The Silk Road: A Tapestry Of Trade And Cultural Exchange In Ancient China
The Silk Road: A Tapestry of Trade and Cultural Exchange in Ancient China
Related Articles: The Silk Road: A Tapestry of Trade and Cultural Exchange in Ancient China
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Silk Road: A Tapestry of Trade and Cultural Exchange in Ancient China. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Silk Road: A Tapestry of Trade and Cultural Exchange in Ancient China

The Silk Road, a network of trade routes that spanned thousands of kilometers across Asia, played a pivotal role in shaping the cultural, economic, and political landscape of ancient China. This intricate web of paths, extending from the easternmost reaches of China to the Mediterranean Sea, facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and people, forging lasting connections between civilizations and leaving an indelible mark on history.
A Pathway of Trade and Cultural Diffusion:
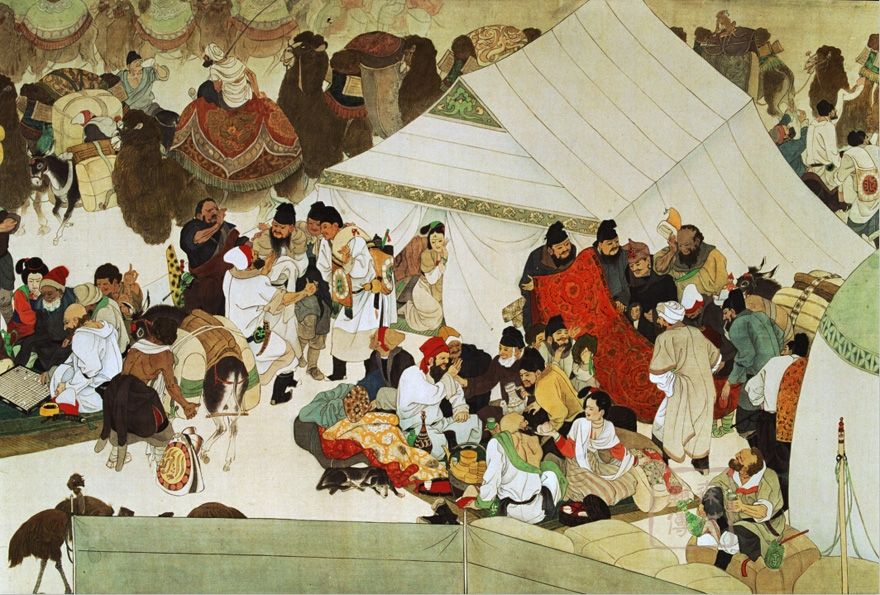
The Silk Road, as its name suggests, was renowned for its trade in silk, a luxurious commodity produced in China and highly sought after in the West. However, the network carried a vast array of goods, from spices, precious metals, and textiles to religious texts, philosophical ideas, and artistic creations. This exchange of goods, facilitated by merchants and travelers, spurred economic growth and cultural enrichment across the regions it connected.
The Silk Road’s Impact on Ancient China:
The Silk Road had a profound impact on ancient China, shaping its economic prosperity, cultural development, and political landscape.
-
Economic Prosperity: The trade in silk and other goods generated significant revenue for the Chinese government, bolstering its treasury and funding infrastructure projects. The influx of foreign goods stimulated domestic production, creating new industries and employment opportunities.
-
Cultural Exchange and Innovation: The Silk Road facilitated the exchange of ideas, technologies, and artistic styles between China and the West. Buddhist teachings, for example, traveled eastward along the Silk Road, influencing Chinese philosophy and art. Chinese inventions, such as gunpowder and papermaking, also spread westward, impacting other cultures.
-
Political Influence: The Silk Road enabled China to establish diplomatic relations with other civilizations, forging alliances and securing trade agreements. It also allowed China to project its influence and power across vast distances, bolstering its international standing.
