Unraveling The Complexity Of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide To SAN Maps
Unraveling the Complexity of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to SAN Maps
Related Articles: Unraveling the Complexity of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to SAN Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Complexity of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to SAN Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Complexity of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to SAN Maps

The world of spatial data is intricate and multifaceted, encompassing vast amounts of information about our planet’s physical features and human-made structures. Navigating this landscape requires sophisticated tools, and one such tool is the SAN map, a powerful instrument for understanding and analyzing geographic information. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of SAN maps, exploring their origins, functionalities, and applications in various fields.
Understanding the Fundamentals of SAN Maps
The acronym "SAN" stands for Spatial Analysis Network, a term that encapsulates the core purpose of these maps. SAN maps are not simply static representations of geographic data; they are dynamic systems designed to analyze, visualize, and manipulate spatial information.
Key Features of SAN Maps:
- Network Structure: SAN maps are built on a network structure, where nodes represent geographic locations and links represent connections between these locations. This network structure allows for the analysis of relationships and flows between different points on the map.
- Data Integration: SAN maps can integrate diverse types of spatial data, including geographic coordinates, demographic information, environmental data, and social indicators. This integration enables a holistic understanding of complex spatial phenomena.
-
Analytical Capabilities: SAN maps offer a wide range of analytical capabilities, including:
- Network analysis: Identifying optimal routes, analyzing traffic patterns, and understanding network connectivity.
- Spatial autocorrelation: Measuring the degree of spatial dependence between data points, revealing patterns and clusters.
- Proximity analysis: Determining the distance and proximity between locations, facilitating site selection and resource allocation.
- Spatial interpolation: Estimating data values at unobserved locations based on known values at neighboring points.
- Visualization Tools: SAN maps utilize powerful visualization tools to present complex spatial data in a clear and understandable manner. This includes thematic maps, choropleth maps, and network diagrams.
Applications of SAN Maps Across Disciplines
The versatility of SAN maps makes them indispensable tools in a wide range of disciplines, including:
1. Transportation and Logistics:
- Route Optimization: SAN maps enable the identification of the most efficient routes for transportation, minimizing travel time and costs.
- Traffic Flow Analysis: Understanding traffic patterns and congestion points helps optimize traffic management and infrastructure planning.
- Emergency Response Planning: SAN maps facilitate efficient deployment of emergency services by analyzing the shortest routes and optimal resource allocation.
2. Urban Planning and Development:
- Site Selection: SAN maps aid in identifying suitable locations for new developments based on factors like proximity to amenities, infrastructure, and population density.
- Infrastructure Planning: Analyzing the spatial distribution of infrastructure elements like roads, utilities, and public transportation helps optimize network design and expansion.
- Community Development: SAN maps can be used to identify areas with social vulnerability and inform targeted interventions for community development.
3. Environmental Management:
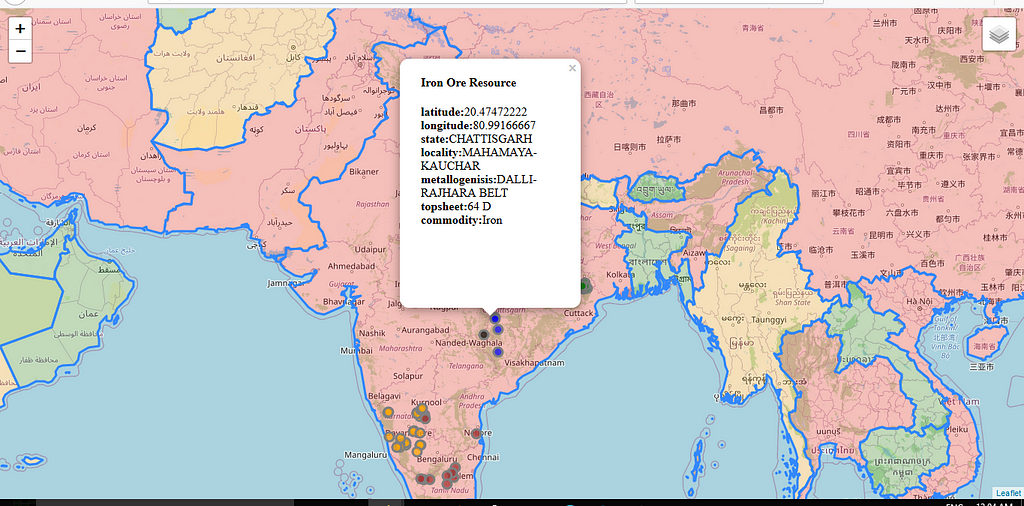
- Resource Management: Analyzing the spatial distribution of natural resources like water, forests, and minerals helps optimize their management and conservation.
- Pollution Monitoring and Control: SAN maps facilitate the identification of pollution sources and hotspots, supporting environmental monitoring and remediation efforts.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Understanding the spatial impacts of climate change on ecosystems and human populations enables informed adaptation strategies.
4. Public Health and Epidemiology:
- Disease Surveillance: SAN maps assist in tracking the spatial spread of diseases, identifying outbreaks, and implementing effective control measures.
