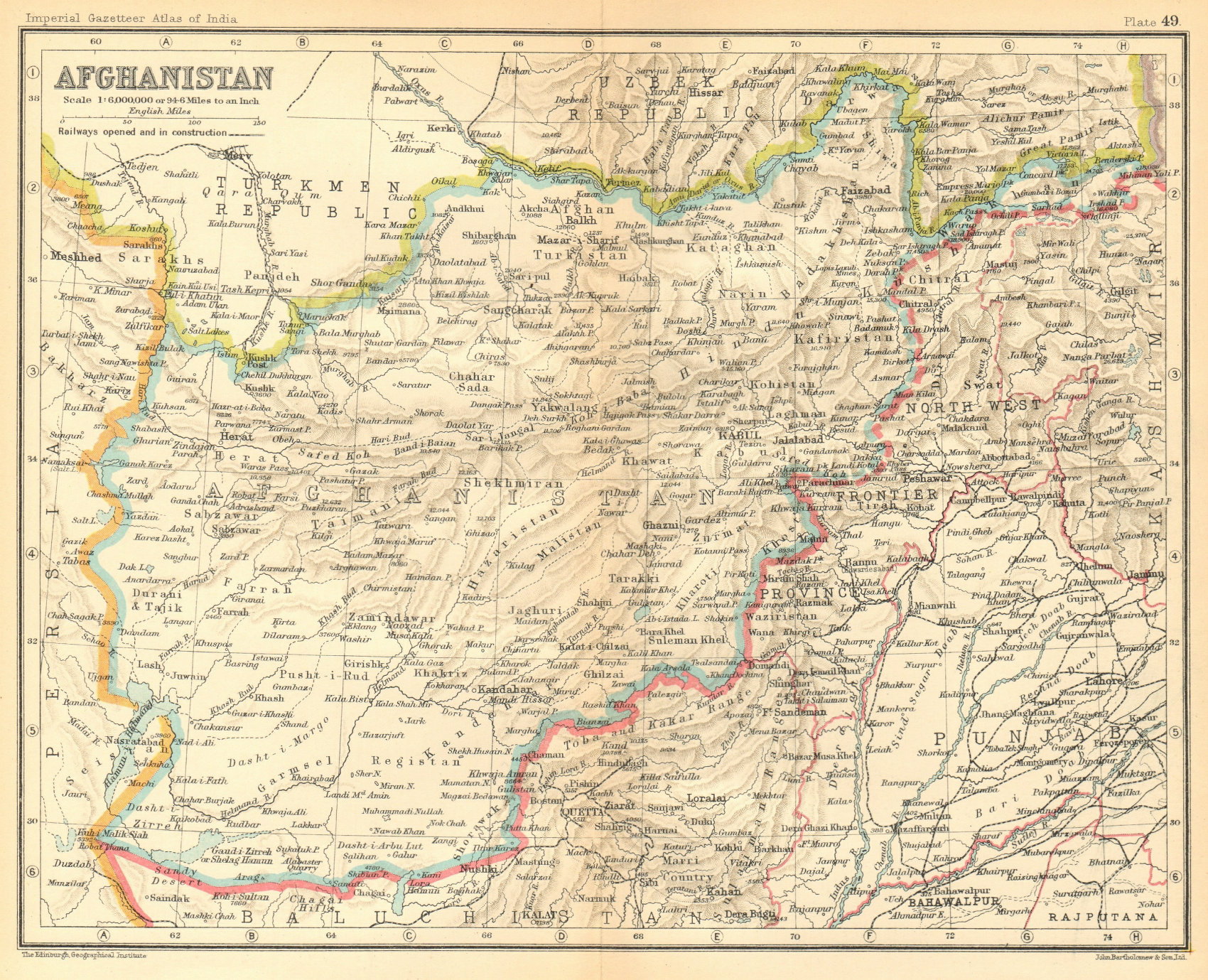
Afghanistan, a landlocked nation in Central Asia, has a rich and complex history. Its geographical location at the crossroads of civilizations has made it a battleground for empires and a melting pot of cultures. Understanding this history requires not only textual records but also a visual exploration of the land itself, and this is where old maps of Afghanistan become invaluable tools.
