Unveiling The Secrets Beneath: Understanding Pennsylvania’s Soil Map
Unveiling the Secrets Beneath: Understanding Pennsylvania’s Soil Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets Beneath: Understanding Pennsylvania’s Soil Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets Beneath: Understanding Pennsylvania’s Soil Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets Beneath: Understanding Pennsylvania’s Soil Map

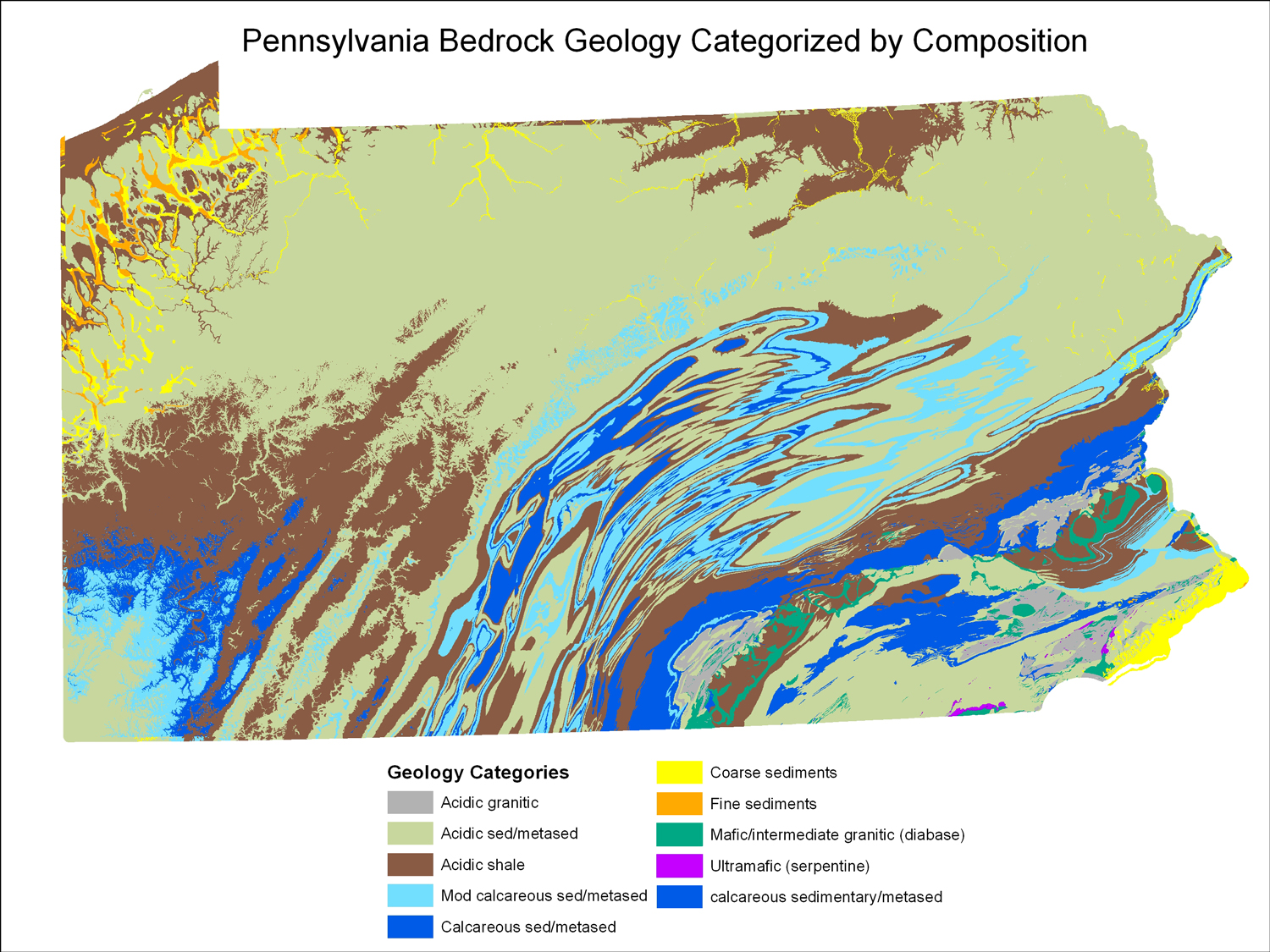
Pennsylvania, with its diverse topography and history, boasts a rich tapestry of soils. The Pennsylvania Soil Survey, a collaborative effort between the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) and the Pennsylvania Department of Agriculture, has meticulously mapped these soils, providing a detailed picture of the state’s subsurface. This comprehensive resource, known as the Pennsylvania Soil Map, serves as an invaluable tool for a wide range of stakeholders, from farmers and land developers to environmental scientists and policymakers.
Delving into the Depths: A Glimpse into Soil Mapping
Soil mapping is a complex process that involves a combination of fieldwork, laboratory analysis, and interpretation. Soil scientists meticulously examine the landscape, taking soil samples at regular intervals. These samples are then analyzed in laboratories to determine their physical and chemical properties, including texture, structure, drainage, and nutrient content. Based on these findings, soils are classified into different categories, each with unique characteristics that influence its suitability for various land uses.
