Unveiling Africa’s Green Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look At The Continent’s Forests
Unveiling Africa’s Green Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Continent’s Forests
Related Articles: Unveiling Africa’s Green Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Continent’s Forests
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Africa’s Green Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Continent’s Forests. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling Africa’s Green Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Continent’s Forests
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling Africa’s Green Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Continent’s Forests
- 3.1 Mapping Africa’s Forest Cover: A Visual Representation of Life
- 3.2 The Significance of Africa’s Forests: A Multifaceted Ecosystem
- 3.3 Challenges Facing Africa’s Forests: A Call for Action
- 3.4 Navigating the Future of Africa’s Forests: A Path Towards Sustainability
- 3.5 FAQs about Africa’s Forests and Maps:
- 3.6 Tips for Using Africa Forest Maps:
- 3.7 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Unveiling Africa’s Green Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Continent’s Forests

Africa, a continent renowned for its diverse landscapes and rich biodiversity, harbors a vast expanse of forests that play a crucial role in the global ecosystem. These forested areas, ranging from dense rainforests to sprawling savannas, are not just scenic wonders but vital for the livelihoods of millions, the preservation of countless species, and the regulation of Earth’s climate. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of these forests is essential for their effective management and conservation.
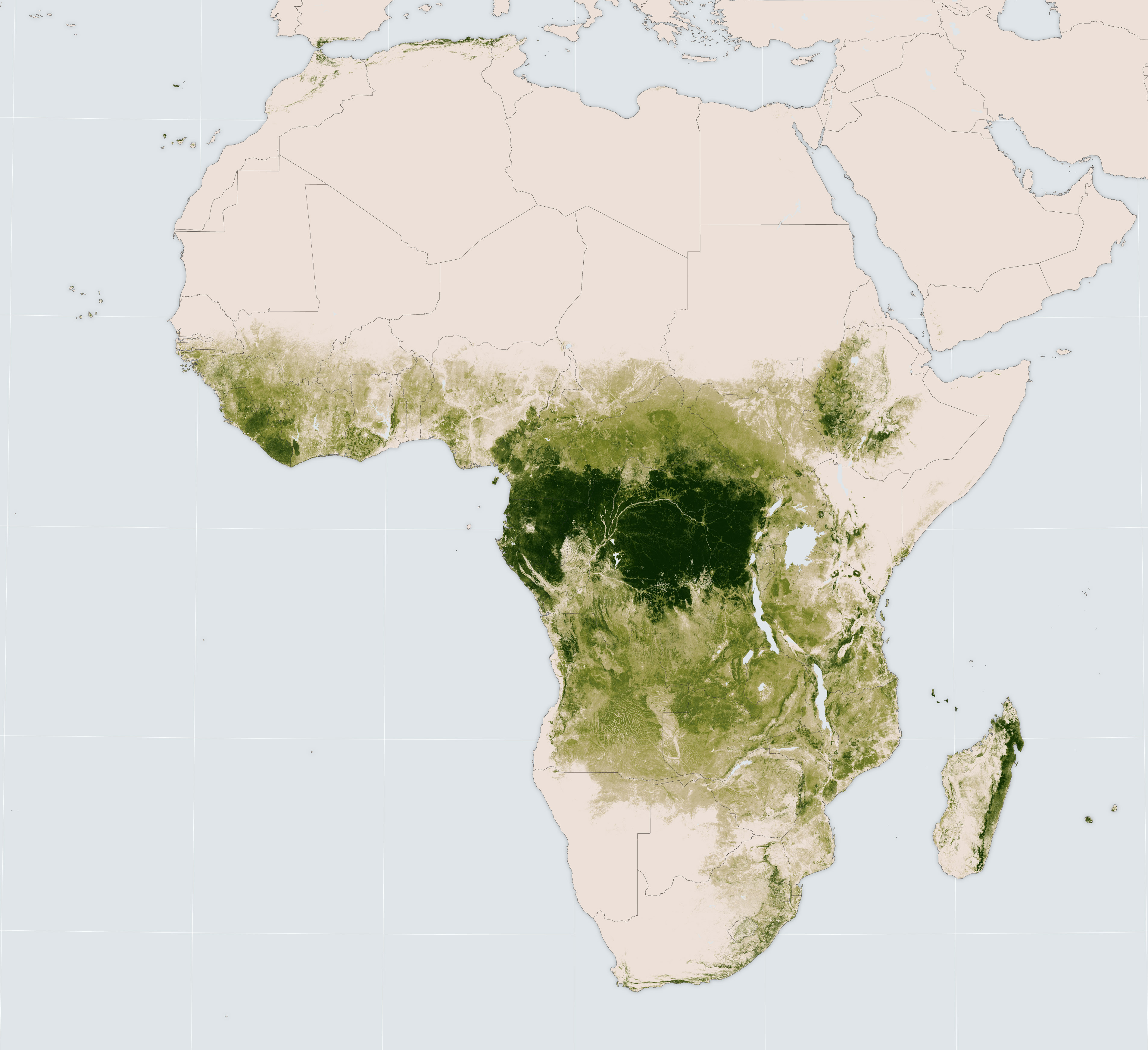
Mapping Africa’s Forest Cover: A Visual Representation of Life
An Africa forest map serves as a powerful tool for visualizing the continent’s forested areas, providing valuable insights into their extent, distribution, and types. These maps, often created using satellite imagery and geographic information systems (GIS), offer a comprehensive overview of the intricate tapestry of vegetation that covers Africa.
Key Features of an Africa Forest Map:
- Forest Cover: Maps clearly delineate areas covered by different types of forests, such as tropical rainforests, dry forests, and montane forests.
- Forest Types: The map distinguishes between various forest types, highlighting the unique characteristics of each, from the dense canopy of rainforests to the open woodlands of savannas.
- Forest Degradation: Areas experiencing deforestation, degradation, and fragmentation are often indicated, providing a visual representation of the threats faced by these ecosystems.