The Evolution of Cartography in Afghanistan:
The earliest maps of Afghanistan, dating back to antiquity, were primarily created for practical purposes. They served as guides for travelers, merchants, and military leaders, depicting major cities, trade routes, and geographical features. These maps were often hand-drawn and lacked the precision of modern cartography.
During the Islamic Golden Age, cartography flourished in the region. Arab scholars and travelers compiled detailed descriptions of the Afghan landscape, including its mountains, rivers, and deserts. These accounts, often accompanied by sketches, provided valuable insights into the geographical knowledge of the time.
With the arrival of European explorers in the 16th and 17th centuries, more accurate maps of Afghanistan began to emerge. These maps, based on European expeditions and surveys, incorporated new information about the region’s topography, political boundaries, and ethnic groups.
The Significance of Old Maps:
Old maps of Afghanistan serve as historical documents, offering insights into the region’s political, social, and economic landscape over time. They reveal the evolving understanding of Afghanistan’s geography, the shifting boundaries of empires, and the impact of historical events on the land.
Political Boundaries:
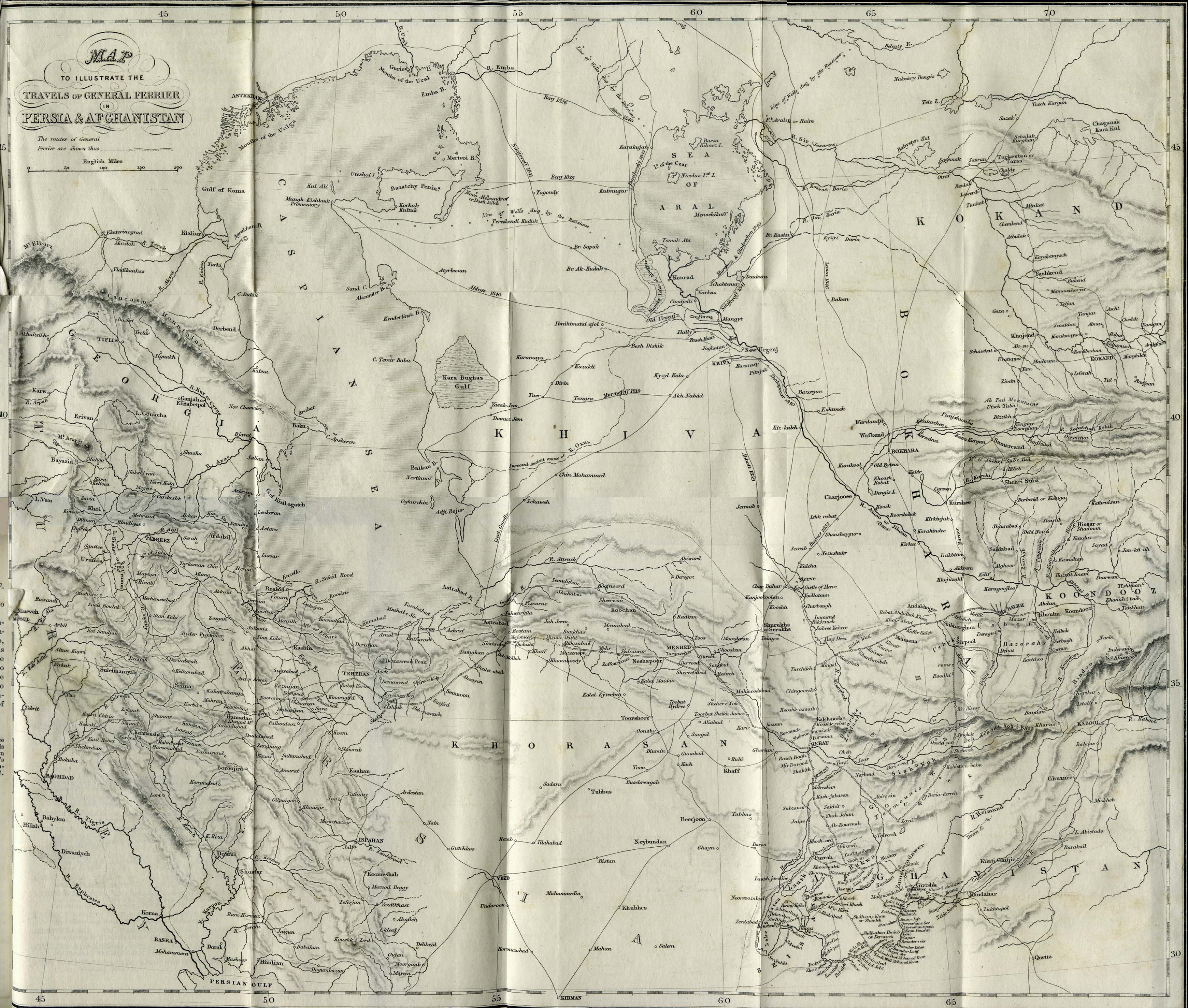
Old maps depict the fluctuating political boundaries of Afghanistan throughout history. They show the rise and fall of empires, the influence of foreign powers, and the internal divisions within the country. For instance, maps from the 19th century illustrate the Great Game, a period of rivalry between the British and Russian empires for control of Central Asia.
