The Songhai Empire: A Legacy Etched On The Map Of West Africa
The Songhai Empire: A Legacy Etched on the Map of West Africa
Related Articles: The Songhai Empire: A Legacy Etched on the Map of West Africa
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Songhai Empire: A Legacy Etched on the Map of West Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Songhai Empire: A Legacy Etched on the Map of West Africa

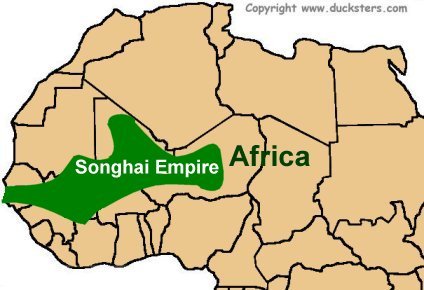
The Songhai Empire, a powerful and influential civilization that flourished in West Africa between the 13th and 16th centuries, left an indelible mark on the history and culture of the region. Its vast territory, encompassing present-day Mali, Niger, and parts of Burkina Faso and Algeria, was a testament to the empire’s military prowess and sophisticated administrative system. Today, the Songhai legacy continues to resonate, shaping the landscape, culture, and identity of the West African nations that once fell under its sway.
A Journey Through Time: Tracing the Songhai on the Map
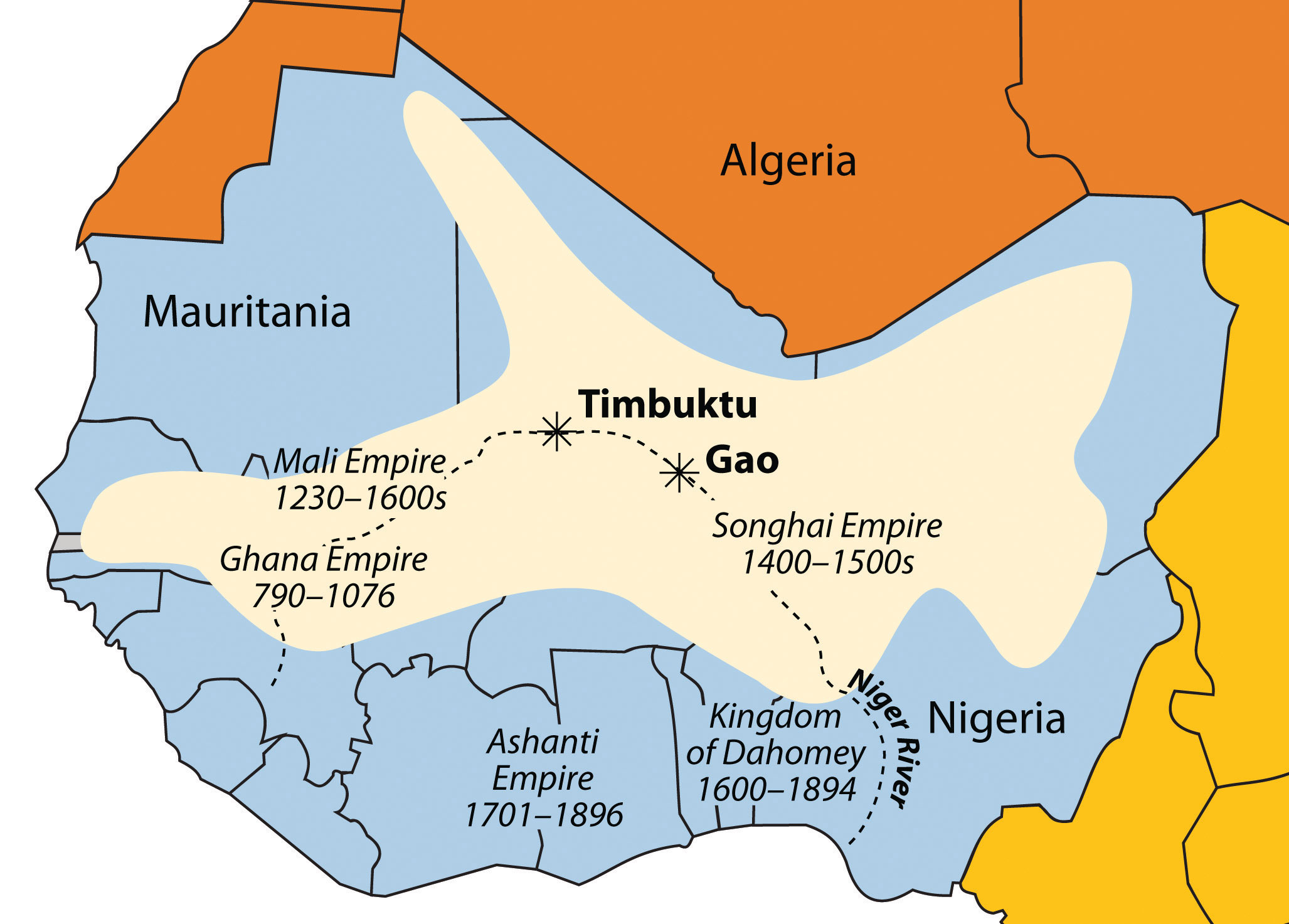
To understand the Songhai’s influence, it is crucial to visualize their geographical footprint. The empire’s core territory stretched along the Niger River, a vital artery that provided access to trade routes, fertile lands, and abundant resources. The city of Gao, located in present-day Mali, served as the empire’s capital, strategically positioned at the crossroads of trans-Saharan trade networks.
