Unraveling The Democratic Republic Of Congo’s Provinces: A Geographic And Administrative Perspective
Unraveling the Democratic Republic of Congo’s Provinces: A Geographic and Administrative Perspective
Related Articles: Unraveling the Democratic Republic of Congo’s Provinces: A Geographic and Administrative Perspective
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Democratic Republic of Congo’s Provinces: A Geographic and Administrative Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Democratic Republic of Congo’s Provinces: A Geographic and Administrative Perspective
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Democratic Republic of Congo’s Provinces: A Geographic and Administrative Perspective
- 3.1 A Historical Journey: From Provinces to Regions and Back
- 3.2 The Importance of Provincial Boundaries
- 3.3 Navigating the DRC’s Provincial Landscape: A Detailed Look
- 3.4 FAQs: Navigating the DRC’s Provincial Landscape
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding the DRC’s Provincial Map
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Complex and Dynamic Landscape
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Democratic Republic of Congo’s Provinces: A Geographic and Administrative Perspective
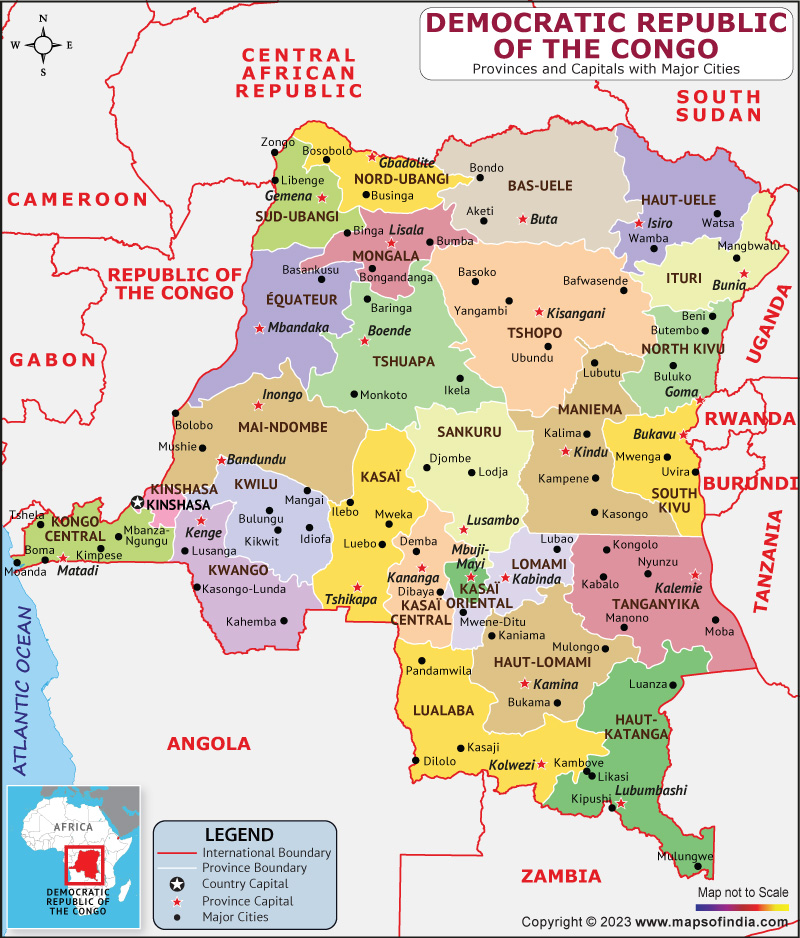
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), a vast nation in Central Africa, is a complex tapestry of diverse landscapes, rich resources, and a vibrant population. Understanding its administrative structure, particularly its provincial divisions, is crucial for comprehending the country’s political, economic, and social dynamics. This article delves into the intricate geography of the DRC, exploring its provinces, their boundaries, and the significance of this administrative framework.
