Unveiling The Landscape Of West Virginia: A Comprehensive Analysis Of Population Density
Unveiling the Landscape of West Virginia: A Comprehensive Analysis of Population Density
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of West Virginia: A Comprehensive Analysis of Population Density
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape of West Virginia: A Comprehensive Analysis of Population Density. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape of West Virginia: A Comprehensive Analysis of Population Density

West Virginia, a state renowned for its rugged Appalachian beauty, boasts a unique and intricate population distribution. Understanding this distribution, often visualized through population density maps, offers crucial insights into the state’s social, economic, and environmental landscape.
Understanding Population Density: A Vital Metric
Population density, a fundamental concept in geography and demography, quantifies the number of people residing within a given area. It is calculated by dividing the total population of a region by its land area, usually expressed as people per square kilometer or square mile. Population density maps, therefore, provide a visual representation of population concentration, highlighting areas with high and low population densities.
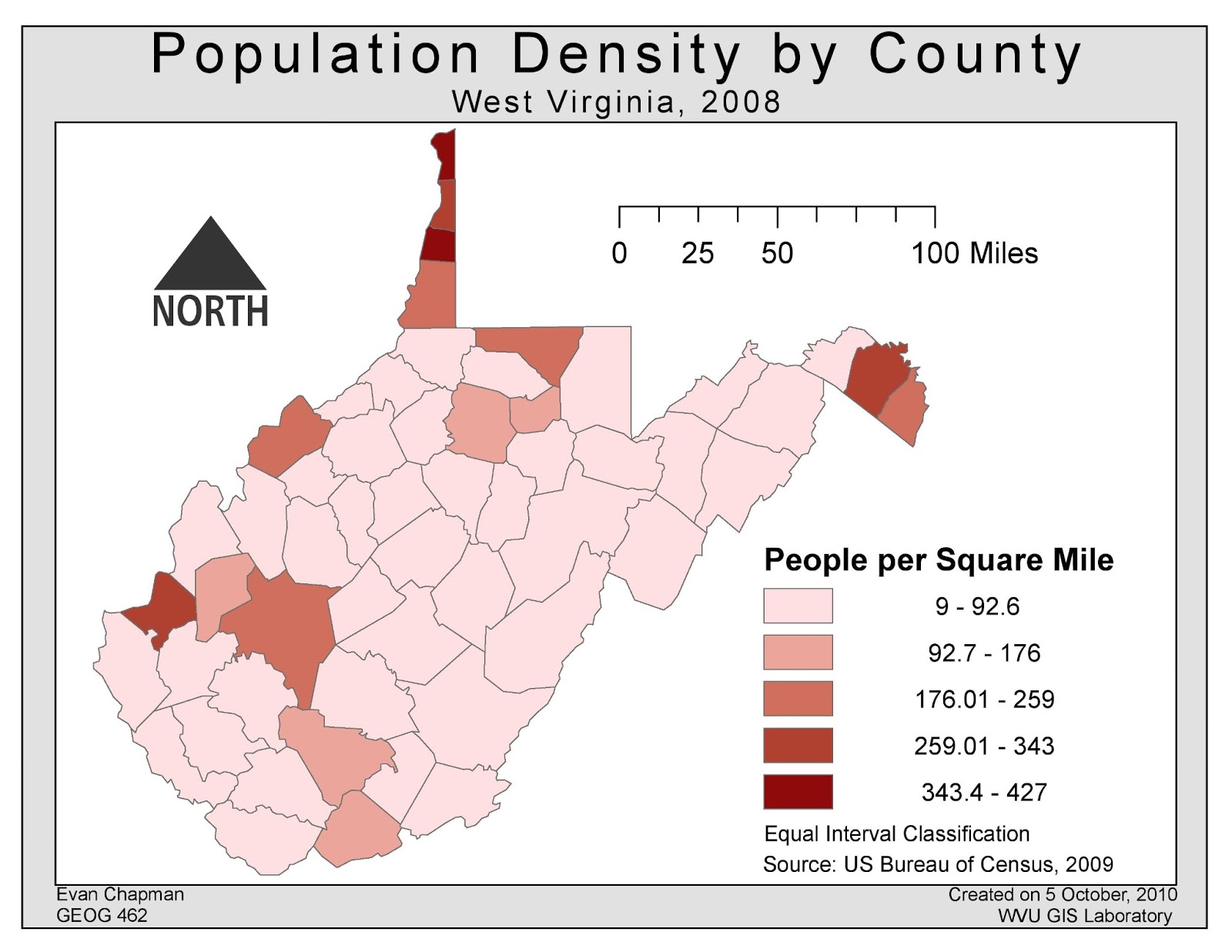
West Virginia’s Population Density: A Tale of Two Landscapes
West Virginia’s population density map reveals a stark contrast between its urban and rural areas. The northern panhandle, encompassing cities like Wheeling and Charleston, exhibits higher population densities, reflecting the presence of industrial centers and urban development. In contrast, the vast majority of the state, particularly the mountainous regions, displays low population densities. This pattern is a direct consequence of historical factors, including the state’s reliance on resource extraction industries, geographical constraints, and migration patterns.
