Understanding The Alpha-Gal Syndrome Tick Map: A Guide To Prevention And Awareness
Understanding the Alpha-Gal Syndrome Tick Map: A Guide to Prevention and Awareness
Related Articles: Understanding the Alpha-Gal Syndrome Tick Map: A Guide to Prevention and Awareness
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Alpha-Gal Syndrome Tick Map: A Guide to Prevention and Awareness. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Alpha-Gal Syndrome Tick Map: A Guide to Prevention and Awareness
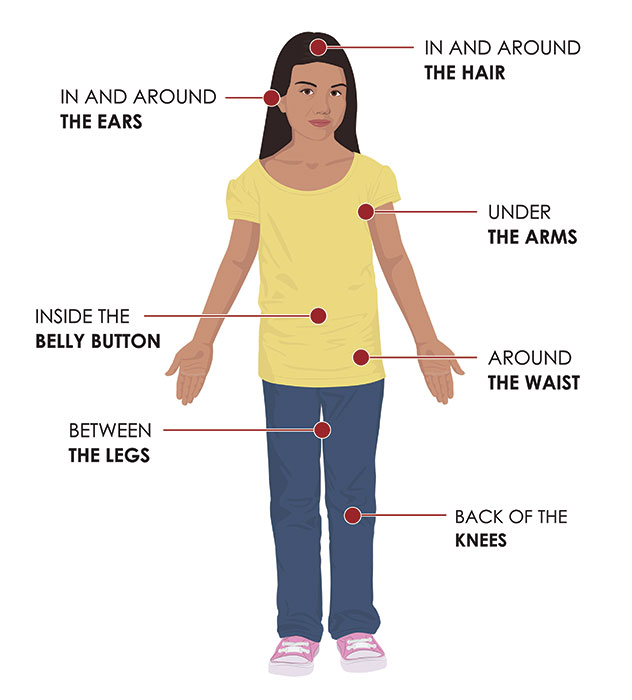
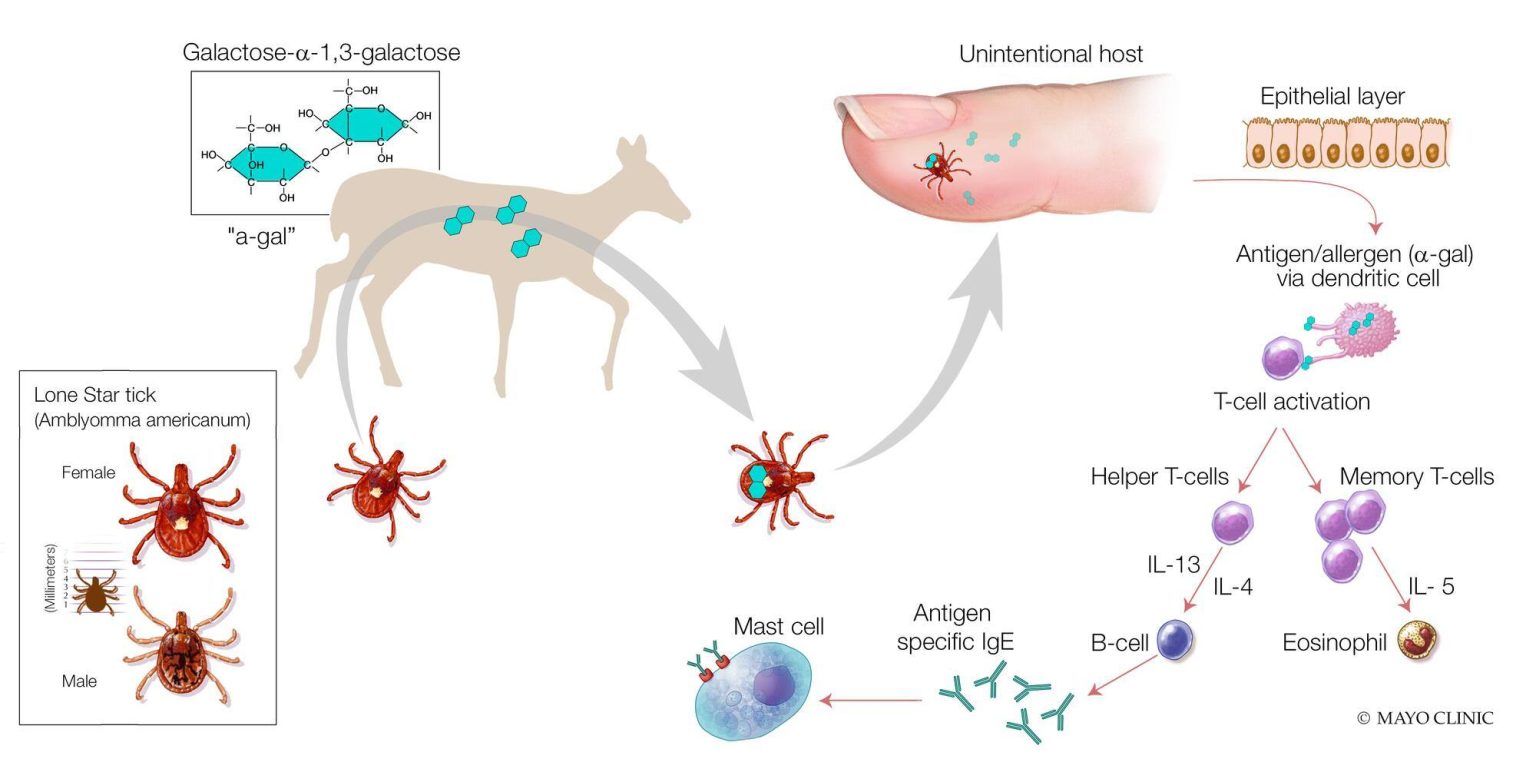
Alpha-gal syndrome (AGS) is a newly recognized food allergy that affects individuals who develop an allergic reaction to the sugar molecule alpha-gal, found in the meat of mammals like beef, pork, lamb, and even certain dairy products. While the exact cause of AGS is not fully understood, the primary