A Historical Journey: From Provinces to Regions and Back
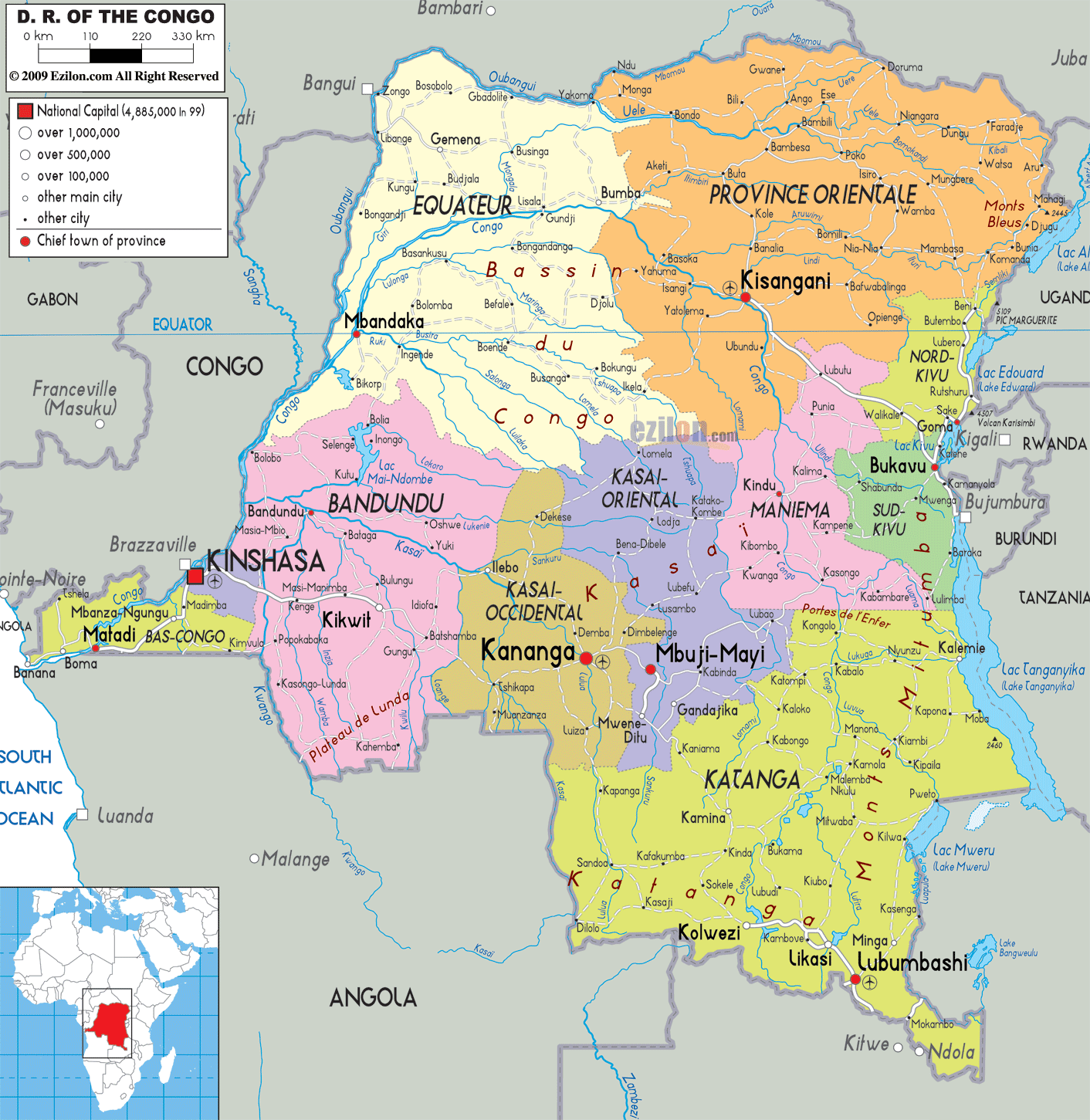
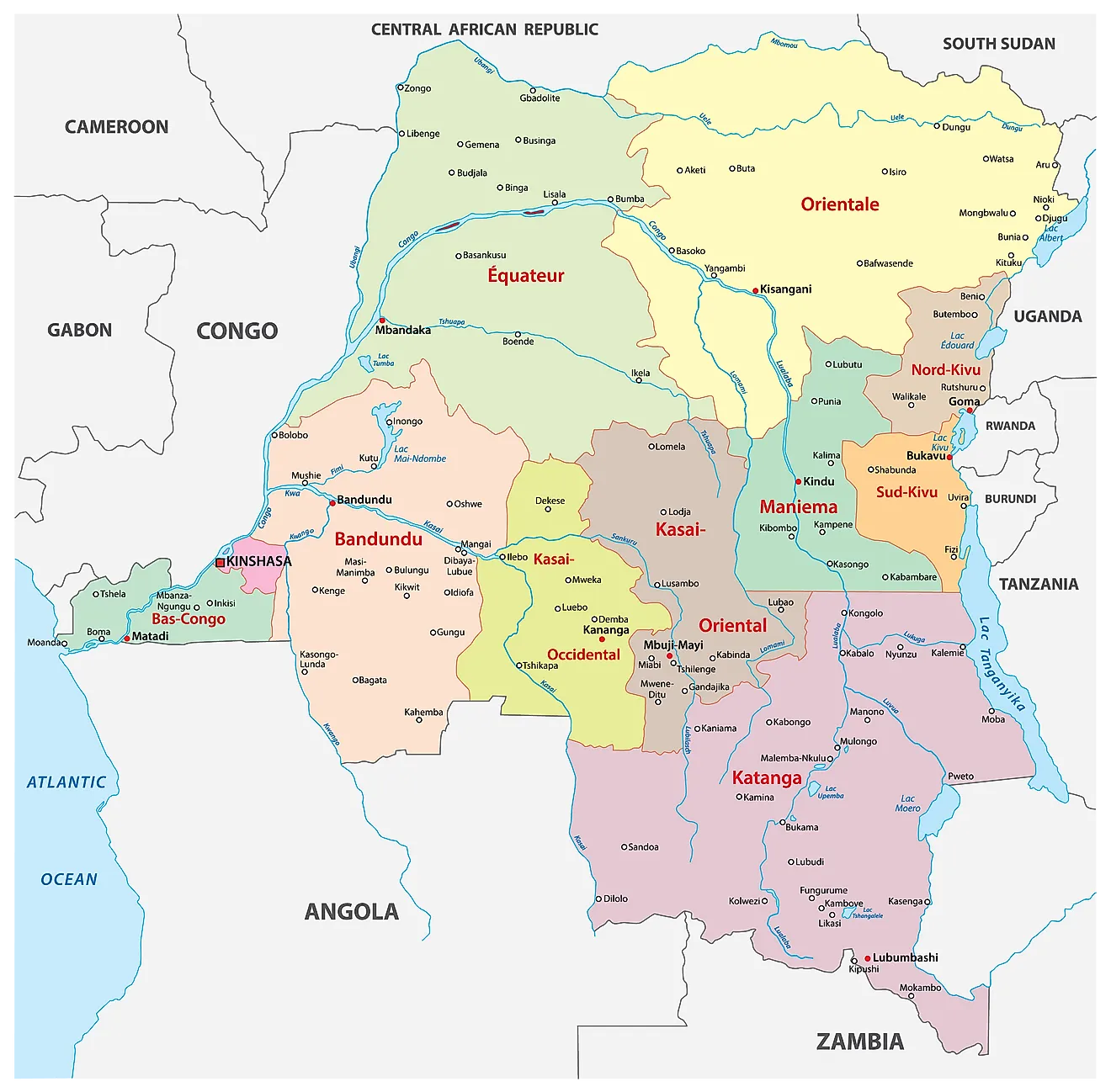
The DRC’s provincial map has undergone significant transformations over the years, reflecting the country’s turbulent political history. Initially, the country was divided into six provinces: Bandundu, Equateur, Kasai Occidental, Kasai Oriental, Katanga, and Kivu. However, in 1966, these provinces were replaced by 21 regions, a system that lasted for over three decades.
In 2006, following the adoption of a new constitution, the DRC transitioned back to a provincial system, this time with 11 provinces. This change aimed to decentralize power and enhance regional autonomy. The new provinces were:
- Bandundu: Located in the west-central region, known for its vast forests and agricultural potential.
- Equateur: Situated in the northwest, encompassing the Congo River basin and its tributaries.
- Kasai Occidental: Located in the southwest, characterized by its fertile plains and diamond mining activities.
- Kasai Oriental: Situated in the southeast, known for its rich agricultural lands and mineral resources.
- Katanga: Located in the southeast, renowned for its copper and cobalt deposits.
- Kivu: Split into North Kivu and South Kivu, both provinces are situated in the eastern region, known for their rugged mountains and volcanic activity.