The Rise of a Powerful Empire:
The Songhai’s rise to prominence can be traced back to the 13th century, when they established a powerful kingdom in the region. Under the leadership of the Sonni dynasty, the Songhai gradually expanded their territory, conquering neighboring states and consolidating their control over the lucrative trans-Saharan trade routes.
The empire’s military prowess was legendary. Its army, equipped with sophisticated weaponry and skilled horsemen, proved formidable in battle. The Songhai’s strategic brilliance was evident in their ability to utilize alliances, diplomacy, and military force to secure their dominion.
A Flourishing Society:
The Songhai Empire was not merely a military power; it also fostered a rich and vibrant culture. The empire’s rulers patronized the arts, literature, and scholarship, leading to a flourishing intellectual environment. The city of Timbuktu, a renowned center of learning, became a hub for scholars, traders, and travelers from across the Sahara.
The Songhai also established a sophisticated administrative system, with a complex network of officials, bureaucrats, and judges responsible for managing the vast empire. This system ensured stability and order, contributing to the empire’s longevity.
The Legacy of the Songhai Empire:
The Songhai Empire’s collapse in the 16th century, at the hands of the Moroccan invasion, marked a significant turning point in West African history. However, the empire’s legacy continues to shape the region’s cultural landscape.
The Songhai’s influence can be seen in:
- Language: The Songhai language, spoken by millions across West Africa, is a testament to the empire’s enduring cultural impact.
- Architecture: The impressive mud-brick architecture of Timbuktu, with its mosques and universities, reflects the Songhai’s architectural prowess and their commitment to learning.
- Trade and Commerce: The trans-Saharan trade routes, established and strengthened by the Songhai, continue to play a vital role in the economic life of the region.
- Political and Social Structures: The Songhai’s administrative and legal systems left a lasting imprint on the political and social structures of West African societies.
FAQs about the Songhai Empire:
1. What were the major cities of the Songhai Empire?
The major cities of the Songhai Empire included Gao (the capital), Timbuktu, Jenne, and Walata. These cities were strategic centers for trade, administration, and intellectual life.
2. What were the main sources of wealth for the Songhai Empire?
The Songhai Empire derived its wealth primarily from the trans-Saharan trade routes, which facilitated the exchange of goods like salt, gold, slaves, and textiles. The empire also controlled fertile agricultural lands along the Niger River, producing crops like millet, sorghum, and rice.
3. What was the role of Islam in the Songhai Empire?
Islam played a significant role in Songhai society, influencing its legal system, education, and social practices. The empire’s rulers were devout Muslims, and they patronized the construction of mosques and the establishment of Islamic schools.
4. How did the Songhai Empire decline?
The Songhai Empire’s decline was triggered by a series of factors, including internal strife, the rise of powerful neighboring states, and the invasion of the Moroccan army in the 16th century.
5. What are the lasting legacies of the Songhai Empire?
The Songhai Empire left a lasting legacy in West Africa, influencing its language, architecture, trade networks, political structures, and cultural practices. Its influence can still be seen in the region’s cultural landscape today.
Tips for Studying the Songhai Empire:
- Explore primary sources: Consult historical texts written by Arab travelers, European explorers, and Songhai chroniclers to gain insights into the empire’s daily life, governance, and culture.
- Analyze archaeological evidence: The remains of Songhai cities, fortifications, and artifacts provide valuable clues about the empire’s material culture and technological advancements.
- Study the Songhai language: Learning the Songhai language can provide a deeper understanding of the empire’s cultural heritage and its connection to present-day West Africa.
- Compare and contrast the Songhai with other West African empires: Examining the similarities and differences between the Songhai and other empires, such as Ghana and Mali, can provide a broader perspective on the historical development of the region.
Conclusion:
The Songhai Empire stands as a testament to the ingenuity, resilience, and cultural richness of West African civilizations. Its influence continues to resonate in the region’s language, architecture, trade networks, and cultural practices. By studying the Songhai’s history, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and fascinating tapestry of West African history and its enduring legacy.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Songhai Empire: A Legacy Etched on the Map of West Africa. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!