culprit is a bite from a lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum). These ticks carry a specific type of alpha-gal sugar in their saliva, which is transferred to the host during feeding.
The Alpha-Gal Tick Map: A Visual Representation of Risk
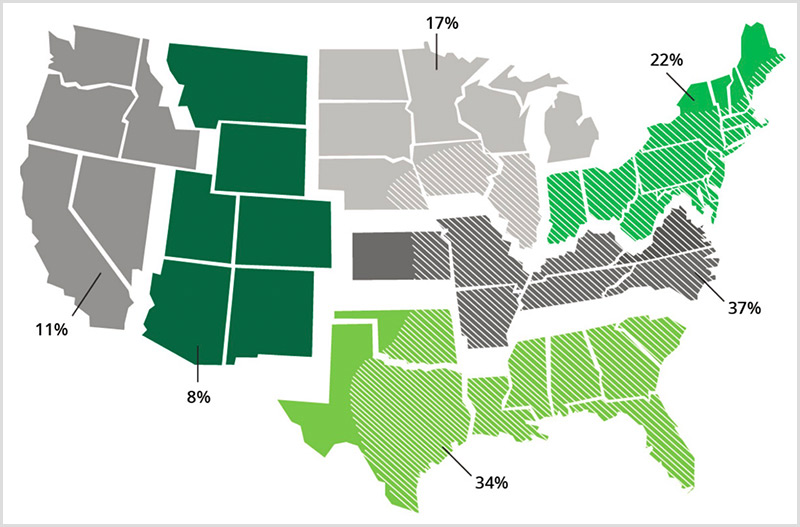
The alpha-gal tick map is a valuable tool for understanding the geographical distribution of AGS. It visually represents the areas where the lone star tick is prevalent, offering insights into regions with a higher risk of contracting alpha-gal syndrome.
Factors Affecting Tick Distribution and Alpha-Gal Syndrome Prevalence:
The prevalence of AGS is directly linked to the geographical distribution of the lone star tick. Several factors contribute to the spread of these ticks, including:
- Climate and Temperature: Lone star ticks thrive in warm, humid environments with ample vegetation.