Cultural Landscapes:
Old maps provide a glimpse into the cultural landscape of Afghanistan. They highlight the locations of ancient cities, religious sites, and trade routes that have shaped the country’s identity. The presence of specific features, such as mosques, caravanserais, and irrigation systems, reveals the influence of various cultures and religions on the region.
Geographical Features:
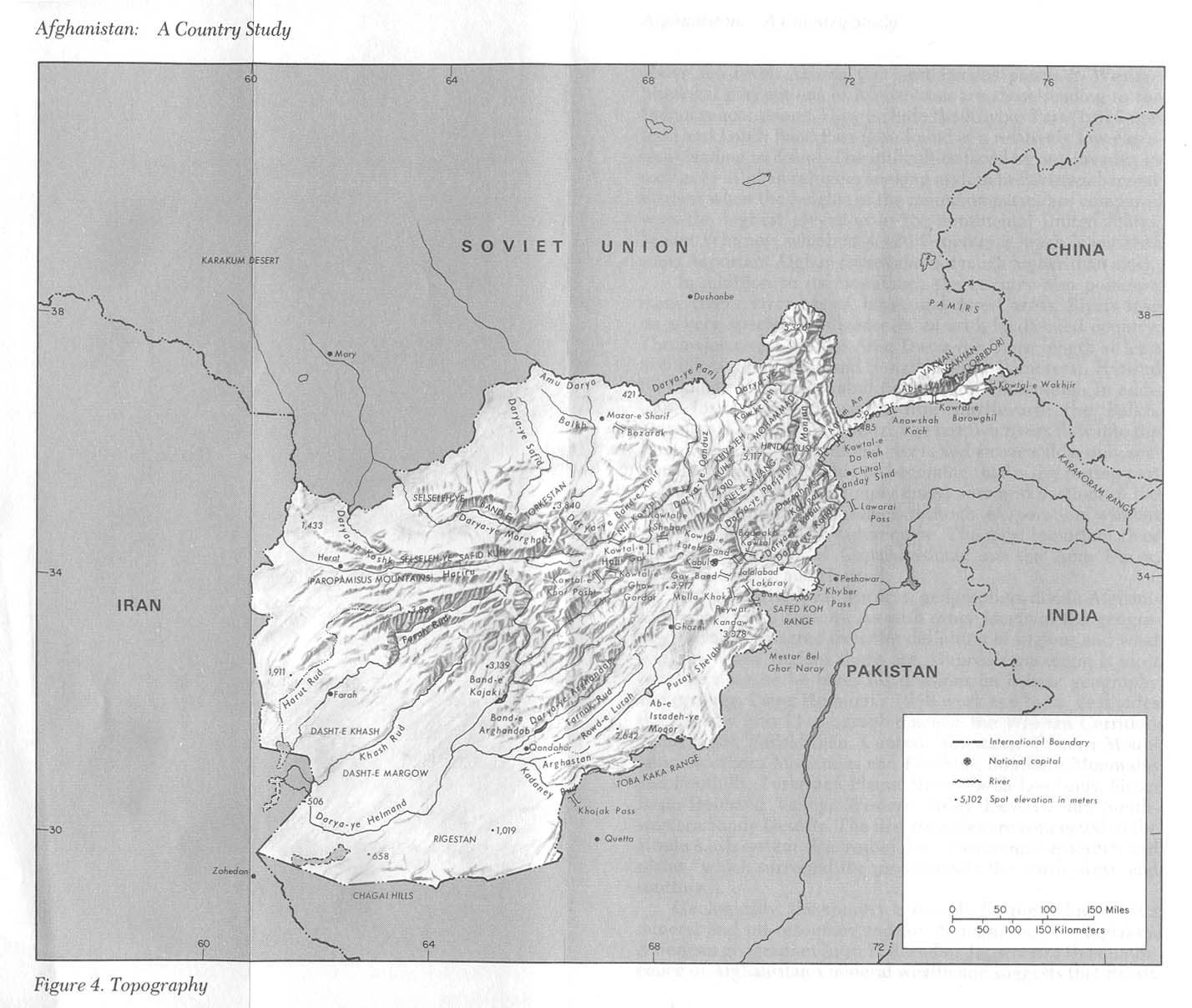
Old maps offer valuable information about the geographical features of Afghanistan, including its mountains, rivers, and deserts. They show the distribution of natural resources, the challenges faced by travelers, and the impact of climate on human settlements. This information is crucial for understanding the region’s environmental history and the challenges of sustainable development.
Beyond the Lines:
Old maps of Afghanistan are not merely static representations of the land. They are also windows into the minds of the cartographers who created them. The choices they made in depicting certain features, omitting others, and using specific symbols reflect their biases, perspectives, and the knowledge available to them at the time.
Exploring Old Maps of Afghanistan:
Several resources are available for those interested in exploring old maps of Afghanistan:
- Libraries and Archives: National libraries and archives, such as the British Library, the Library of Congress, and the National Archives of Afghanistan, hold vast collections of historical maps.
