Unveiling The City: A Comprehensive Guide To GIS City Maps
Unveiling the City: A Comprehensive Guide to GIS City Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the City: A Comprehensive Guide to GIS City Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the City: A Comprehensive Guide to GIS City Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the City: A Comprehensive Guide to GIS City Maps

In an era of data-driven decision making, the ability to visualize and analyze information about our urban environments is paramount. GIS city maps, a powerful tool utilizing Geographic Information Systems (GIS), offer a comprehensive and interactive platform for understanding and managing the complexities of modern cities.
Understanding GIS City Maps: A Visual Language for Urban Data
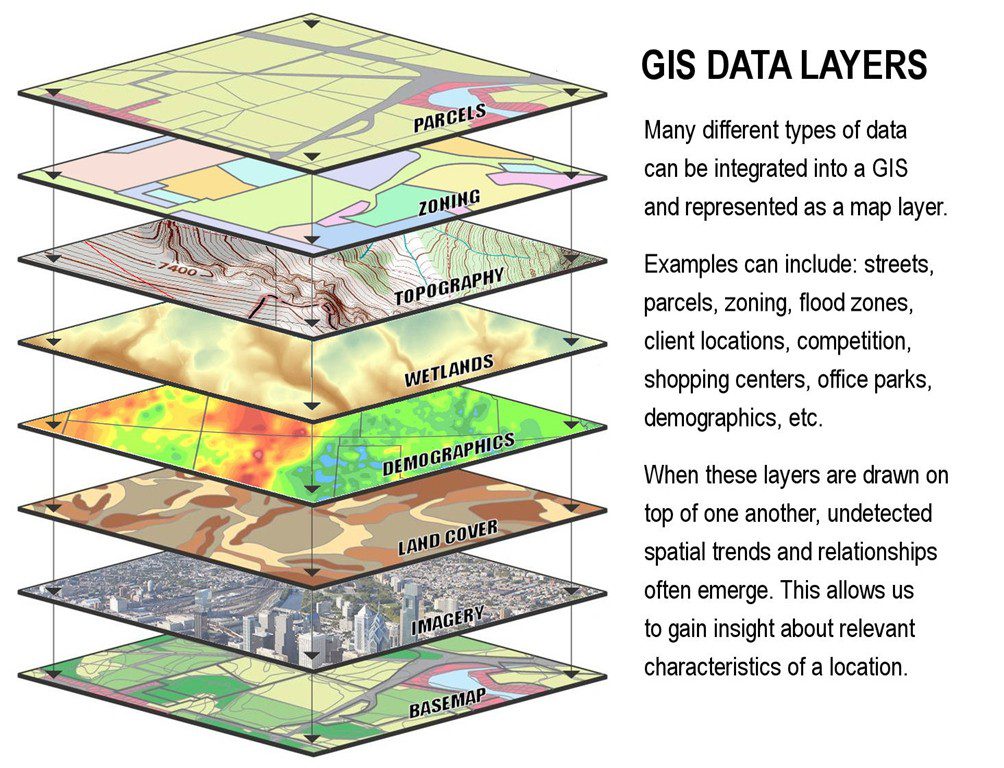
GIS city maps, at their core, are digital representations of urban landscapes, integrating various layers of data to provide a multi-dimensional view. These maps go beyond simple visual representations; they are dynamic tools that allow users to explore, analyze, and interact with information about a city in a meaningful way.
Key Components of a GIS City Map:
- Base Map: This forms the foundation of the map, depicting the physical layout of the city, including streets, buildings, and natural features.
- Data Layers: These layers overlay the base map, providing information on various aspects of the city, such as population density, crime rates, infrastructure, transportation networks, and environmental conditions.
- Interactive Features: GIS city maps are often equipped with interactive features that allow users to zoom, pan, and filter data, creating customized views to address specific questions or needs.
- Analytical Tools: GIS software provides a range of analytical tools that enable users to perform spatial analysis, such as calculating distances, identifying patterns, and modeling scenarios.
Benefits of GIS City Maps: A Comprehensive View of the Urban Fabric
GIS city maps offer a multitude of benefits across various sectors, empowering informed decision-making and efficient resource allocation.
1. Urban Planning and Development:
- Infrastructure Planning: GIS maps aid in visualizing the impact of new infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and public transportation lines, on existing infrastructure and traffic flow.
- Land Use Planning: By analyzing land use patterns and zoning regulations, GIS maps help planners optimize land allocation for residential, commercial, and industrial development.
- Urban Renewal Projects: GIS maps facilitate the identification of areas in need of revitalization, allowing for targeted investments in infrastructure, housing, and public spaces.
