Understanding Scale: A Comprehensive Look At Area Measurement On Maps
Understanding Scale: A Comprehensive Look at Area Measurement on Maps
Related Articles: Understanding Scale: A Comprehensive Look at Area Measurement on Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Scale: A Comprehensive Look at Area Measurement on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Scale: A Comprehensive Look at Area Measurement on Maps

Maps are powerful tools for visualizing and understanding the world around us. They provide a condensed representation of vast landscapes, allowing us to navigate, explore, and analyze spatial relationships. A key element in map interpretation is the concept of scale, which dictates the relationship between distances on the map and corresponding distances in the real world. One common way to express scale is through area measurement, often represented in square miles.
Defining Area Measurement
Area measurement quantifies the two-dimensional extent of a surface. In the context of maps, it helps us understand the size and relative proportions of geographical features. Square miles are a unit of area measurement commonly used in the United States and other countries. One square mile is equivalent to 640 acres or 2.59 square kilometers.
Visualizing 1,000 Square Miles on a Map
To grasp the magnitude of 1,000 square miles, it’s helpful to visualize it in relation to familiar geographical features.
- Cities: 1,000 square miles is roughly the size of a medium-sized city like San Francisco, California, or Denver, Colorado.
- National Parks: Many national parks, such as Yellowstone National Park or Glacier National Park, encompass an area larger than 1,000 square miles.
- States: States like Delaware or Rhode Island are smaller than 1,000 square miles.
The Significance of Area Measurement on Maps
Area measurement plays a crucial role in various disciplines and applications:
- Geography and Cartography: Area measurement is fundamental to map creation, allowing cartographers to accurately represent the size and proportions of geographical features.
- Environmental Studies: Area measurement helps researchers understand the extent of natural habitats, deforestation, or land use changes.
- Urban Planning and Development: Area measurement is essential for planning urban growth, allocating resources, and managing infrastructure.
- Resource Management: Area measurement aids in assessing the availability and distribution of natural resources like water, minerals, and timber.
- Agriculture and Forestry: Area measurement helps farmers and foresters manage land use, track crop yields, and assess timber resources.
Factors Influencing Area Measurement on Maps
