The Legacy Of The German Democratic Republic: A Map Of Division And Reunification
The Legacy of the German Democratic Republic: A Map of Division and Reunification
Related Articles: The Legacy of the German Democratic Republic: A Map of Division and Reunification
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Legacy of the German Democratic Republic: A Map of Division and Reunification. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Legacy of the German Democratic Republic: A Map of Division and Reunification
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Legacy of the German Democratic Republic: A Map of Division and Reunification
- 3.1 A Divided Nation: The Map of East Germany
- 3.2 Beyond the Borders: The Berlin Wall and the Iron Curtain
- 3.3 The Legacy of East Germany: Beyond the Map
- 3.4 Importance and Benefits of Studying the Map of East Germany
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions About the Map of East Germany
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding the Map of East Germany
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Legacy of the German Democratic Republic: A Map of Division and Reunification
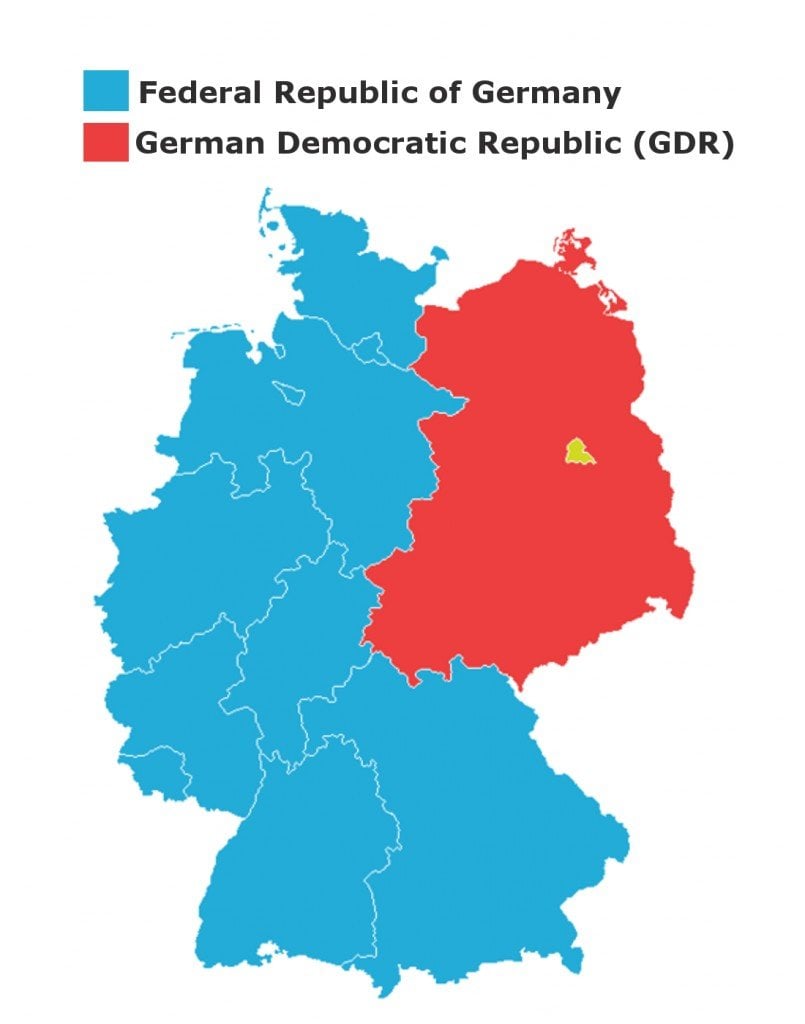
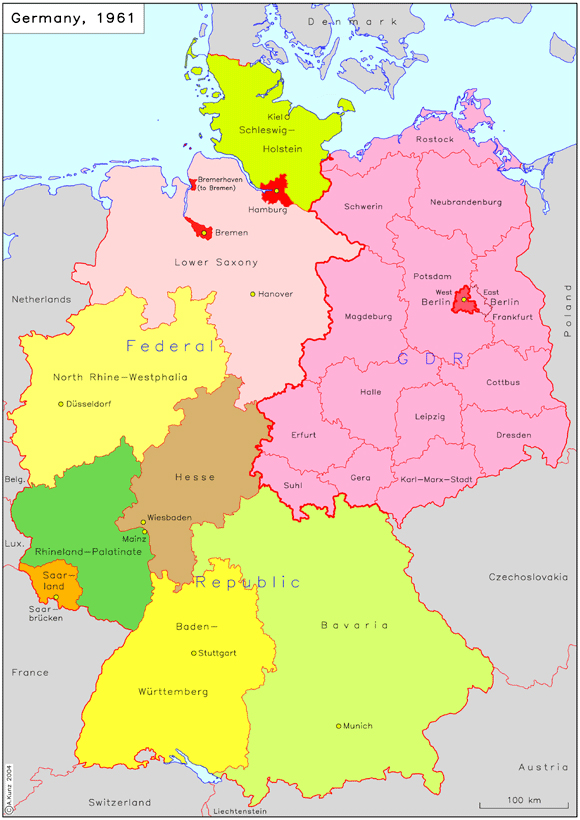
The map of the German Democratic Republic (GDR), commonly known as East Germany, is a powerful visual representation of a complex historical period. From its establishment in 1949 to its reunification with West Germany in 1990, the GDR existed as a separate entity, defined by its unique political and social structures. This map, while representing a physical division, also embodies the ideological and cultural divides that shaped the lives of millions.