2. Public Safety and Emergency Response:
- Crime Mapping: GIS maps are used to analyze crime patterns, identify hotspots, and deploy resources effectively to combat crime and improve public safety.
- Emergency Response Planning: GIS maps help first responders visualize the location of critical infrastructure, evacuation routes, and potential hazards, enabling efficient response during emergencies.
- Disaster Risk Assessment: GIS maps can be used to model the potential impact of natural disasters, such as floods, earthquakes, and wildfires, enabling the development of mitigation strategies and preparedness plans.
3. Transportation and Logistics:
- Route Optimization: GIS maps assist in optimizing delivery routes, reducing travel time, and improving efficiency for transportation companies.
- Traffic Management: GIS maps can be used to analyze traffic flow patterns, identify congestion points, and implement traffic management strategies to improve road safety and reduce travel time.
- Public Transit Planning: GIS maps help planners develop efficient public transit systems, optimize bus routes, and ensure accessibility for all citizens.
4. Environmental Management:
- Pollution Monitoring: GIS maps allow for the visualization and analysis of air, water, and soil pollution levels, enabling targeted interventions to improve environmental quality.
- Resource Management: GIS maps can be used to track and manage natural resources, such as forests, water bodies, and agricultural land, promoting sustainable use and conservation efforts.
- Climate Change Adaptation: GIS maps help assess the impact of climate change on urban environments, enabling the development of adaptation strategies to mitigate the risks associated with rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and other climate-related challenges.
5. Public Health and Social Services:
- Disease Surveillance: GIS maps aid in tracking the spread of diseases, identifying outbreaks, and targeting public health interventions.
- Social Services Planning: GIS maps can be used to analyze the distribution of social services, such as healthcare facilities, schools, and community centers, ensuring equitable access for all citizens.
- Population Demographics: GIS maps provide valuable insights into population distribution, age, income, and other demographic factors, supporting the development of targeted social programs and policies.
FAQs about GIS City Maps:
1. What are the key data sources used in creating GIS city maps?
Data sources for GIS city maps are diverse and include:
- Government Agencies: Municipal governments, transportation authorities, and environmental agencies provide data on infrastructure, demographics, land use, and environmental conditions.
- Private Companies: Utility companies, telecommunications providers, and real estate firms contribute data on infrastructure, property boundaries, and economic activity.
- Citizen Data: Citizen-generated data, such as social media posts, GPS locations, and online reviews, can provide valuable insights into community needs and preferences.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial photography provide valuable data for mapping urban landscapes, infrastructure, and environmental changes.
2. How are GIS city maps used in urban planning?
GIS city maps are essential tools for urban planning, enabling planners to:
- Analyze existing conditions: GIS maps allow planners to visualize and analyze data on population density, land use, transportation infrastructure, and environmental factors.
- Model potential scenarios: GIS maps facilitate the modeling of different development scenarios, such as the impact of new infrastructure projects or changes in zoning regulations.
- Communicate plans to stakeholders: GIS maps provide a clear and intuitive way to communicate planning proposals to the public, facilitating engagement and feedback.
3. What are the limitations of GIS city maps?
Despite their numerous benefits, GIS city maps have limitations:
- Data Availability: The accuracy and completeness of data used in GIS maps can vary depending on the source and availability.
- Data Quality: Data quality can be a concern, as data errors or inconsistencies can lead to inaccurate conclusions.
- Complexity: GIS software can be complex to use, requiring specialized training and technical expertise.
- Privacy Concerns: The use of personal data in GIS maps raises privacy concerns, requiring careful consideration of data security and ethical implications.
Tips for Utilizing GIS City Maps:
- Define your objectives: Clearly identify your goals for using GIS city maps to ensure you are using the appropriate data and analysis tools.
- Select relevant data layers: Choose data layers that are relevant to your objectives and ensure the data is accurate and up-to-date.
- Perform spatial analysis: Utilize the analytical tools available in GIS software to explore relationships, identify patterns, and make informed decisions.
- Collaborate with experts: Engage with GIS experts to ensure you are using the software effectively and interpreting results correctly.
- Communicate results effectively: Use maps and visualizations to communicate your findings to stakeholders in a clear and understandable manner.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Shaping Our Cities
GIS city maps have become an indispensable tool for understanding, managing, and shaping our urban environments. By integrating data from various sources and providing interactive visualizations, these maps empower decision-makers in government, industry, and the public sector to address complex urban challenges, optimize resource allocation, and create more sustainable and resilient cities. As technology continues to advance, GIS city maps are poised to play an even greater role in shaping the future of our urban landscapes.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the City: A Comprehensive Guide to GIS City Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!