- Online Databases: Digital libraries and online databases, such as the David Rumsey Map Collection and the World Digital Library, offer access to digitized maps.
- Museums: Museums dedicated to history, geography, and cartography often display old maps of Afghanistan as part of their exhibits.
FAQs about Old Maps of Afghanistan:
Q: What are some of the most important old maps of Afghanistan?
A: Some of the most important old maps include:
- The Ptolemy Map: A 2nd-century Greek map that depicts the region of Ariana, which corresponds to present-day Afghanistan.
- The Tabula Peutingeriana: A 4th-century Roman road map that shows a route through Afghanistan, known as the Silk Road.
- The Idrisi Map: An 12th-century Arab map that depicts Afghanistan as part of the Islamic world.
- The Rennel Map: An 18th-century British map that provides a detailed depiction of Afghanistan’s geography.
- The Afghan Boundary Commission Maps: A series of maps created in the 19th century to define the borders of Afghanistan.
Q: How accurate are old maps of Afghanistan?
A: The accuracy of old maps varies depending on the time period, the cartographic techniques used, and the available knowledge. Early maps were often based on limited information and may contain inaccuracies in terms of scale, location, and details. However, as cartographic techniques improved over time, maps became more accurate and detailed.
Q: What can we learn from old maps of Afghanistan?
A: Old maps provide insights into:
- The evolving understanding of Afghanistan’s geography.
- The shifting political boundaries of the region.