- Conservation Areas: Protected areas, national parks, and other conservation zones are typically highlighted, showcasing efforts to safeguard these vital ecosystems.
- Land Use: Maps often incorporate information about land use patterns, illustrating the interplay between forests and human activities, such as agriculture, mining, and urbanization.
The Significance of Africa’s Forests: A Multifaceted Ecosystem
Africa’s forests are not just a collection of trees but a complex and interconnected ecosystem with profound implications for the continent and the world.
Ecological Importance:
- Biodiversity Hotspot: African forests are home to a staggering diversity of plant and animal species, including many endemic species found nowhere else on Earth.
- Carbon Sink: Forests act as vital carbon sinks, absorbing vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating the effects of climate change.
- Water Cycle Regulation: Forests play a crucial role in regulating the water cycle, influencing rainfall patterns, and ensuring water availability for surrounding communities.
- Soil Health: Forests protect soil from erosion, enhance soil fertility, and provide habitats for beneficial organisms that contribute to soil health.
Socioeconomic Importance:
- Livelihoods: Forests provide essential resources for millions of people across Africa, supporting livelihoods through timber harvesting, agriculture, and hunting.
- Medicinal Resources: Traditional medicine relies heavily on plants found in African forests, providing valuable remedies for various ailments.
- Cultural Significance: Forests hold deep cultural significance for many African communities, serving as sacred sites, places of spiritual connection, and sources of traditional knowledge.
- Tourism: Africa’s forests attract tourists from around the world, generating revenue and supporting local economies.
Challenges Facing Africa’s Forests: A Call for Action
Despite their immense value, Africa’s forests face a multitude of challenges that threaten their integrity and sustainability.
- Deforestation: Driven by factors such as agricultural expansion, logging, and urbanization, deforestation continues to be a major threat, reducing forest cover and fragmenting habitats.
- Climate Change: Climate change, with its associated impacts of drought, extreme weather events, and rising temperatures, is putting significant stress on African forests, leading to increased vulnerability to pests and diseases.
- Land Degradation: Unsustainable land use practices, such as overgrazing and poor agricultural practices, contribute to land degradation, reducing the capacity of forests to regenerate.
- Illegal Logging: Illegal logging, often fueled by corruption and weak governance, depletes forest resources and undermines efforts to conserve these valuable ecosystems.