Deciphering the Map: Insights into West Virginia’s Demographics
The West Virginia population density map provides a wealth of information about the state’s demographics and socio-economic landscape.
1. Rural Dominance: The map underscores West Virginia’s predominantly rural character. The majority of the state’s counties are characterized by low population densities, with sprawling landscapes and limited urban development. This rural dominance has significant implications for various aspects of life in West Virginia, including:
* **Economic Development:** Rural areas often face challenges in attracting businesses and industries, leading to limited employment opportunities and economic disparities.
* **Infrastructure Development:** Rural communities may have limited access to essential services such as healthcare, education, and transportation infrastructure.
* **Social Services:** The distribution of social services, including healthcare facilities and educational institutions, can be uneven, potentially creating disparities in access to essential resources.2. Urban Concentrations: While rural areas dominate, the map also highlights pockets of urban concentration, primarily in the northern panhandle and along the Ohio River. These urban centers serve as hubs for economic activity, attracting residents from surrounding rural areas. However, they also face unique challenges, including:
* **Population Growth:** Rapid population growth in urban areas can strain infrastructure and resources, leading to challenges in providing adequate housing, transportation, and public services.
* **Urban Sprawl:** The expansion of urban areas into surrounding rural landscapes can contribute to environmental degradation and loss of natural habitats.
* **Social Disparities:** Urban areas often exhibit higher levels of poverty and crime, highlighting the need for targeted social programs and community development initiatives.3. Migration Patterns: The population density map can also shed light on migration patterns within the state. Over the past few decades, West Virginia has experienced a net population loss, with residents moving to other states in search of better economic opportunities. This outward migration has contributed to the decline in population density in certain areas, while others have remained relatively stable.
4. Environmental Considerations: Population density plays a crucial role in shaping the state’s environmental landscape. Areas with high population densities often experience higher levels of pollution, resource consumption, and environmental degradation. Conversely, sparsely populated areas may face challenges in managing natural resources and protecting sensitive ecosystems.
5. Policy Implications: Understanding the distribution of population in West Virginia is crucial for policymakers seeking to address the state’s economic, social, and environmental challenges. Population density maps provide valuable data for:
* **Economic Development Strategies:** Identifying areas with high growth potential and tailoring economic development programs to address the specific needs of rural and urban communities.
* **Infrastructure Planning:** Allocating resources efficiently to address infrastructure needs in both rural and urban areas, ensuring equitable access to essential services.
* **Social Programs:** Targeting social programs to areas with high poverty rates and limited access to healthcare and education.
* **Environmental Management:** Implementing sustainable land use practices and managing natural resources effectively to mitigate the environmental impacts of population growth and development.Beyond the Map: Factors Shaping Population Density
While the population density map provides a valuable snapshot of West Virginia’s population distribution, it’s essential to consider the underlying factors that contribute to these patterns. Some key factors include:
- Historical Factors: West Virginia’s history, particularly its reliance on resource extraction industries, has shaped its population distribution. The decline of these industries and subsequent outmigration have contributed to the state’s low overall population density.
- Geographical Constraints: The state’s rugged terrain and mountainous landscape have historically limited population growth and development, particularly in remote areas.
- Economic Opportunities: The availability of jobs and economic opportunities plays a significant role in attracting and retaining residents. Areas with limited employment options often experience population decline, while those with thriving industries attract new residents.