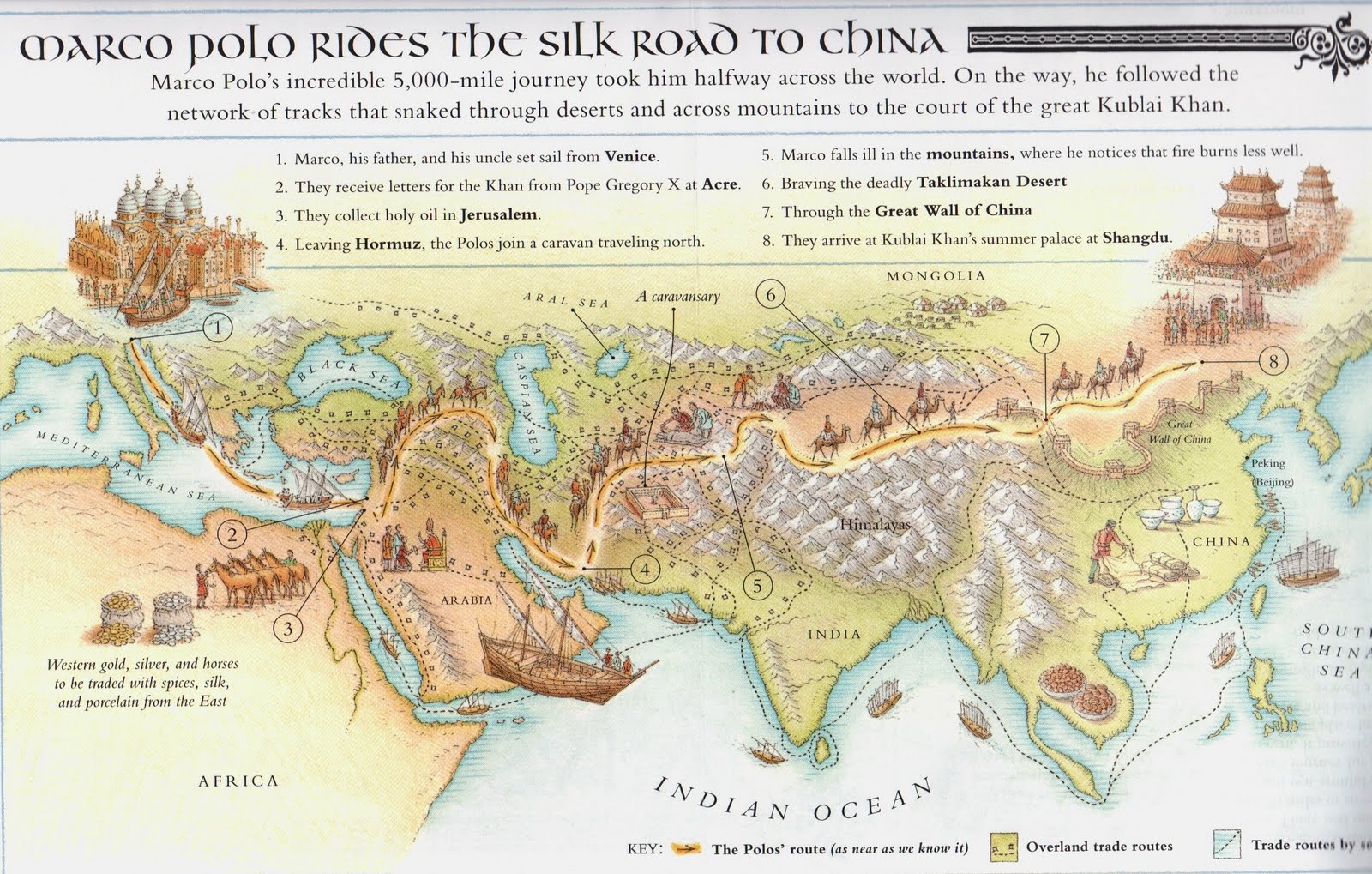
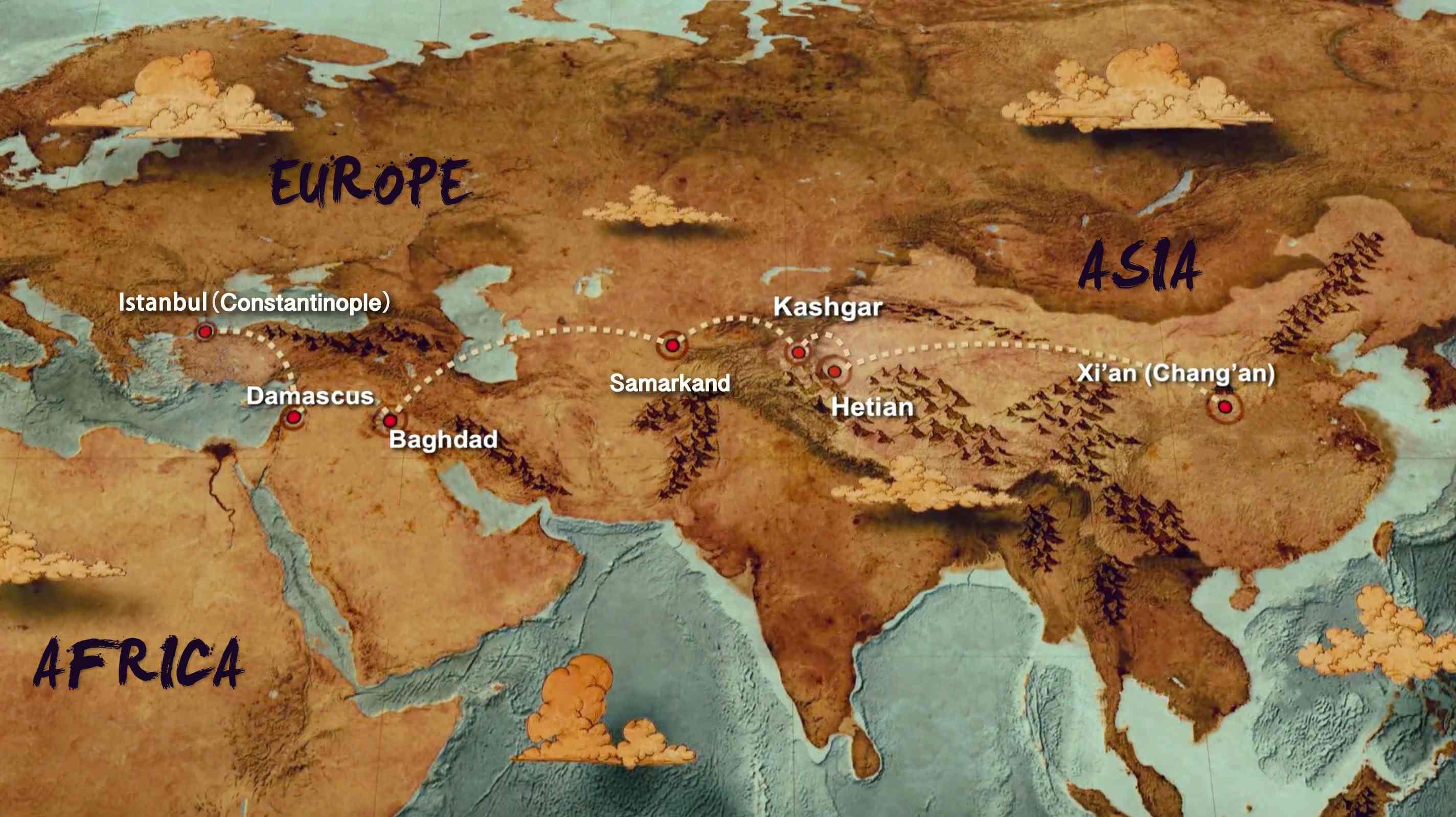
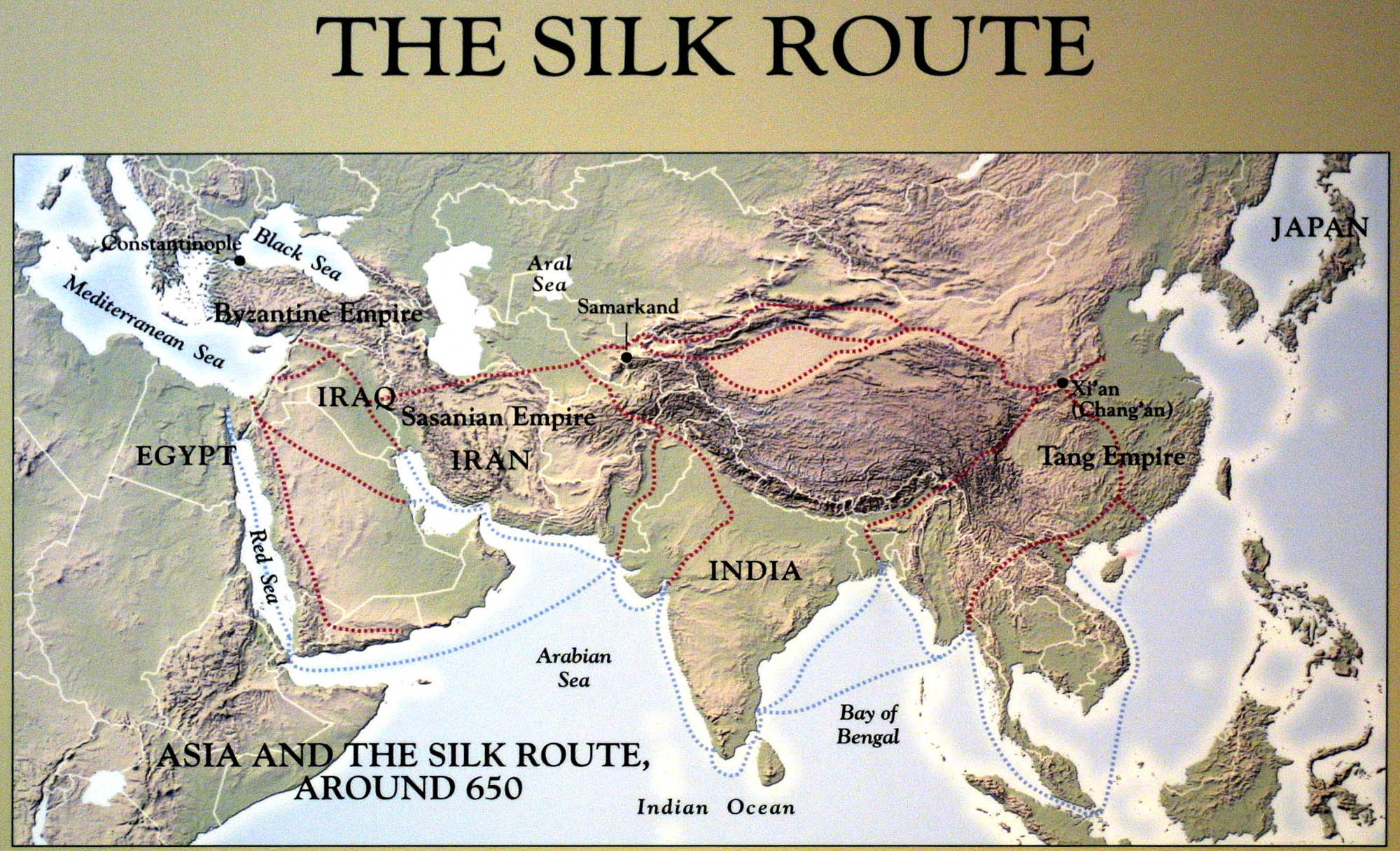
A Journey Through Time: Mapping the Silk Road:
The Silk Road was not a single, clearly defined path but a network of interconnected routes that evolved over time. Its routes varied depending on the era, political climate, and geographic conditions. However, some key segments and cities stand out as significant hubs of trade and cultural exchange:
-
Eastern Starting Point: The Silk Road originated in the ancient Chinese capital of Xi’an, located in the Shaanxi province. This city served as a central hub for trade and a gateway to the west.