A Divided Nation: The Map of East Germany
The map of East Germany is a stark reminder of the division of Germany after World War II. The country was divided into four occupation zones, with the Soviet Union controlling the eastern region. This region, encompassing the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Saxony, and Berlin (excluding West Berlin), became the German Democratic Republic.
The map reflects the political and ideological realities of the Cold War era. The GDR was a socialist state, heavily influenced by the Soviet Union, with a strong emphasis on centralized planning and state control. This is reflected in the map’s representation of the GDR’s industrial centers, particularly in the eastern regions, which were heavily focused on heavy industry and manufacturing.
Beyond the Borders: The Berlin Wall and the Iron Curtain
The map of East Germany also highlights the presence of the Berlin Wall, a physical manifestation of the ideological divide that ran through the heart of Germany. Built in 1961, the wall separated East and West Berlin, symbolizing the impenetrable barrier between the two Germanys.
The Berlin Wall, along with the Iron Curtain that separated Eastern Europe from Western Europe, are powerful reminders of the Cold War’s impact on the map of Europe. The map of East Germany, with its border running through the heart of Berlin, becomes a symbol of the Cold War’s division, not just of Germany, but of Europe as a whole.
The Legacy of East Germany: Beyond the Map
The map of East Germany is not just a geographical representation; it also embodies the legacy of a unique social and cultural experience. The GDR developed its own distinct identity, with its own language, music, and cultural traditions. This is reflected in the map’s representation of East German cities like Dresden, Leipzig, and Weimar, each with their own rich cultural heritage.
The reunification of Germany in 1990 erased the physical division on the map, but the legacy of East Germany remains. The map serves as a reminder of the complexities of German history, the impact of the Cold War, and the challenges of building a unified nation from a divided past.
Importance and Benefits of Studying the Map of East Germany
Understanding the map of East Germany offers several benefits:
- Historical Context: It provides a visual representation of the Cold War’s impact on Germany and Europe, offering a deeper understanding of the historical context of the period.
- Social and Cultural Insights: It sheds light on the unique social and cultural experiences of East Germans, fostering empathy and understanding of the complexities of the GDR’s history.
- Political Analysis: It helps analyze the political and economic systems of the GDR, offering valuable insights into the challenges of socialist governance and the transition to a unified economy.
- Contemporary Relevance: The map serves as a reminder of the fragility of peace and the importance of dialogue and understanding in resolving political and ideological differences.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Map of East Germany
Q: Why was Germany divided after World War II?
A: Germany was divided into four occupation zones by the Allied powers after World War II. The Soviet Union controlled the eastern zone, which eventually became the German Democratic Republic. The division reflected the ideological differences between the Soviet Union and the Western Allies.
Q: What was the purpose of the Berlin Wall?
A: The Berlin Wall was constructed by the East German government in 1961 to prevent East Germans from fleeing to West Berlin. It served as a physical manifestation of the ideological divide between East and West Germany.
Q: How did the reunification of Germany happen?
A: The reunification of Germany occurred in 1990, following the fall of the Berlin Wall and the collapse of the Soviet Union. The process involved negotiations between the two German states and the international community, leading to the formal unification of the two Germanys.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced by East Germany after reunification?
A: East Germany faced significant challenges after reunification, including economic disparities, social tensions, and cultural differences. The transition to a unified economy and the integration of East German institutions into the West German system presented significant obstacles.
Q: What is the significance of the map of East Germany today?
A: The map of East Germany serves as a reminder of the Cold War’s impact on Germany and Europe. It also provides a historical context for understanding the challenges of reunification and the continuing process of building a unified German identity.
Tips for Understanding the Map of East Germany
- Consult Historical Maps: Examine maps from different periods, including the immediate post-World War II era, the Cold War, and the period leading up to reunification.
- Study Primary Sources: Explore historical documents, diaries, and interviews from individuals who lived in East Germany.
- Explore Cultural Artifacts: Examine East German art, music, and literature to gain insights into the unique cultural experiences of the period.
- Engage in Discussion: Discuss the map with others, sharing perspectives and interpretations to foster a deeper understanding of the complex historical context.
Conclusion
The map of East Germany is a powerful visual representation of a complex historical period. It serves as a reminder of the division of Germany after World War II, the impact of the Cold War, and the challenges of building a unified nation from a divided past. By studying the map and its historical context, we gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of German history, the importance of dialogue and understanding in resolving political and ideological differences, and the ongoing process of building a unified German identity.


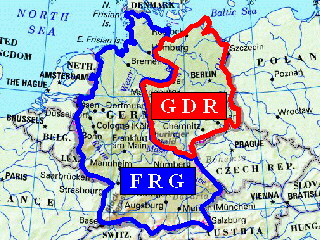

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Legacy of the German Democratic Republic: A Map of Division and Reunification. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
