The Power Of Precision: Understanding Maps Drawn To Scale
The Power of Precision: Understanding Maps Drawn to Scale
Related Articles: The Power of Precision: Understanding Maps Drawn to Scale
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Precision: Understanding Maps Drawn to Scale. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Precision: Understanding Maps Drawn to Scale

Maps, ubiquitous tools for navigating our world, are often taken for granted. Yet, their accuracy, particularly in their ability to represent distances and proportions faithfully, is crucial for a multitude of applications. This accuracy is achieved through the concept of scale, a fundamental principle in cartography.
Scale: The Bridge Between Reality and Representation
A map drawn to scale serves as a miniature representation of the real world, meticulously maintaining the proportions between distances on the map and their corresponding distances on the ground. This crucial aspect allows for accurate measurement and analysis of geographical features, fostering a deeper understanding of spatial relationships.
Types of Map Scales
Map scales can be expressed in various ways, each offering a different perspective on the relationship between map and reality:
-
Verbal Scale: This straightforward method states the ratio between map distance and ground distance in words, such as "1 centimeter on the map represents 10 kilometers on the ground."
-
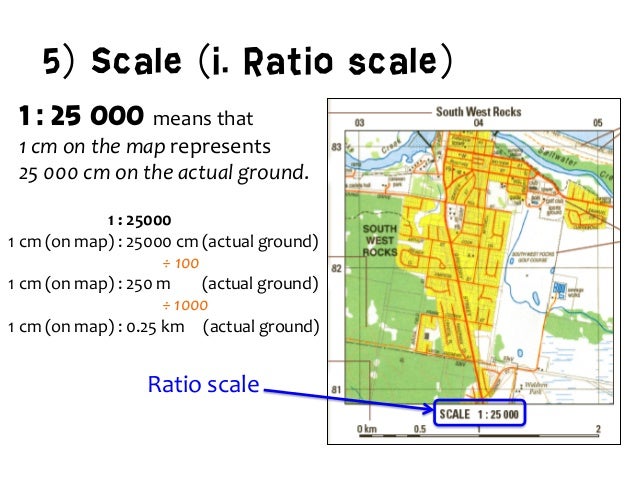
Representative Fraction (RF): This numerical representation expresses the scale as a fraction, with the numerator representing the map distance and the denominator representing the corresponding ground distance. For instance, a scale of 1:100,000 indicates that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
-
Graphic Scale: This visual representation utilizes a line divided into segments, with each segment representing a specific distance on the ground. This allows for quick and easy measurements directly from the map.
The Importance of Scale in Mapping
The significance of maps drawn to scale extends far beyond mere navigation. They are indispensable tools in a wide range of disciplines, enabling:
-
Accurate Distance Measurement: Measuring distances on maps drawn to scale provides precise information about the actual distance between locations, crucial for transportation planning, resource management, and infrastructure development.
-
Spatial Analysis: By maintaining accurate proportions, these maps facilitate analysis of spatial relationships, allowing for the identification of patterns, trends, and correlations between geographical features.
-
Land Use Planning: Precise land measurements and area calculations are essential for effective land management, urban planning, and environmental conservation efforts.
-
Resource Management: Maps drawn to scale aid in understanding the distribution and accessibility of natural resources, facilitating informed decisions about resource extraction, conservation, and sustainable development.
-
Emergency Response: Accurate maps are critical for emergency response teams to navigate efficiently and effectively during natural disasters, accidents, and other crises.
The Benefits of Using Maps Drawn to Scale
The use of maps drawn to scale offers numerous advantages:
-
Enhanced Precision: The ability to accurately measure distances and areas enables precise planning and decision-making across various sectors.
-
Improved Communication: Shared understanding of spatial relationships fosters effective communication and collaboration among stakeholders.
-
Informed Decision-Making: Maps drawn to scale provide reliable data that supports informed decision-making in various fields, from urban planning to environmental management.
-
Increased Efficiency: Precise measurements and spatial analysis facilitate efficient resource allocation and task execution, saving time and resources.
-
Enhanced Accuracy: Maps drawn to scale contribute to a more accurate understanding of the world, leading to better planning and more effective solutions to real-world problems.
FAQs about Maps Drawn to Scale
1. What is the difference between a map drawn to scale and a general map?
A map drawn to scale maintains a consistent relationship between distances on the map and their corresponding distances on the ground, ensuring accuracy in measurements and spatial analysis. General maps, on the other hand, may not be drawn to scale, providing a more general overview of the area without precise measurements.
2. How do I determine the scale of a map?
The scale of a map is typically indicated on the map itself, either verbally, numerically (representative fraction), or graphically. If the scale is not explicitly stated, it can be calculated by comparing a known distance on the map with the corresponding distance on the ground.
3. What are the limitations of maps drawn to scale?
Maps drawn to scale are still representations of the real world and are subject to limitations:
-
Distortion: Maps, especially those covering large areas, are prone to distortion, particularly in areas with significant curvature of the Earth’s surface.
-
Simplification: Maps simplify complex features for clarity, potentially omitting details or altering proportions to some extent.
-
Outdated Information: Maps can become outdated due to changes in the landscape, infrastructure, or other factors.
4. How are maps drawn to scale created?
The creation of maps drawn to scale involves a complex process that includes:
-
Data Collection: Gathering accurate data about the area, including elevation, land cover, and infrastructure.
-
Projection: Transforming the spherical Earth onto a flat map surface using a projection method, which introduces some distortion.
-
Generalization: Simplifying complex features for clarity and legibility, while maintaining the overall accuracy of the map.
-
Scale Determination: Selecting an appropriate scale that balances detail with legibility and the intended purpose of the map.
Tips for Using Maps Drawn to Scale
-
Identify the Scale: Always check the scale of the map before using it for measurement or analysis.
-
Understand the Projection: Be aware of the projection used to create the map, as it can influence the accuracy of measurements, particularly in areas with significant curvature.
-
Use Appropriate Tools: Employ suitable tools for measuring distances and areas on the map, such as rulers, compasses, or digital mapping software.
-
Consider the Context: Remember that maps are representations of reality and may not reflect all details or changes in the landscape.
Conclusion
Maps drawn to scale are essential tools for understanding and interacting with our world. Their ability to maintain accurate proportions between map and reality empowers us to measure distances, analyze spatial relationships, and make informed decisions in various fields. By embracing the principles of scale and understanding its limitations, we can leverage the power of maps to navigate our world, manage resources, and shape a more sustainable future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Precision: Understanding Maps Drawn to Scale. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!