The accuracy of area measurement on maps depends on several factors:
- Map Projection: Different map projections distort the shape and size of geographical features.
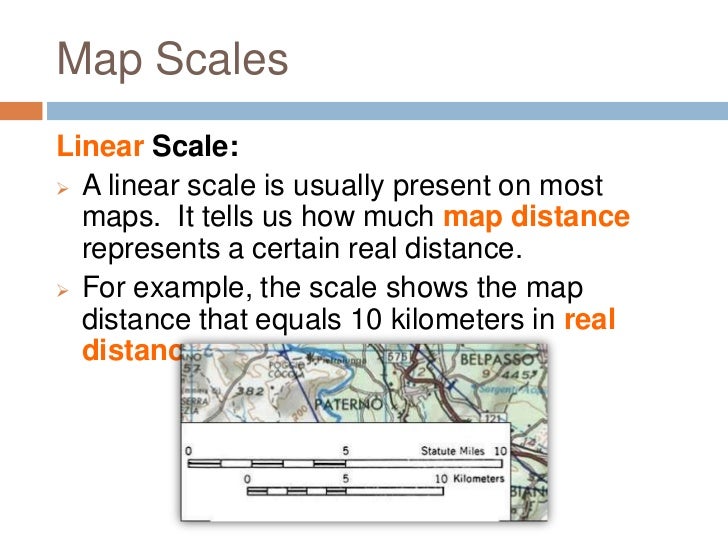
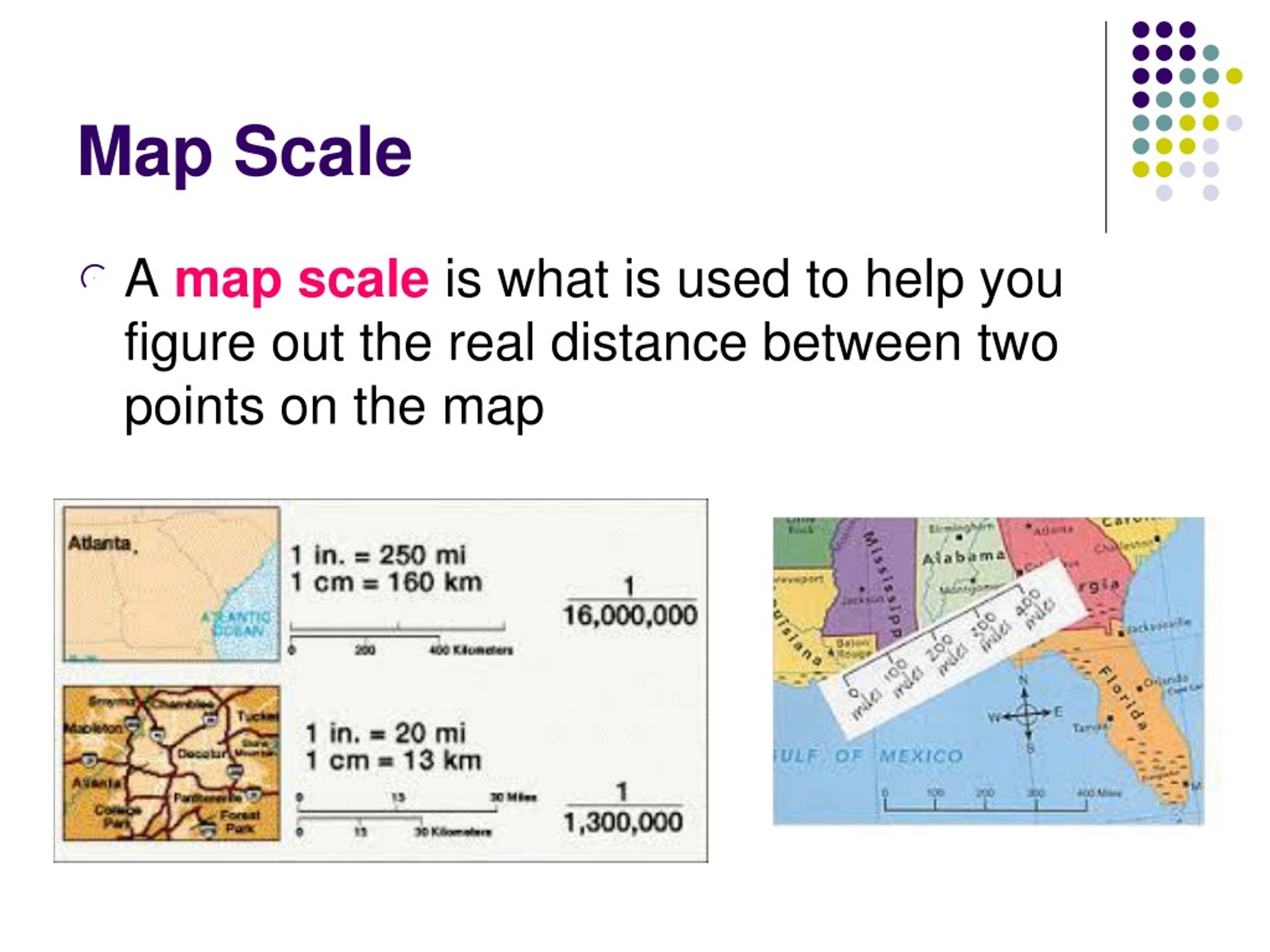
- Map Scale: Larger-scale maps (more detailed) provide more accurate area measurements than smaller-scale maps.
- Data Source: The accuracy of area measurement depends on the quality and precision of the underlying data used to create the map.
- Measurement Technique: Various techniques, like grid-based methods or digital analysis tools, are used for area measurement, each with its own level of accuracy.
FAQs about Area Measurement on Maps
Q: What is the difference between square miles and miles?
A: Miles measure distance, while square miles measure area. A mile is a linear unit of measurement, while a square mile is a two-dimensional unit representing the area of a square with sides of one mile each.
Q: How can I calculate the area of a region on a map?
A: You can use grid-based methods, digital analysis software, or online tools that allow you to measure the area of a selected region on a map.
Q: What are the limitations of area measurement on maps?
A: Map projections, scale, and data quality can all introduce inaccuracies in area measurement. It’s crucial to be aware of these limitations and interpret area measurements with caution.
Tips for Using Area Measurement on Maps
- Check the Map Scale: Always verify the map scale to understand the relationship between map distances and real-world distances.
- Consider the Map Projection: Be aware of the map projection used, as it can influence area measurements.
- Use Appropriate Measurement Tools: Utilize reliable grid-based methods, digital analysis tools, or online resources for accurate area measurement.
- Interpret Results with Caution: Recognize that area measurements on maps can be influenced by various factors and may not always reflect the exact area in the real world.
Conclusion
Area measurement on maps is a fundamental concept that helps us understand the size and proportions of geographical features. By visualizing 1,000 square miles in relation to familiar landmarks and exploring its significance across various disciplines, we gain a deeper appreciation for the power and limitations of maps as tools for spatial analysis. As we navigate the complex world of spatial data, a clear understanding of area measurement and its nuances will continue to be crucial for accurate interpretation and informed decision-making.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Scale: A Comprehensive Look at Area Measurement on Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!