Navigating the Future of Africa’s Forests: A Path Towards Sustainability
Addressing the challenges facing Africa’s forests requires a multi-pronged approach that involves governments, communities, and international organizations.
Key Strategies for Forest Conservation:
- Sustainable Forest Management: Implementing sustainable forest management practices, such as selective logging, reforestation, and community-based forest management, can help ensure the long-term health and productivity of forests.
- Protected Area Expansion: Expanding the network of protected areas and strengthening existing ones can safeguard critical habitats and biodiversity hotspots.
- Combating Illegal Logging: Enforcing stricter regulations, combating corruption, and promoting transparency in the timber trade are essential steps to curb illegal logging.
- Community Engagement: Engaging local communities in forest management and conservation efforts is crucial for ensuring their long-term success, as communities often hold valuable knowledge and have a vested interest in protecting their forests.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and implementing adaptation measures to address climate change impacts are crucial for protecting forests from the effects of climate change.
FAQs about Africa’s Forests and Maps:
Q1: What are the main types of forests found in Africa?
A: Africa is home to a diverse array of forest types, including:
- Tropical Rainforests: Found in Central and West Africa, these forests are characterized by high rainfall, dense vegetation, and a rich diversity of species.
- Dry Forests: These forests occur in regions with lower rainfall, typically found in eastern and southern Africa, and are characterized by deciduous trees that shed their leaves during the dry season.
- Montane Forests: Found in mountainous areas, these forests experience cooler temperatures and higher rainfall, supporting unique species adapted to these conditions.
- Mangrove Forests: These unique forests grow in coastal areas with brackish water and are essential for coastal protection and biodiversity.
- Savannas: While not strictly forests, savannas are open grasslands with scattered trees, covering vast areas of Africa and providing habitat for diverse wildlife.
Q2: How are Africa forest maps used in conservation efforts?
A: Africa forest maps play a vital role in conservation efforts by:
- Identifying Priority Areas: Maps help identify areas with high forest cover, biodiversity, or ecological significance, guiding conservation efforts towards areas of greatest need.
- Monitoring Deforestation: Maps allow for the monitoring of deforestation rates and patterns, providing data for assessing the effectiveness of conservation interventions.
- Planning and Management: Maps assist in planning and managing protected areas, ensuring the sustainable use of forest resources.
- Raising Awareness: Maps can be used to raise awareness about the importance of forests and the threats they face, mobilizing public support for conservation efforts.
Q3: What are the challenges of mapping Africa’s forests?
A: Mapping Africa’s forests presents a number of challenges, including:
- Data Accessibility: Obtaining accurate and up-to-date data on forest cover and distribution can be challenging, especially in remote areas.
- Technological Constraints: Mapping vast areas with high resolution and accuracy requires advanced technology and resources.
- Political and Economic Factors: Access to data can be restricted due to political or economic factors, hindering the ability to create comprehensive forest maps.
Q4: What are some of the key organizations involved in mapping Africa’s forests?
A: Numerous organizations are involved in mapping Africa’s forests, including:
- World Resources Institute (WRI): WRI is a global research organization that produces data and maps on forest cover and deforestation.
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): FAO collects and analyzes data on forest resources worldwide, including Africa.
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP): UNEP focuses on environmental issues, including forest conservation, and uses mapping to assess forest health and threats.
- National Governments: Many African countries have their own agencies and institutions responsible for mapping and managing forest resources.
Tips for Using Africa Forest Maps:
- Understanding Scale: Be aware of the scale of the map and its limitations in representing detailed information.
- Data Source: Check the data source and methodology used to create the map to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Interpreting Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used on the map to understand the different forest types and land use patterns.
- Comparing Maps: Compare different maps from different sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the forest landscape.
- Integrating Data: Combine forest maps with other relevant data, such as population density, climate data, and socioeconomic information, for a more holistic view.
Conclusion:
Africa’s forests are a vital asset, providing numerous ecological, socioeconomic, and cultural benefits. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of these forests through maps is essential for their effective management and conservation. By recognizing the challenges facing these ecosystems and implementing sustainable practices, we can ensure that Africa’s green tapestry continues to thrive for generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Africa’s Green Tapestry: A Comprehensive Look at the Continent’s Forests. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!