Delving Into The Realm Of 1 Bar MAP Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide
Delving into the Realm of 1 Bar MAP Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Delving into the Realm of 1 Bar MAP Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Realm of 1 Bar MAP Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Delving into the Realm of 1 Bar MAP Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Delving into the Realm of 1 Bar MAP Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Essence of MAP Sensors: A Primer
- 3.2 1 Bar MAP Sensors: A Deeper Dive
- 3.3 Advantages of 1 Bar MAP Sensors
- 3.4 Applications of 1 Bar MAP Sensors
- 3.5 Understanding the 1 Bar MAP Sensor’s Role in Engine Management
- 3.6 Common Issues with 1 Bar MAP Sensors
- 3.7 Troubleshooting 1 Bar MAP Sensor Issues
- 3.8 FAQs Regarding 1 Bar MAP Sensors
- 3.9 Tips for Maintaining a 1 Bar MAP Sensor
- 3.10 Conclusion: The Importance of 1 Bar MAP Sensors in Modern Automotive Systems
- 4 Closure
Delving into the Realm of 1 Bar MAP Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide
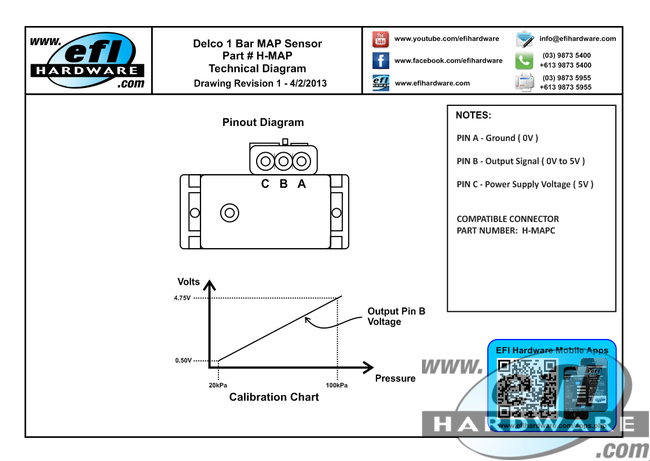
In the intricate world of automotive engineering, a multitude of sensors play crucial roles in ensuring optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Among these, the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor stands out as a vital component, meticulously monitoring the pressure within the engine’s intake manifold. This article delves into the specific realm of 1 bar MAP sensors, providing a comprehensive understanding of their functionality, applications, and significance in modern automotive systems.
The Essence of MAP Sensors: A Primer
MAP sensors serve as the engine’s "ears," constantly listening to the pressure fluctuations within the intake manifold. This pressure, a direct reflection of the air density entering the cylinders, provides a crucial input for the engine control unit (ECU) to calculate the precise amount of fuel required for optimal combustion.
1 Bar MAP Sensors: A Deeper Dive
1 bar MAP sensors, as the name suggests, are designed to measure pressure up to 1 bar (14.5 psi). This pressure range aligns with naturally aspirated engines, which are prevalent in a vast array of gasoline-powered vehicles. These sensors employ a diaphragm-based mechanism, where pressure variations cause the diaphragm to flex, altering the resistance within an integrated electrical circuit. This change in resistance is translated into an electrical signal, which the ECU interprets to determine the manifold pressure.
Advantages of 1 Bar MAP Sensors
1 bar MAP sensors offer several advantages, making them a preferred choice for many automotive applications:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to higher-pressure MAP sensors, 1 bar sensors are generally more affordable, making them a budget-friendly option for a wide range of vehicles.
- Reliability: Their simple design and robust construction contribute to their exceptional reliability, ensuring consistent and accurate pressure readings over extended periods.
- Accuracy: 1 bar MAP sensors deliver precise pressure measurements within their operational range, contributing to optimized engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- Compatibility: Their compatibility with naturally aspirated engines makes them a suitable choice for a vast majority of gasoline-powered vehicles.
Applications of 1 Bar MAP Sensors
1 bar MAP sensors find widespread application in various automotive systems, including:
- Gasoline Engines: These sensors are integral to the engine management systems of most gasoline-powered vehicles, providing essential data for fuel injection and ignition timing.
- Turbocharged Engines: While primarily associated with naturally aspirated engines, 1 bar MAP sensors can also be utilized in turbocharged applications, provided the boost pressure remains within the sensor’s measurement range.
- Off-Road Vehicles: 1 bar MAP sensors are commonly found in off-road vehicles, where their robust design and reliable performance are crucial for navigating challenging terrains.
Understanding the 1 Bar MAP Sensor’s Role in Engine Management
The 1 bar MAP sensor’s contribution to optimal engine performance stems from its crucial role in the following processes:
- Fuel Injection: The ECU utilizes the manifold pressure data to determine the precise amount of fuel to inject into the cylinders. By adjusting fuel delivery based on the pressure readings, the engine operates efficiently, minimizing fuel consumption and emissions.
- Ignition Timing: The MAP sensor also plays a role in optimizing ignition timing. The ECU analyzes the pressure readings to determine the optimal spark timing, ensuring efficient combustion and maximizing power output.
- Boost Control (Turbocharged Engines): In turbocharged applications, the 1 bar MAP sensor provides data for boost control. The ECU uses this information to regulate the boost pressure, ensuring optimal performance and preventing damage to the engine.