- Host Availability: The availability of suitable hosts, such as deer, rabbits, and other mammals, plays a crucial role in their survival and spread.
- Human Activity: Human activities like urbanization, deforestation, and landscape changes can inadvertently create favorable conditions for tick populations.
Interpreting the Alpha-Gal Tick Map:
The alpha-gal tick map is not a definitive indicator of AGS prevalence. It provides a general overview of areas with a higher risk of encountering the lone star tick. However, it is important to note that:
- Ticks can migrate: Lone star ticks are known to travel long distances, potentially expanding their range beyond the areas depicted on the map.
- Local factors can influence risk: The presence of specific host populations and environmental conditions can influence the local prevalence of AGS, even in areas where the tick is not considered widespread.
The Importance of the Alpha-Gal Tick Map:
The alpha-gal tick map serves as a valuable tool for:
- Public health awareness: It helps raise awareness about the potential risk of AGS in specific regions, encouraging individuals to take preventive measures.
- Clinical diagnosis: Physicians can use the map as a reference point when evaluating patients presenting with symptoms suggestive of AGS, especially in areas with high tick prevalence.
- Research and monitoring: The map provides valuable data for researchers studying the epidemiology of AGS and its potential impact on public health.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Risk of Alpha-Gal Syndrome
While the alpha-gal tick map offers a valuable visual representation of risk, it is crucial to remember that AGS can occur in areas beyond those depicted on the map. The following factors can increase the risk of contracting AGS:
- Outdoor activities: Individuals who spend significant time outdoors, particularly in wooded or grassy areas, are more likely to encounter ticks.
- Pet ownership: Pets, especially dogs, can carry ticks and introduce them into homes, potentially increasing the risk of exposure for family members.
- Travel: Traveling to areas with a high prevalence of lone star ticks can increase the risk of being bitten.
FAQs about Alpha-Gal Syndrome and the Tick Map
1. How do I know if I have alpha-gal syndrome?
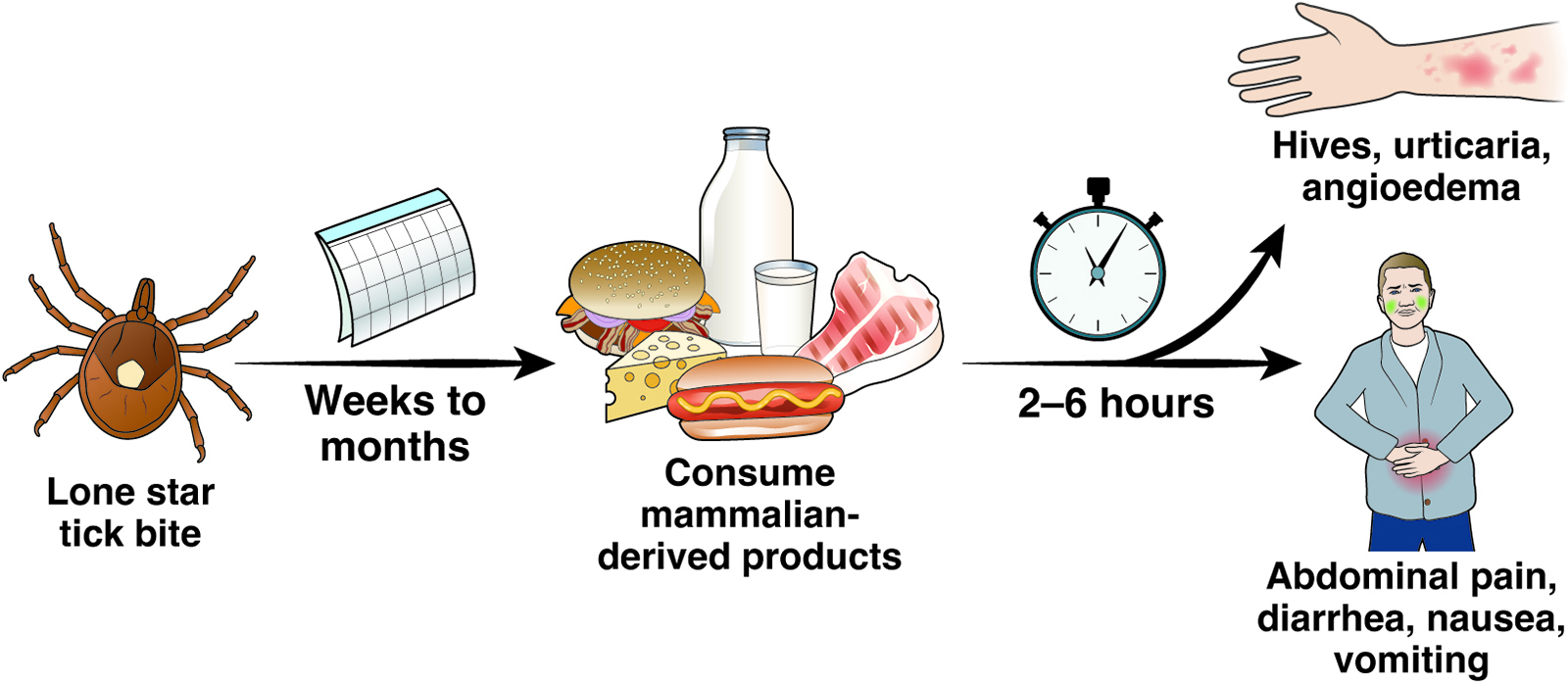
Symptoms of AGS typically appear 3-6 hours after consuming red meat and can include:
- Skin reactions: Hives, itching, swelling
- Gastrointestinal issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain
- Respiratory problems: Wheezing, shortness of breath