- Maniema: Located in the east-central region, known for its dense forests and mining potential.
- Bas-Congo: Situated in the west, bordering the Atlantic Ocean, known for its coastal plains and agriculture.
- Oriental: Located in the northeast, encompassing the vast Ituri Forest and its diverse wildlife.
- Kinshasa: The capital city, serving as a separate province, is a major economic and cultural hub.
- Lualaba: Created in 2015, this province was carved out of Katanga, focusing on mining and industrial development.
The Importance of Provincial Boundaries
The DRC’s provincial map is not merely a geographical division; it plays a vital role in shaping the country’s governance, development, and identity.
1. Administrative Decentralization: The provincial system aims to distribute power and resources more equitably across the country, empowering regional governments to address local needs and priorities. This fosters a sense of ownership and participation in decision-making processes.
2. Economic Development: Each province possesses unique resources and economic potential. By focusing on specific industries and sectors within each province, the government can promote tailored development strategies and attract investments.
3. Cultural Identity: The provinces often reflect distinct cultural identities, languages, and traditions. The provincial system acknowledges and celebrates this diversity, contributing to a more inclusive and harmonious society.
4. Security and Stability: The provincial structure provides a framework for managing security challenges within specific regions, allowing for more targeted interventions and resource allocation.
5. Resource Management: The provinces are responsible for managing natural resources within their territories, ensuring sustainable utilization and promoting environmental conservation.
Navigating the DRC’s Provincial Landscape: A Detailed Look
1. Bandundu: This province, encompassing the central region, is characterized by its vast forests, rich agricultural potential, and a diverse population. Key industries include forestry, agriculture, and fishing.
2. Equateur: Located in the northwest, this province is defined by its sprawling Congo River basin and its tributaries. Agriculture, fishing, and forestry are major economic activities, while the province also holds significant oil and gas reserves.
3. Kasai Occidental: Situated in the southwest, this province is known for its fertile plains and diamond mining activities. Agriculture, particularly the production of cassava and palm oil, plays a crucial role in the economy.
4. Kasai Oriental: Located in the southeast, this province is characterized by its rich agricultural lands and mineral resources, including diamonds and gold. Agriculture, mining, and forestry are key industries.
5. Katanga: This province, located in the southeast, is renowned for its copper and cobalt deposits, making it a major mining hub in Africa. Other industries include agriculture, fishing, and forestry.
6. North Kivu: Situated in the eastern region, this province is known for its rugged mountains, volcanic activity, and its diverse population. Coffee and tea are major agricultural products, while the province also holds significant gold and tin deposits.
7. South Kivu: Located in the eastern region, this province shares similar geographical features with North Kivu, including mountainous terrain and volcanic activity. Agriculture, mining, and tourism are key industries.
8. Maniema: This province, located in the east-central region, is characterized by its dense forests and mining potential. Agriculture, forestry, and mining are major economic activities.
9. Bas-Congo: Situated in the west, this province is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and is known for its coastal plains and agriculture. Key industries include agriculture, fishing, and tourism.
10. Oriental: This province, located in the northeast, encompasses the vast Ituri Forest and its diverse wildlife. Agriculture, forestry, and mining are major economic activities.
11. Kinshasa: The capital city, serving as a separate province, is a major economic and cultural hub. Kinshasa is home to various industries, including banking, finance, trade, and services.
12. Lualaba: Carved out of Katanga in 2015, this province focuses on mining and industrial development, leveraging its rich copper and cobalt resources.