Common Issues with 1 Bar MAP Sensors
While generally reliable, 1 bar MAP sensors can experience certain issues over time, impacting engine performance:
- Contamination: Dust, debris, and oil contamination can affect the sensor’s diaphragm, leading to inaccurate pressure readings.
- Electrical Failures: Worn or damaged wiring can disrupt the electrical signal transmission, causing malfunctions.
- Sensor Degradation: Over time, the sensor’s diaphragm may become less flexible, impacting its ability to accurately measure pressure.
Troubleshooting 1 Bar MAP Sensor Issues
Diagnosing issues with a 1 bar MAP sensor requires a systematic approach:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any visible damage to the sensor or its wiring.
- Pressure Testing: Utilize a pressure gauge to verify the sensor’s readings against the actual manifold pressure.
- Electrical Testing: Use a multimeter to check the sensor’s electrical resistance and confirm proper signal transmission.
FAQs Regarding 1 Bar MAP Sensors
Q: What are the common symptoms of a faulty 1 bar MAP sensor?
A: A faulty MAP sensor can manifest in various symptoms, including:
- Rough Idle: The engine may idle erratically or stall.
- Reduced Power: The engine may experience a loss of power, particularly during acceleration.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: The engine may consume more fuel than usual due to inaccurate fuel injection.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light may illuminate, indicating a fault code related to the MAP sensor.
Q: Can I replace a 1 bar MAP sensor myself?
A: Replacing a 1 bar MAP sensor is a relatively straightforward procedure that can be performed by individuals with basic mechanical skills. However, it’s crucial to refer to the vehicle’s repair manual for specific instructions and ensure proper installation to avoid damaging the sensor or other components.
Q: How often should I replace a 1 bar MAP sensor?
A: There’s no specific replacement interval for 1 bar MAP sensors. However, if you experience any of the symptoms associated with a faulty sensor, it’s advisable to have it inspected and replaced if necessary.
Q: Can I use a different type of MAP sensor in place of a 1 bar sensor?
A: Using a different type of MAP sensor, such as a higher-pressure sensor, can potentially lead to inaccurate readings and engine problems. It’s crucial to use a sensor specifically designed for the vehicle’s application.
Tips for Maintaining a 1 Bar MAP Sensor
- Regular Maintenance: Perform routine engine maintenance, including air filter replacement and oil changes, to minimize contamination of the sensor.
- Avoid Harsh Environments: Protect the sensor from exposure to extreme temperatures, moisture, and corrosive substances.
- Professional Inspection: If you suspect any issues with the sensor, have it inspected by a qualified mechanic.
Conclusion: The Importance of 1 Bar MAP Sensors in Modern Automotive Systems
1 bar MAP sensors play a crucial role in ensuring optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency in a wide range of gasoline-powered vehicles. Their ability to accurately measure manifold pressure provides essential data for the ECU to precisely control fuel injection, ignition timing, and boost pressure, ultimately contributing to a smooth and efficient driving experience. Understanding the function, applications, and potential issues associated with 1 bar MAP sensors empowers vehicle owners to maintain their vehicles effectively and ensure their longevity.
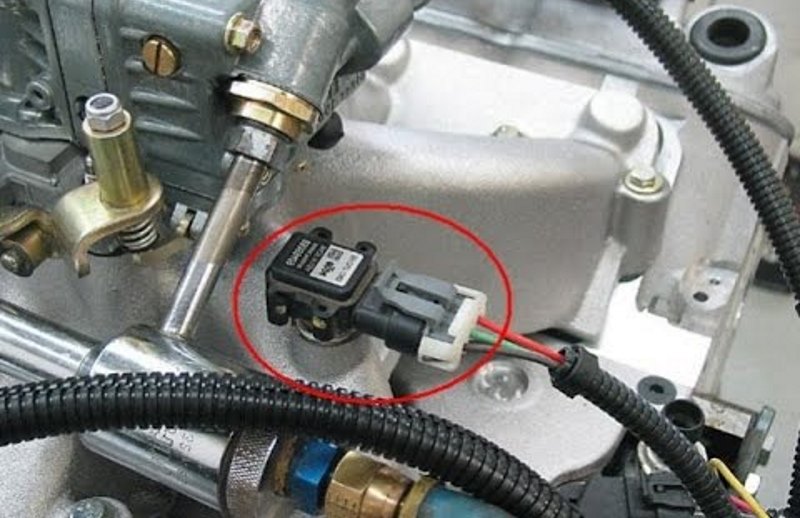



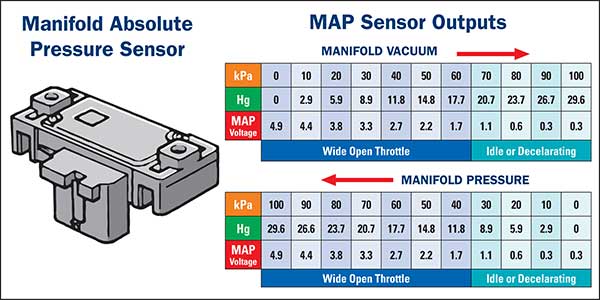




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Realm of 1 Bar MAP Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!