- Anaphylaxis: A severe, life-threatening allergic reaction
If you suspect you have AGS, consult with your doctor for proper diagnosis and management.
2. Can I be tested for alpha-gal syndrome?
Yes, blood tests can be used to detect the presence of alpha-gal antibodies, indicating a potential allergy.
3. How can I prevent alpha-gal syndrome?
- Tick prevention: Use insect repellent containing DEET or picaridin, wear light-colored clothing to spot ticks easily, and check for ticks regularly after spending time outdoors.
- Tick removal: Remove ticks promptly and carefully using tweezers.
- Avoidance of red meat: If you suspect you have AGS, avoid red meat and dairy products from mammals.
4. Is there a cure for alpha-gal syndrome?
Currently, there is no cure for AGS. However, avoiding red meat and dairy products from mammals can effectively manage symptoms.
5. What is the long-term outlook for people with alpha-gal syndrome?
The long-term outlook for individuals with AGS is generally good. By avoiding triggers and managing symptoms, most people can live normal lives. However, some individuals may experience more severe reactions or require ongoing medical management.
Tips for Preventing Alpha-Gal Syndrome
- Wear protective clothing: When outdoors, wear light-colored clothing, long pants, and tucked-in shirts to minimize skin exposure.
- Use insect repellent: Apply DEET or picaridin-based insect repellent to exposed skin and clothing.
- Check for ticks regularly: Conduct thorough tick checks after spending time in tick-infested areas.
- Remove ticks carefully: If you find a tick, remove it promptly and carefully using tweezers.
- Keep pets protected: Treat pets with tick prevention medication and check them regularly for ticks.
- Avoid tick-infested areas: If possible, avoid areas known to have high tick populations.
Conclusion
The alpha-gal tick map is a valuable tool for understanding the geographical distribution of AGS and raising awareness about the potential risk of this emerging allergy. By understanding the factors that influence tick prevalence and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of contracting AGS. While there is no cure for AGS, avoiding triggers and managing symptoms effectively can allow individuals to live normal lives. Continued research and public health initiatives are crucial for addressing this growing concern and improving the lives of individuals affected by alpha-gal syndrome.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Alpha-Gal Syndrome Tick Map: A Guide to Prevention and Awareness. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!