FAQs: Navigating the DRC’s Provincial Landscape
1. What is the current administrative structure of the DRC?
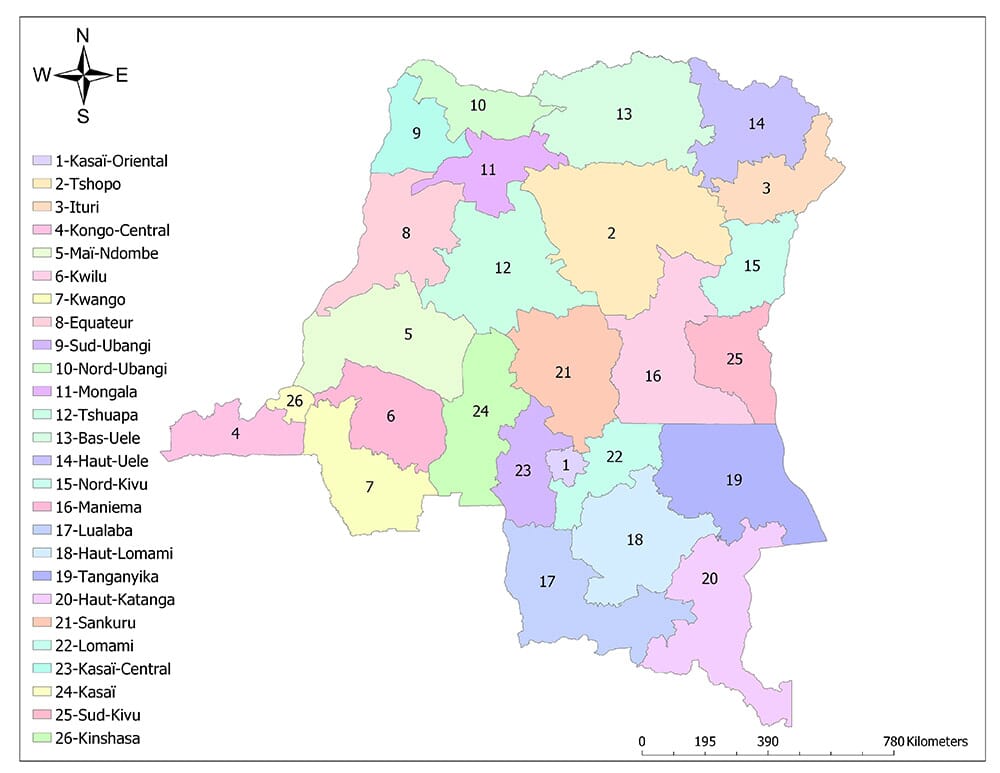
The DRC is currently divided into 26 provinces, each with its own elected government and administrative structure.
2. How many provinces were there before the 2006 reforms?
Prior to the 2006 constitutional reforms, the DRC was divided into 11 provinces.
3. What is the purpose of the provincial system in the DRC?
The provincial system aims to decentralize power and resources, promote regional development, and foster a sense of ownership and participation in decision-making processes.
4. What are the key economic activities in each province?
Each province possesses unique resources and economic potential. Key economic activities vary depending on the province’s geography, resources, and infrastructure. For example, Katanga is known for its mining industry, while Equateur focuses on agriculture and fishing.
5. What are the major challenges facing the provinces in the DRC?
The provinces in the DRC face various challenges, including poverty, lack of infrastructure, armed conflict, and environmental degradation.
6. How can the provincial system be strengthened in the DRC?
Strengthening the provincial system in the DRC requires addressing issues related to resource allocation, capacity building, and institutional reforms.
7. What are the implications of the provincial system for the DRC’s future?
The provincial system is crucial for the DRC’s future, as it provides a framework for decentralized governance, regional development, and social cohesion.
Tips for Understanding the DRC’s Provincial Map
1. Utilize online resources: Several websites and online platforms provide detailed maps and information about the DRC’s provinces, including their boundaries, population, and economic activities.
2. Explore geographical features: Understanding the geographical characteristics of each province, such as its climate, terrain, and natural resources, is essential for comprehending its economic potential and development challenges.
3. Analyze socio-economic data: Examining data on population, income, education, and health indicators can provide insights into the socio-economic situation in each province.
4. Stay updated on current events: Monitoring news and reports about political developments, economic activities, and social issues in each province can provide a comprehensive understanding of the current situation.
5. Engage in discussions: Participating in discussions and forums about the DRC’s provinces can foster a deeper understanding of the complexities and challenges faced by each region.
Conclusion: A Complex and Dynamic Landscape
The Democratic Republic of Congo’s provincial map is a complex and dynamic landscape, reflecting the country’s rich history, diverse geography, and ongoing development challenges. Understanding the provincial divisions and their significance is crucial for comprehending the DRC’s political, economic, and social dynamics. By navigating this intricate administrative framework, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the country’s unique identity and the multifaceted challenges it faces in its journey towards stability and prosperity.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Democratic Republic of Congo’s Provinces: A Geographic and Administrative Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!