Demystifying The ASHRAE Climate Zone Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Climate Data For Building Design
Demystifying the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Climate Data for Building Design
Related Articles: Demystifying the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Climate Data for Building Design
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Demystifying the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Climate Data for Building Design. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demystifying the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Climate Data for Building Design
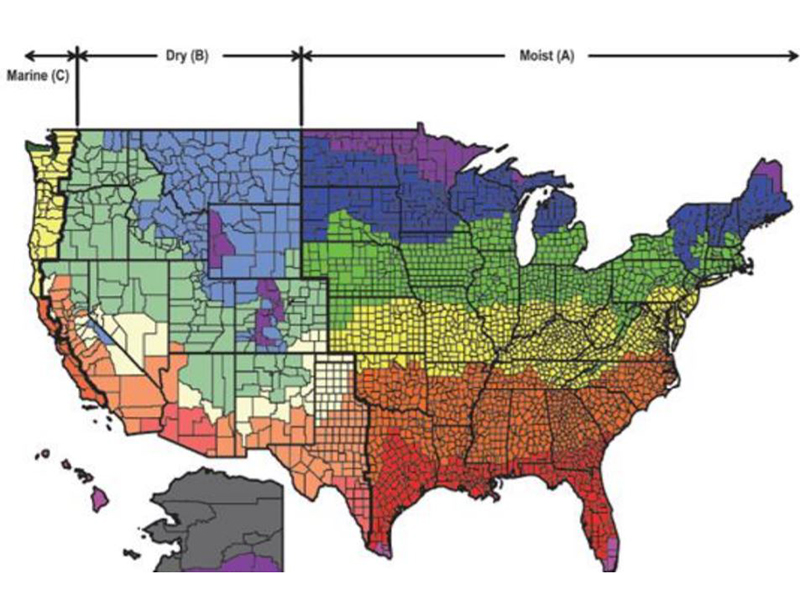
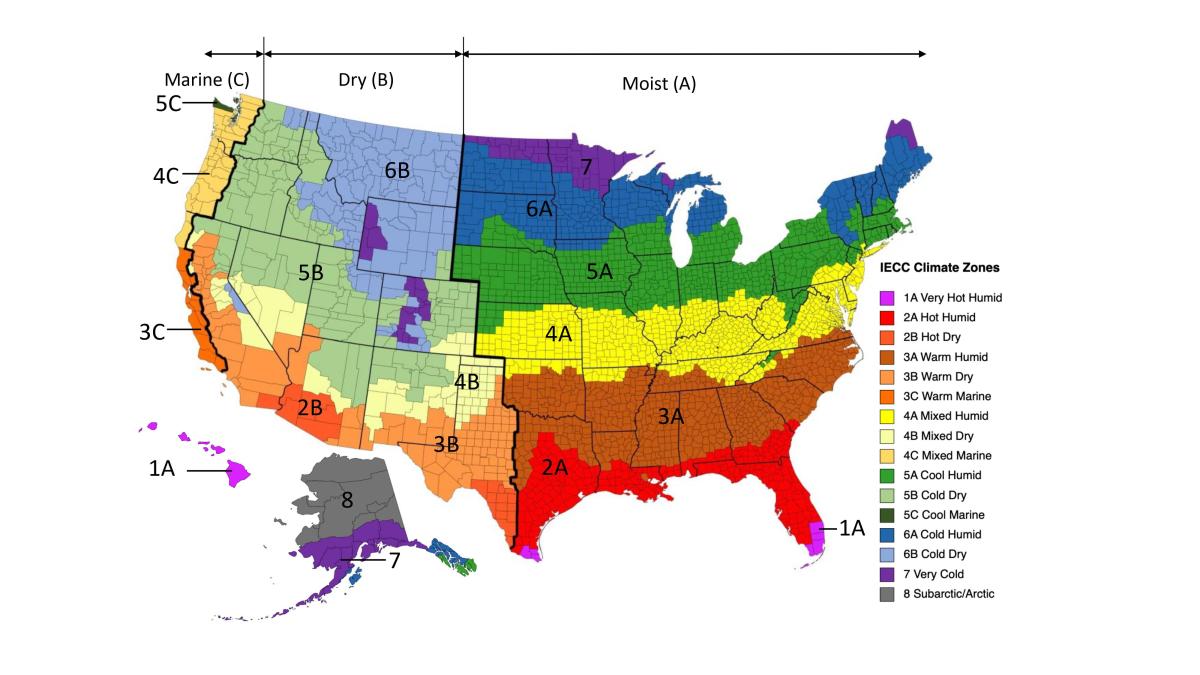
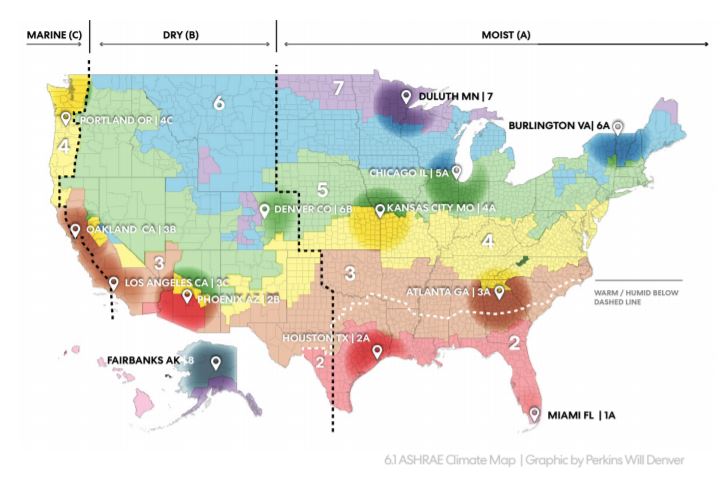
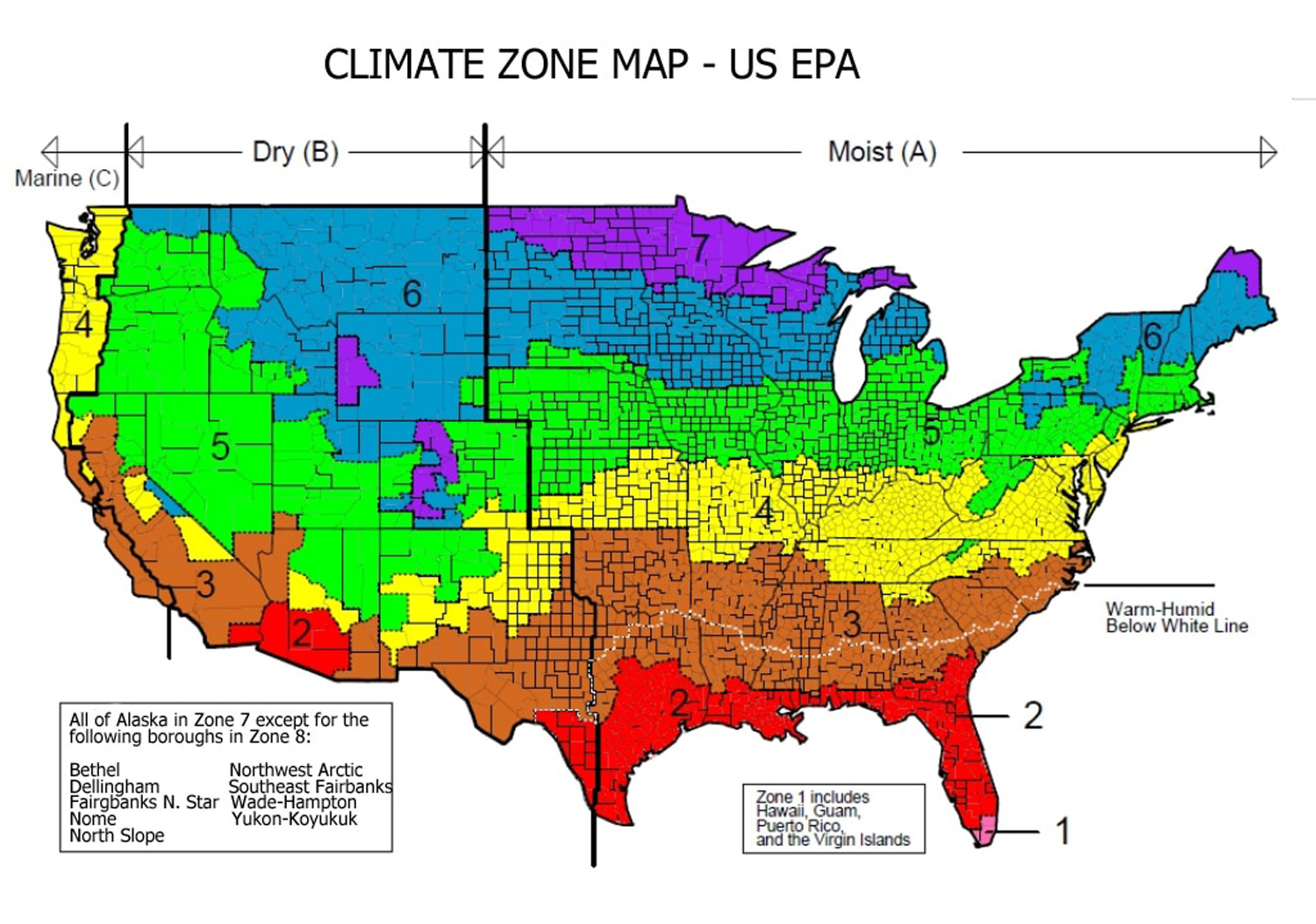
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) Climate Zone Map is an essential tool for architects, engineers, and building professionals. This map, updated in 2016, provides a standardized framework for understanding the climatic conditions across North America, aiding in informed design decisions for buildings.
Understanding the Map’s Purpose and Structure:
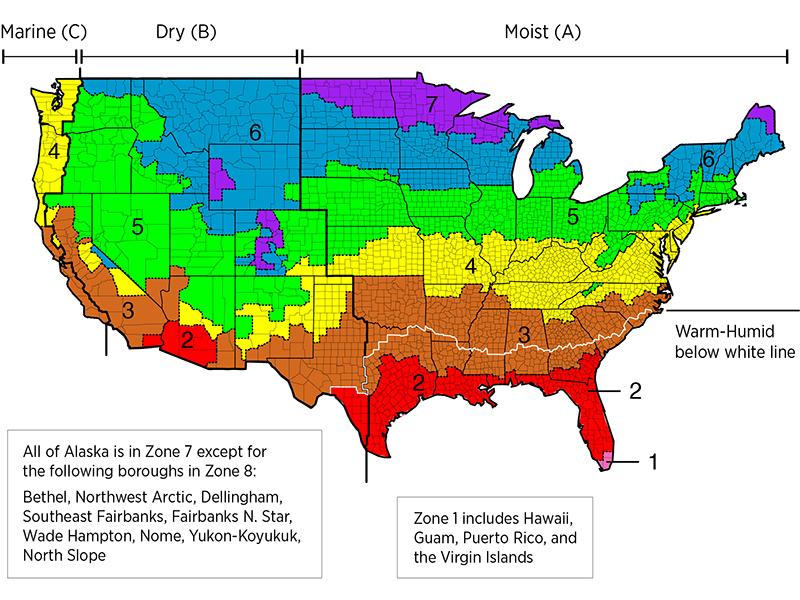
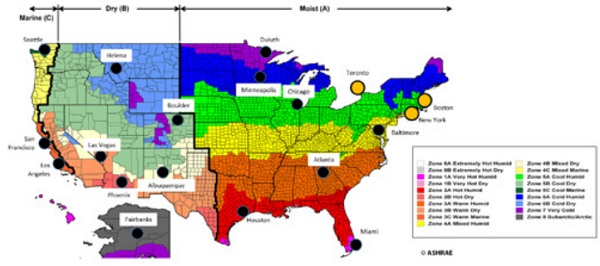
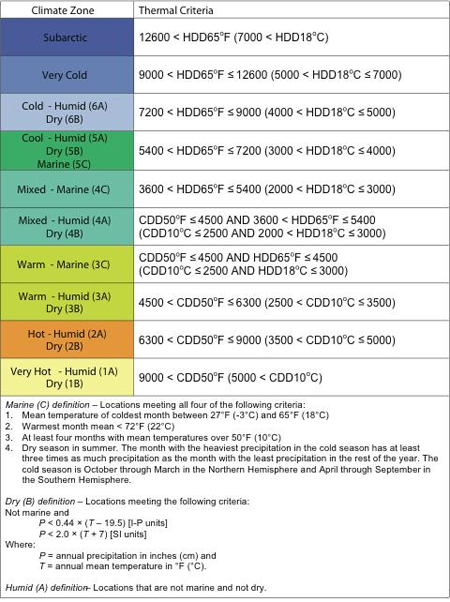
The ASHRAE Climate Zone Map is designed to categorize regions based on their average outdoor temperatures and humidity levels. This data, crucial for building energy efficiency and occupant comfort, is categorized into 16 climate zones, each represented by a unique color on the map. These zones are further subdivided into sub-zones based on specific temperature and humidity characteristics, providing a more nuanced understanding of regional climate variations.