- Health Service Planning: Analyzing the spatial distribution of health facilities and population demographics helps optimize service delivery and resource allocation.
- Environmental Health Risk Assessment: SAN maps can be used to assess the spatial distribution of environmental health risks and identify vulnerable populations.
5. Business and Marketing:
- Market Analysis: SAN maps help businesses understand the spatial distribution of their target market, identify growth opportunities, and optimize marketing campaigns.
- Site Selection: Choosing optimal locations for retail outlets, distribution centers, or manufacturing facilities based on factors like customer density and accessibility.
- Supply Chain Management: SAN maps facilitate the analysis of supply chain networks, optimizing transportation routes and inventory management.
FAQs: Demystifying the SAN Map
1. What is the difference between a SAN map and a traditional map?
Traditional maps focus on static representations of geographic features, while SAN maps are dynamic systems that analyze, manipulate, and visualize spatial data. They are designed to go beyond simple visualization and delve into the relationships and interactions between geographic locations and data points.
2. What are the benefits of using SAN maps?
SAN maps offer numerous benefits, including:
- Data-driven decision making: Providing insights based on spatial data analysis, leading to more informed and effective decisions.
- Improved efficiency: Optimizing processes like transportation, resource allocation, and emergency response.
- Enhanced understanding: Facilitating a deeper understanding of complex spatial phenomena and their interconnections.
- Visual clarity: Presenting spatial data in a clear and understandable manner, enabling better communication and collaboration.
3. What software is used to create and analyze SAN maps?
Various software tools are available for creating and analyzing SAN maps, including:
- ArcGIS: A comprehensive GIS software suite offering advanced spatial analysis capabilities.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software widely used for spatial data analysis and map creation.
- Gephi: A powerful software for network analysis and visualization, particularly useful for analyzing complex relationships within spatial data.
4. Are SAN maps suitable for all types of geographic data?
While SAN maps are highly versatile, their suitability depends on the specific type of data and the analytical objectives. For example, they are particularly well-suited for data involving connections and relationships between locations, like transportation networks, infrastructure systems, or disease spread.
5. What are some limitations of SAN maps?
Despite their numerous benefits, SAN maps have certain limitations:
- Data availability: The effectiveness of SAN maps depends on the availability of accurate and comprehensive spatial data.
- Complexity: Analyzing and interpreting SAN maps can be complex, requiring specialized skills and knowledge.
- Cost: Implementing and maintaining a SAN mapping system can be costly, especially for complex applications.
Tips for Effective SAN Map Utilization
- Define clear objectives: Clearly define the specific goals and questions you wish to address through SAN map analysis.
- Ensure data quality: Use reliable and accurate spatial data sources to ensure the validity of your analysis.
- Choose appropriate tools: Select software and techniques that are suitable for your specific data and objectives.
- Collaborate with experts: Engage with specialists in GIS, spatial analysis, and relevant subject areas to maximize the effectiveness of your analysis.
- Communicate effectively: Present your findings clearly and concisely using appropriate visualization techniques and communication strategies.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Spatial Analysis
SAN maps are powerful tools for understanding and analyzing geographic information, enabling informed decision-making and problem-solving across diverse fields. By leveraging their analytical capabilities, users can gain valuable insights into spatial patterns, relationships, and trends, driving progress in areas like transportation, urban planning, environmental management, public health, and business. As the world becomes increasingly data-driven, SAN maps play a crucial role in harnessing the power of spatial data for a more informed and sustainable future.


![]()



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Complexity of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to SAN Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!