Delving Into The Complex Tapestry Of Georgia’s Soils: A Comprehensive Guide To The State’s Soil Types Map
Delving into the Complex Tapestry of Georgia’s Soils: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Soil Types Map
Related Articles: Delving into the Complex Tapestry of Georgia’s Soils: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Soil Types Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Complex Tapestry of Georgia’s Soils: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Soil Types Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Complex Tapestry of Georgia’s Soils: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Soil Types Map

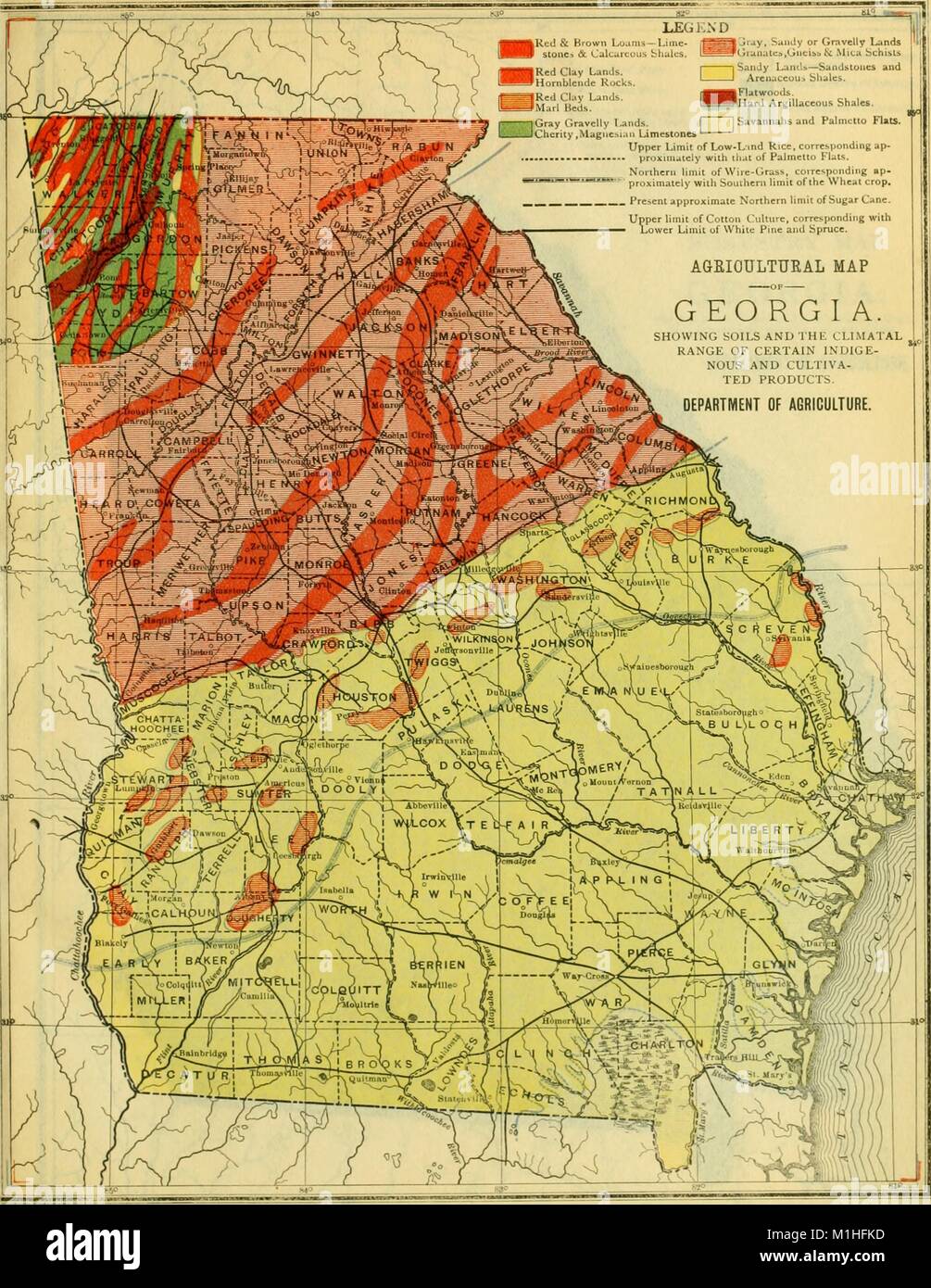
Georgia, a state known for its diverse landscape, boasts an equally varied soil composition. Understanding the distribution of these soils is crucial for various sectors, including agriculture, forestry, urban planning, and environmental management. This article offers a comprehensive exploration of Georgia’s soil types map, highlighting its significance and providing insights into the intricate relationship between soil characteristics and land use.