-
The Gobi Desert and the Taklamakan Desert: The Silk Road traversed vast, arid landscapes, crossing the Gobi Desert and the Taklamakan Desert, posing significant challenges to travelers.
-
Central Asian Crossroads: The Silk Road passed through important cities in Central Asia, such as Samarkand, Bukhara, and Khiva, which served as crucial trade centers and cultural crossroads.
-
The Middle East and the Mediterranean: The Silk Road extended westward, reaching the Middle East and the Mediterranean, connecting China to civilizations like Persia, the Roman Empire, and the Byzantine Empire.
The Decline of the Silk Road:
The Silk Road’s dominance began to decline in the 15th century due to several factors:
-
The Rise of Maritime Trade: The development of maritime trade routes, facilitated by the advancements in shipbuilding and navigation, offered a more efficient and cost-effective alternative to overland routes.
-
Political Instability: Political instability and warfare across the Silk Road routes disrupted trade and made travel dangerous.
-
The Mongol Empire: The Mongol Empire, while initially promoting trade along the Silk Road, eventually imposed restrictions on trade and travel, leading to its decline.
The Legacy of the Silk Road:
Despite its decline, the Silk Road left an enduring legacy on the world. Its influence can be seen in:
-
Cultural Diffusion: The Silk Road facilitated the exchange of ideas, technologies, and artistic styles, enriching cultures and contributing to the development of new forms of expression.
-
Economic Growth: The trade along the Silk Road spurred economic growth and fostered the development of new industries and trade networks.
-
Global Connections: The Silk Road fostered connections between civilizations, promoting understanding and cultural exchange across vast distances.
FAQs about the Silk Road:
Q: What goods were traded along the Silk Road?
A: The Silk Road facilitated the trade of a vast array of goods, including silk, spices, precious metals, textiles, religious texts, philosophical ideas, and artistic creations.
Q: How did the Silk Road impact Chinese culture?
A: The Silk Road facilitated the exchange of ideas, technologies, and artistic styles between China and the West, influencing Chinese philosophy, art, and religion.
Q: What were the major cities along the Silk Road?
A: Key cities along the Silk Road included Xi’an (China), Samarkand, Bukhara, and Khiva (Central Asia), and cities in the Middle East and the Mediterranean.
Q: Why did the Silk Road decline?
A: The Silk Road’s decline was due to factors such as the rise of maritime trade, political instability, and the Mongol Empire’s restrictions on trade and travel.
Q: What is the legacy of the Silk Road?
A: The Silk Road’s legacy includes its contribution to cultural diffusion, economic growth, and global connections, leaving an enduring impact on the world.
Tips for Studying the Silk Road:
-
Explore maps and historical accounts: Maps and historical accounts provide valuable insights into the routes, cities, and goods traded along the Silk Road.
-
Research different cultures and civilizations: Gaining knowledge about the cultures and civilizations connected by the Silk Road helps understand the exchange of ideas and goods.
-
Visit museums and archaeological sites: Museums and archaeological sites offer tangible evidence of the Silk Road’s existence and its impact on different cultures.
Conclusion:
The Silk Road, a network of trade routes that spanned thousands of kilometers across Asia, played a pivotal role in shaping the cultural, economic, and political landscape of ancient China. It facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and people, fostering connections between civilizations and leaving an enduring legacy on the world. The Silk Road’s impact on cultural diffusion, economic growth, and global connections continues to resonate today, reminding us of the importance of trade and cultural exchange in shaping the course of history.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Silk Road: A Tapestry of Trade and Cultural Exchange in Ancient China. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!