- The cultural landscape of Afghanistan, including ancient cities, religious sites, and trade routes.
- The impact of historical events on the land.
Tips for Studying Old Maps of Afghanistan:
- Consider the context: Understand the time period, the cartographer’s perspective, and the available knowledge when interpreting old maps.
- Compare different maps: Look at multiple maps from different periods to see how perceptions of Afghanistan have changed over time.
- Use other sources: Combine map information with historical texts, archaeological evidence, and oral traditions to gain a comprehensive understanding of the past.
- Focus on specific features: Pay attention to key features such as mountains, rivers, cities, and trade routes to understand their significance in the historical context.
- Engage in critical analysis: Question the map’s purpose, its creator’s biases, and the limitations of the information it presents.
Conclusion:
Old maps of Afghanistan offer a unique and invaluable perspective on the region’s history. They reveal the changing political landscape, the cultural tapestry, and the geographical features that have shaped Afghanistan over centuries. By studying these maps, we gain a deeper understanding of the country’s past and its present-day challenges. These historical documents serve as a reminder that maps are not merely static representations of the world but dynamic reflections of human knowledge, imagination, and the evolving relationship between people and their environment.
![Map of Afghanistan from around 1943 [1068 × 1037]. : ImagesOfAfghanistan](https://external-preview.redd.it/hO9BsR3V5KXaZ_kbWHFKpSRaoQekyF1zHZBUXkmQ8MI.jpg?width=960u0026crop=smartu0026auto=webpu0026s=c4ea4bd98501921e7bd16c673226d5f7bad57e09)
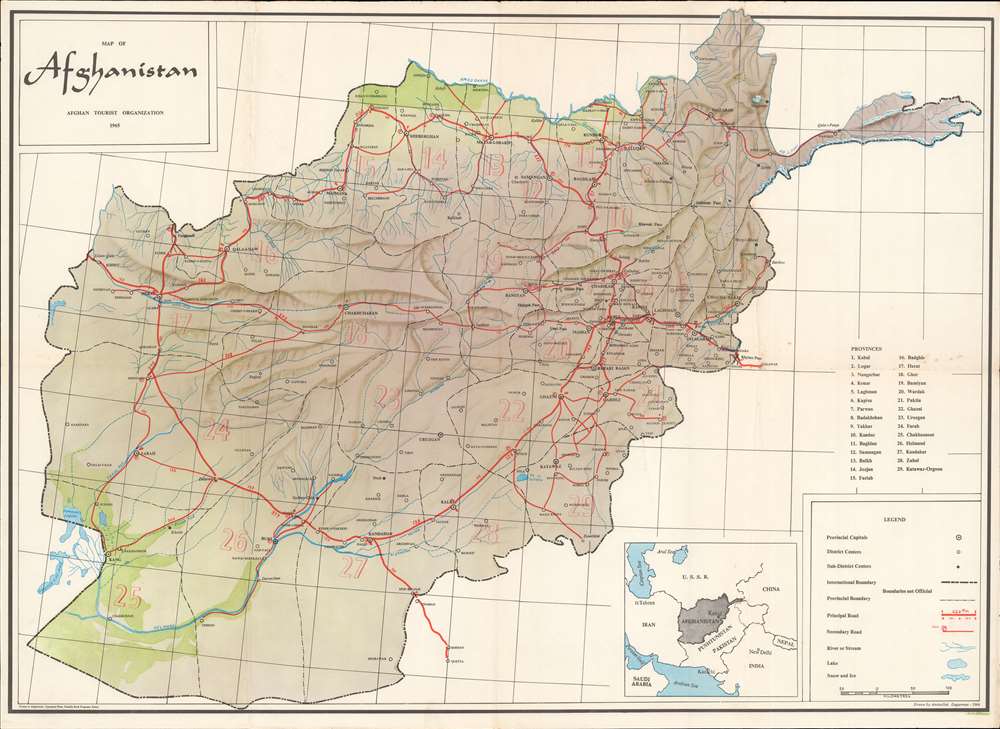

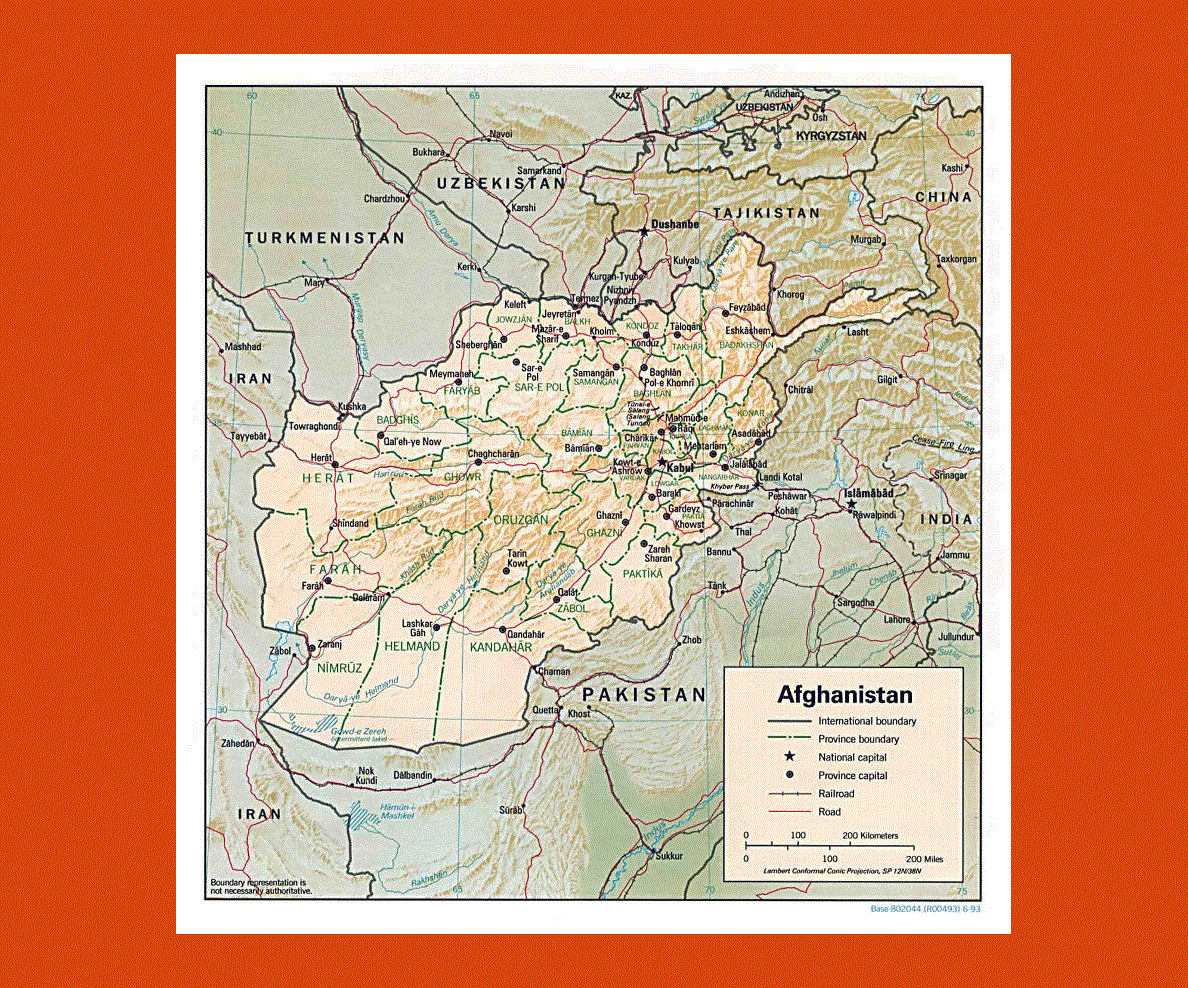

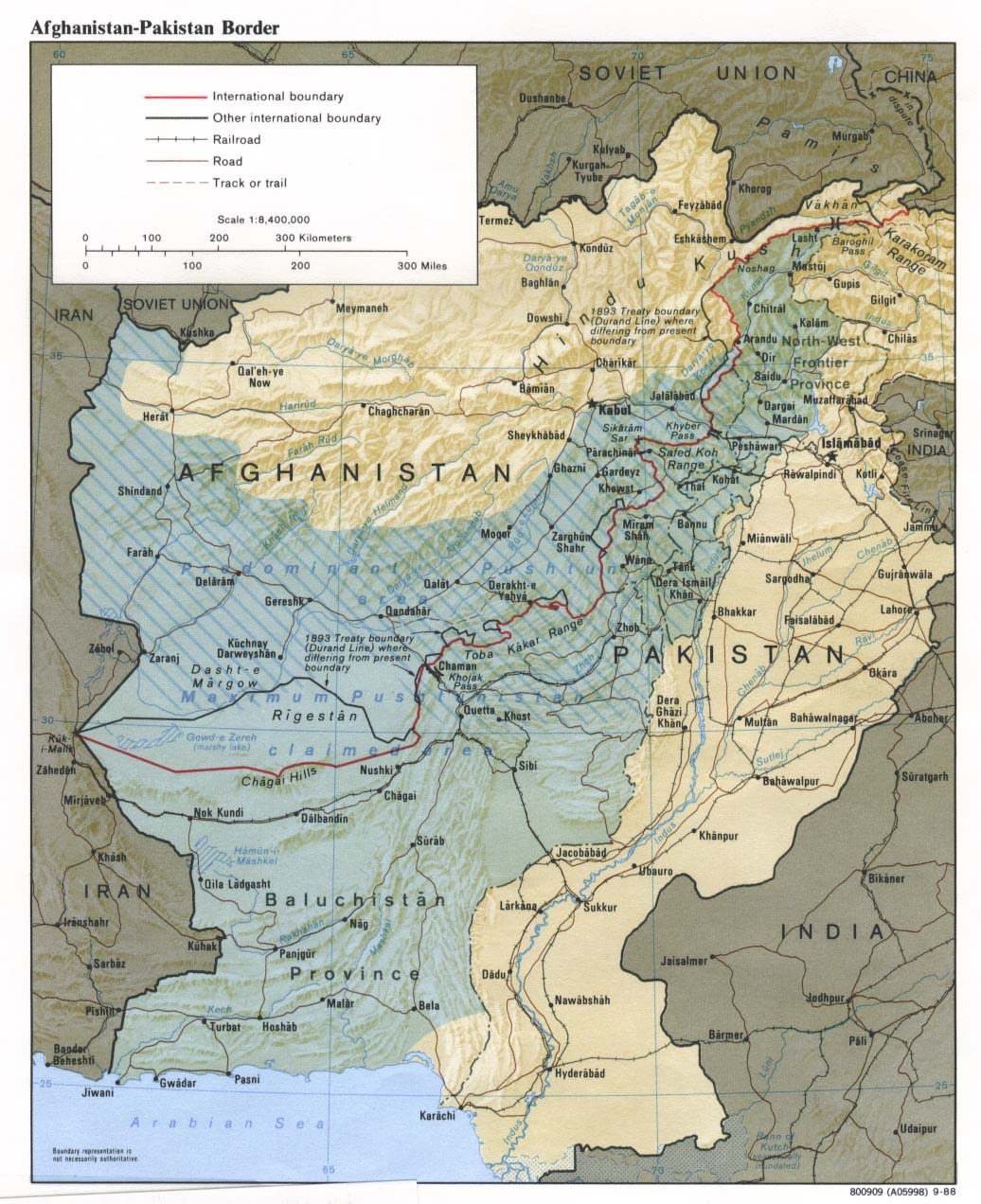
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Past: A Journey Through Old Maps of Afghanistan. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!