Understanding the Foundation: Georgia’s Soil Types
Georgia’s soil types are classified based on the Soil Taxonomy System, a hierarchical system developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). This system considers various factors, including soil texture, structure, color, chemical composition, and drainage characteristics.
Major Soil Orders in Georgia
The soil map of Georgia reveals a complex mosaic of soil orders, each possessing distinct properties:
-
Ultisols: These soils, dominant across the state, are characterized by high levels of iron and aluminum oxides, giving them a reddish or yellowish hue. They are typically acidic and have low fertility, making them suitable for specific crops like peanuts, cotton, and timber.
-
Alfisols: These soils, prevalent in the Piedmont region, exhibit moderate levels of weathering and are generally more fertile than Ultisols. They support a wider range of crops, including corn, soybeans, and pasture grasses.
-
Spodosols: Found in the Coastal Plain, these soils are characterized by a distinct layer of accumulated organic matter and iron oxides. They are often acidic and have low fertility, but are well-suited for pine plantations.
-
Entisols: These soils, typically found in recently deposited areas like floodplains and river terraces, are young and lack well-developed horizons. They are generally fertile but prone to erosion.
-
Inceptisols: These soils, found in various parts of the state, show early stages of development and exhibit moderate weathering. They are often used for pasture and hay production.
-
Mollisols: These soils, primarily found in the northern part of the state, are characterized by a thick, dark, and fertile topsoil. They are well-suited for grain production.
The Importance of Soil Types Map
The Georgia soil types map serves as an invaluable tool for various stakeholders:
-
Agriculture: Farmers rely on the map to select appropriate crops for specific soil types, optimizing yield and minimizing environmental impact.
-
Forestry: Foresters use the map to identify areas suitable for different tree species, ensuring sustainable forest management and maximizing timber production.
-
Urban Planning: Planners utilize the map to understand soil characteristics and potential risks, guiding infrastructure development, minimizing erosion, and promoting sustainable urban growth.
-
Environmental Management: The map assists in identifying areas prone to soil degradation and erosion, facilitating targeted conservation efforts and protecting water quality.
Utilizing the Soil Types Map for Informed Decisions
The Georgia soil types map provides a wealth of information for informed decision-making:
-
Crop Selection: The map helps farmers identify suitable crops based on soil fertility, drainage, and texture. For example, cotton thrives in well-drained Ultisols, while soybeans prefer the more fertile Alfisols.
-
Fertilizer Management: The map helps determine the specific nutrient needs of different soil types, enabling farmers to apply fertilizers efficiently, minimizing waste and environmental impact.
-
Water Management: The map aids in identifying areas prone to flooding or drought, guiding irrigation and drainage strategies for efficient water use.
-
Land Use Planning: The map assists in identifying suitable land for different purposes, promoting sustainable land use practices and minimizing environmental risks.
FAQs Regarding Georgia’s Soil Types Map
Q: Where can I access the Georgia soil types map?
A: The Georgia Soil Survey, a division of the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS), provides access to the soil types map through their website and various publications.
Q: What is the scale of the Georgia soil types map?
A: The map is available at various scales, ranging from detailed county-level maps to broader state-level representations. The specific scale depends on the intended use and level of detail required.
Q: Can I get detailed soil information for a specific location?
A: Yes, the Georgia Soil Survey provides detailed soil reports for specific locations, offering information on soil texture, structure, fertility, and other characteristics.
Q: How frequently is the Georgia soil types map updated?
A: The map is continuously updated as new data becomes available, ensuring accuracy and reflecting changes in soil conditions over time.
Tips for Using the Georgia Soil Types Map Effectively
-
Consult with experts: Reach out to the Georgia Soil Survey or local NRCS offices for guidance on interpreting the map and utilizing its information effectively.
-
Consider multiple factors: When making decisions based on the map, consider not only soil type but also other factors like climate, topography, and land use history.
-
Stay informed: Stay updated on any revisions or updates to the map to ensure you are using the most accurate information.
Conclusion
The Georgia soil types map serves as a crucial tool for understanding and managing the state’s diverse soil resources. Its use spans various sectors, promoting sustainable land use, enhancing agricultural productivity, and safeguarding environmental integrity. By leveraging the insights provided by the map, stakeholders can make informed decisions, optimizing resource utilization and ensuring the long-term health of Georgia’s soils.

.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Complex Tapestry of Georgia’s Soils: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Soil Types Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!