The Pennsylvania Soil Map: A Treasure Trove of Information
The Pennsylvania Soil Map is a visual representation of the state’s soil landscape, providing a detailed overview of the distribution and characteristics of different soil types. This map is a vital resource for a wide range of purposes:
- Agriculture: Farmers rely heavily on the soil map to identify areas suitable for specific crops. Understanding soil texture, drainage, and nutrient content allows farmers to optimize crop selection, fertilization, and irrigation practices, ultimately leading to increased yields and improved soil health.
- Land Development: Developers utilize the soil map to assess the suitability of land for construction projects. This helps them identify areas prone to erosion, flooding, or other soil-related challenges, allowing them to design infrastructure that minimizes environmental impact and ensures long-term stability.
- Environmental Management: Environmental scientists and policymakers use the soil map to monitor and manage natural resources. Understanding soil properties allows them to assess potential risks associated with pollution, erosion, and other environmental concerns. This information is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies and mitigating the impact of human activities on the environment.
- Forestry: The soil map provides valuable insights for forest management practices. Understanding soil drainage and nutrient content helps foresters select appropriate tree species for reforestation and manage existing forests for optimal growth and productivity.
Beyond the Map: Utilizing Soil Information Effectively
The Pennsylvania Soil Map is a powerful tool, but its value lies in its application. Understanding how to interpret and utilize the information it provides is crucial for making informed decisions about land use and management.
Deciphering the Code: Understanding Soil Symbols
The Pennsylvania Soil Map utilizes a standardized system of symbols to represent different soil types. Each symbol represents a unique combination of soil characteristics, including:
- Series: The primary classification unit, indicating the soil’s basic properties and characteristics.
- Horizon: The different layers within the soil profile, each with distinct physical and chemical properties.
- Texture: The relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay, influencing the soil’s water-holding capacity and drainage.
- Drainage: The rate at which water drains from the soil, impacting plant growth and soil stability.
- Slope: The inclination of the land, affecting erosion potential and suitability for different land uses.
Accessing the Information: Tools and Resources
The Pennsylvania Soil Survey provides a wealth of information on soil resources, including:
- Online Soil Survey: The Web Soil Survey (WSS) is an interactive online tool that allows users to explore the Pennsylvania Soil Map, view soil data, and generate custom reports.
- Soil Survey Reports: Detailed reports on specific areas are available online and in print, providing comprehensive information on soil characteristics, land use capabilities, and management recommendations.
- NRCS Field Offices: Local NRCS offices offer personalized assistance and expert guidance on soil-related issues.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Pennsylvania’s Soil
1. What are the most common soil types found in Pennsylvania?
Pennsylvania’s diverse landscape supports a wide range of soil types, with the most common including:
- Ultisols: Found in the Piedmont region, these soils are characterized by low fertility and high acidity.
- Inceptisols: Occurring in the Appalachian Plateau, these soils are moderately fertile and well-drained.
- Alfisols: Common in the Great Valley, these soils are fertile and well-suited for agriculture.
- Mollisols: Found in the northwestern part of the state, these soils are highly fertile and rich in organic matter.
2. How does the soil map help farmers make informed decisions about crop selection?
The soil map provides critical information about soil texture, drainage, and nutrient content, allowing farmers to select crops that are best suited for specific soil conditions. For example, crops requiring well-drained soils would be planted in areas identified as having good drainage, while crops tolerant of high acidity would be selected for soils with low pH.
3. How does the soil map assist land developers in minimizing environmental impact?
The soil map helps developers identify areas prone to erosion, flooding, or other soil-related issues. This allows them to design infrastructure that minimizes environmental impact, for example, by avoiding construction on slopes prone to erosion or incorporating drainage systems to mitigate flooding risks.
4. What are some of the challenges faced by soil scientists in mapping Pennsylvania’s soils?
Mapping Pennsylvania’s soils presents unique challenges due to its complex topography, varied geology, and diverse land uses. These challenges include:
- Accessibility: Reaching remote and mountainous areas can be difficult, requiring specialized equipment and techniques.
- Variability: Soil properties can change significantly over short distances, making it challenging to accurately represent the soil landscape on a map.
- Land Use: Different land uses, such as agriculture, forestry, and urbanization, can significantly impact soil properties, requiring careful consideration during mapping.
Tips for Utilizing the Pennsylvania Soil Map Effectively:
- Consult the Web Soil Survey: This online tool provides a user-friendly interface for exploring soil data and generating custom reports.
- Seek assistance from NRCS field offices: Local NRCS offices offer personalized assistance and expertise on soil-related issues.
- Understand soil symbols: Familiarize yourself with the standardized symbols used to represent different soil types.
- Consider the context: The soil map provides a general overview, but it’s essential to consider the specific location and its surrounding environment when interpreting soil data.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Sustainable Land Management
The Pennsylvania Soil Map is a vital resource for understanding and managing the state’s soil resources. By providing detailed information on soil properties, distribution, and suitability for various land uses, it empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions that promote sustainable land management, protect the environment, and support economic growth. From optimizing agricultural practices to mitigating environmental risks, the soil map serves as a foundation for a brighter future for Pennsylvania’s land and its people.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets Beneath: Understanding Pennsylvania’s Soil Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!