Key Elements of the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map:
-
Design Heating and Cooling Temperatures: Each zone is defined by specific design heating and cooling temperatures, representing the extreme conditions a building is expected to experience. These temperatures are crucial for sizing heating and cooling systems, ensuring adequate thermal comfort for occupants.
-
Humidity Levels: The map also accounts for humidity levels, which significantly impact building energy consumption and occupant comfort. Zones with higher humidity levels require different design considerations for ventilation and dehumidification systems.
-
Solar Radiation: While not explicitly depicted on the map, solar radiation levels are an important factor in building design. The ASHRAE Climate Zone Map provides a framework for understanding the general solar radiation patterns across different regions, influencing decisions on building orientation, glazing, and shading strategies.
Benefits of Utilizing the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map:
-
Energy Efficiency: The map’s data empowers designers to select appropriate building systems and materials, optimizing energy consumption for heating, cooling, and ventilation. This leads to reduced operating costs and a smaller environmental footprint.
-
Occupant Comfort: By understanding the climate conditions, designers can create buildings that provide a comfortable and healthy indoor environment for occupants, regardless of the outdoor temperature.
-
Building Durability: The map helps identify regions prone to extreme weather conditions, enabling designers to incorporate appropriate building materials and construction techniques for enhanced durability and longevity.
-
Standardized Design Practices: The ASHRAE Climate Zone Map provides a common language and framework for building professionals across North America, facilitating collaboration and consistency in design practices.
Beyond the Basics: Delving Deeper into Climate Data:
The ASHRAE Climate Zone Map serves as a starting point for understanding regional climate conditions. However, for more detailed information, designers can refer to the ASHRAE Handbook, which provides comprehensive data on various climatic factors, including:
- Temperature Extremes: Daily and seasonal temperature variations, including extreme highs and lows.
- Humidity Levels: Relative humidity, dew point, and other humidity-related metrics.
- Wind Patterns: Wind speed and direction, crucial for ventilation and building facade design.
- Precipitation: Annual precipitation levels, including rainfall, snowfall, and hail.
FAQs Regarding the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map:
Q: How often is the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map updated?
A: The ASHRAE Climate Zone Map is periodically reviewed and updated based on new climate data and changes in building technologies. The most recent update was in 2016, and the next update is expected in the coming years.
Q: What are the implications of climate change on the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map?
A: Climate change is expected to significantly impact regional climates, necessitating future updates to the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map. Projections indicate shifts in temperature patterns, increased precipitation in some regions, and changes in humidity levels.
Q: Can the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map be applied to regions outside North America?
A: While the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map is specific to North America, similar climate zone maps exist for other regions of the world. These maps, often developed by local organizations or governments, provide comparable climate data for building design.
Tips for Utilizing the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map:
- Consult the ASHRAE Handbook for detailed climate data: The handbook provides in-depth information beyond the basic zone designations.
- Consider regional variations within zones: While the map provides a general overview, specific locations within a zone may experience unique microclimates.
- Integrate climate data with other design factors: Climate information should be considered alongside building orientation, site conditions, and occupant needs.
- Stay informed about updates and revisions: The ASHRAE Climate Zone Map is periodically updated to reflect evolving climate data and building technologies.
Conclusion:
The ASHRAE Climate Zone Map is an indispensable tool for building professionals, providing a standardized framework for understanding regional climate conditions and their impact on building design. By utilizing the map’s data, designers can create energy-efficient, comfortable, and durable buildings, contributing to a more sustainable built environment. As climate change continues to impact the planet, the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map will play an increasingly crucial role in guiding building design practices and ensuring the resilience of our built infrastructure.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying the ASHRAE Climate Zone Map: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Climate Data for Building Design. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!