- Social Factors: Social factors, such as access to healthcare, education, and cultural amenities, also influence population density. Areas with limited access to these services may experience outmigration, while those with strong social infrastructure attract residents.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
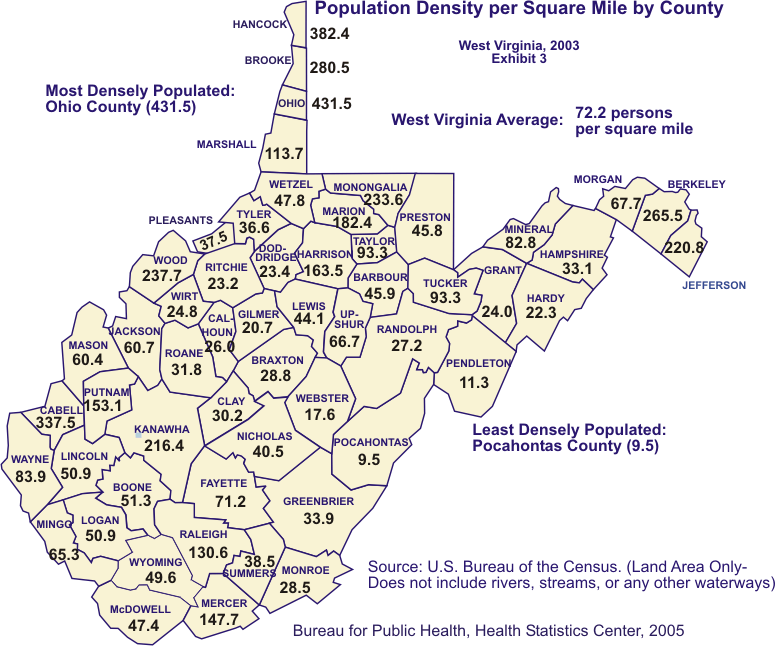
1. What is the average population density of West Virginia?
West Virginia has an average population density of 79 people per square mile, which is significantly lower than the national average of 93 people per square mile.
2. Which counties in West Virginia have the highest population densities?
The counties with the highest population densities in West Virginia include:
- Kanawha County: Home to the state capital, Charleston, Kanawha County has a population density of 340 people per square mile.
- Monongalia County: Located in the northern panhandle, Monongalia County is home to West Virginia University and has a population density of 280 people per square mile.
- Ohio County: The home of Wheeling, Ohio County has a population density of 240 people per square mile.
3. Which counties in West Virginia have the lowest population densities?
The counties with the lowest population densities in West Virginia include:
- Tucker County: Located in the eastern panhandle, Tucker County has a population density of 20 people per square mile.
- Grant County: Situated in the eastern panhandle, Grant County has a population density of 20 people per square mile.
- Pendleton County: Located in the eastern panhandle, Pendleton County has a population density of 15 people per square mile.
4. How has population density changed in West Virginia over time?
West Virginia has experienced a gradual decline in population density over the past few decades, largely due to outmigration and a declining birth rate. However, some areas, particularly those with strong economic growth and attractive amenities, have seen increases in population density.
5. What are the implications of population density for the future of West Virginia?
The state’s future economic growth and social well-being are inextricably linked to its population density. Efforts to address the challenges of rural poverty and limited access to essential services, while simultaneously promoting sustainable urban development, will be crucial for shaping West Virginia’s future.
Tips for Understanding and Using the Map
- Consider the Scale: The scale of the map is crucial for interpreting population density. Maps with larger scales (e.g., 1:10,000) show more detail and are useful for analyzing specific areas, while maps with smaller scales (e.g., 1:1,000,000) provide a broader overview.
- Pay Attention to Legends: The legend of the map provides information about the color scheme and symbols used to represent population density. Understanding the legend is essential for accurate interpretation of the map.
- Compare to Other Maps: Comparing the population density map to other maps, such as elevation maps, land use maps, and economic activity maps, can provide valuable insights into the factors that influence population distribution.
- Consider Context: It is crucial to consider the historical, social, economic, and environmental context when interpreting population density maps.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Landscape
The population density map of West Virginia offers a valuable lens through which to understand the state’s demographic landscape, revealing the interplay of historical factors, geographical constraints, economic opportunities, and social dynamics. As the state navigates the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, understanding the distribution of its population will be crucial for shaping its future. By harnessing the insights gleaned from population density maps, policymakers, planners, and community leaders can foster sustainable growth, address social disparities, and create a brighter future for all West Virginians.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape of West Virginia: A Comprehensive Analysis of Population Density. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!