Unveiling The World: A Comprehensive Look At Satellite Imagery And Its Impact
Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Look at Satellite Imagery and its Impact
Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Look at Satellite Imagery and its Impact
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Look at Satellite Imagery and its Impact. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Look at Satellite Imagery and its Impact
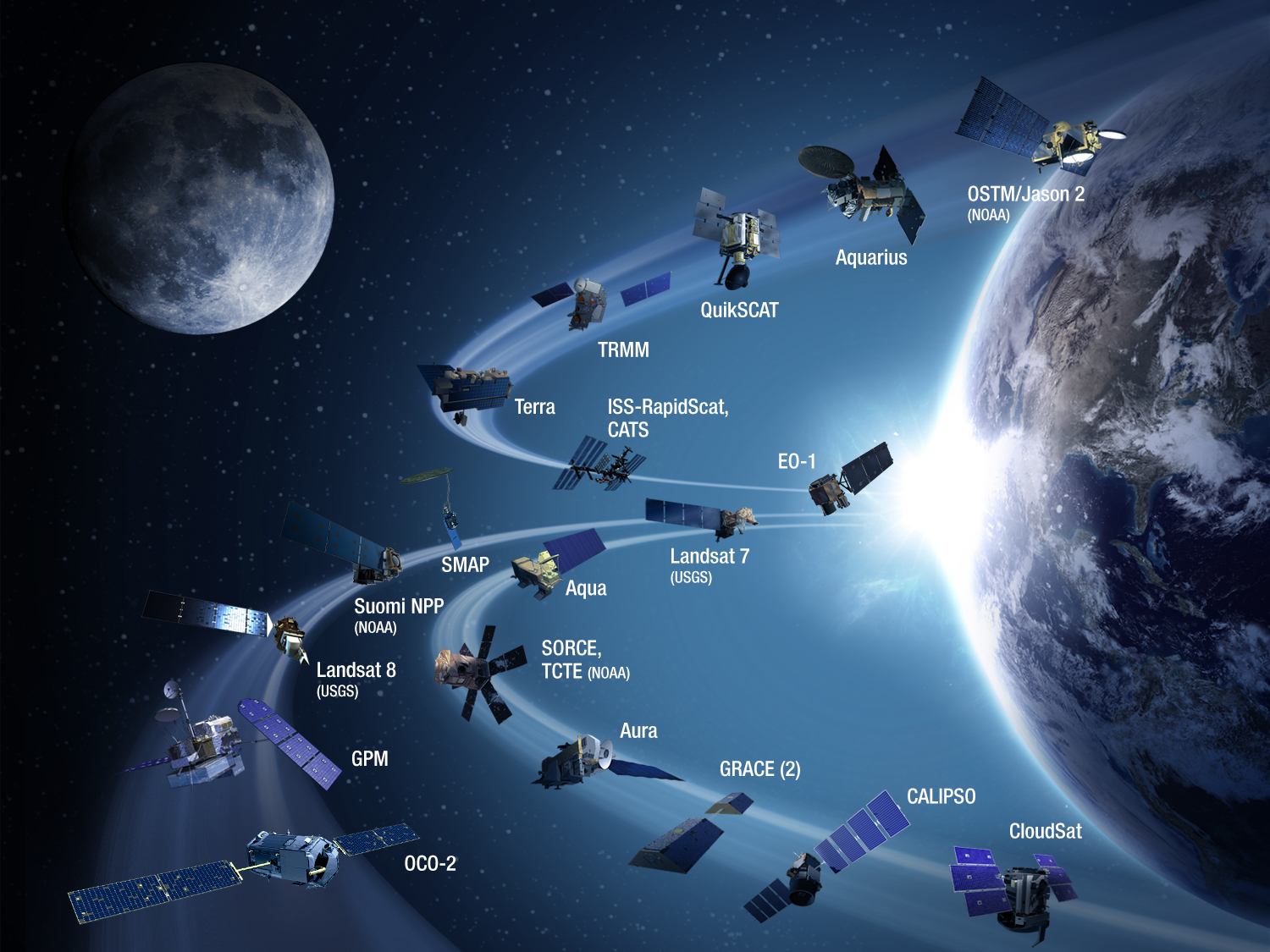

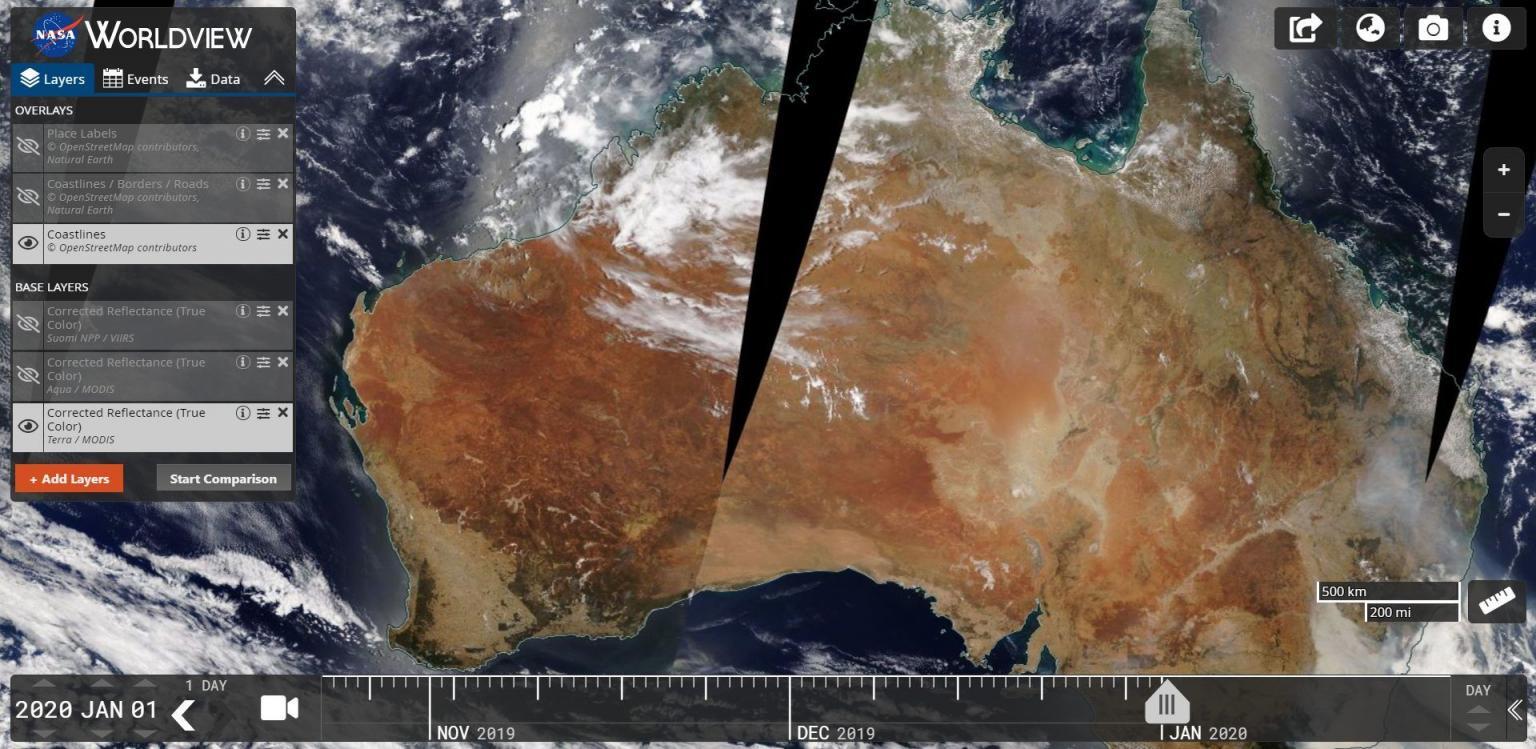
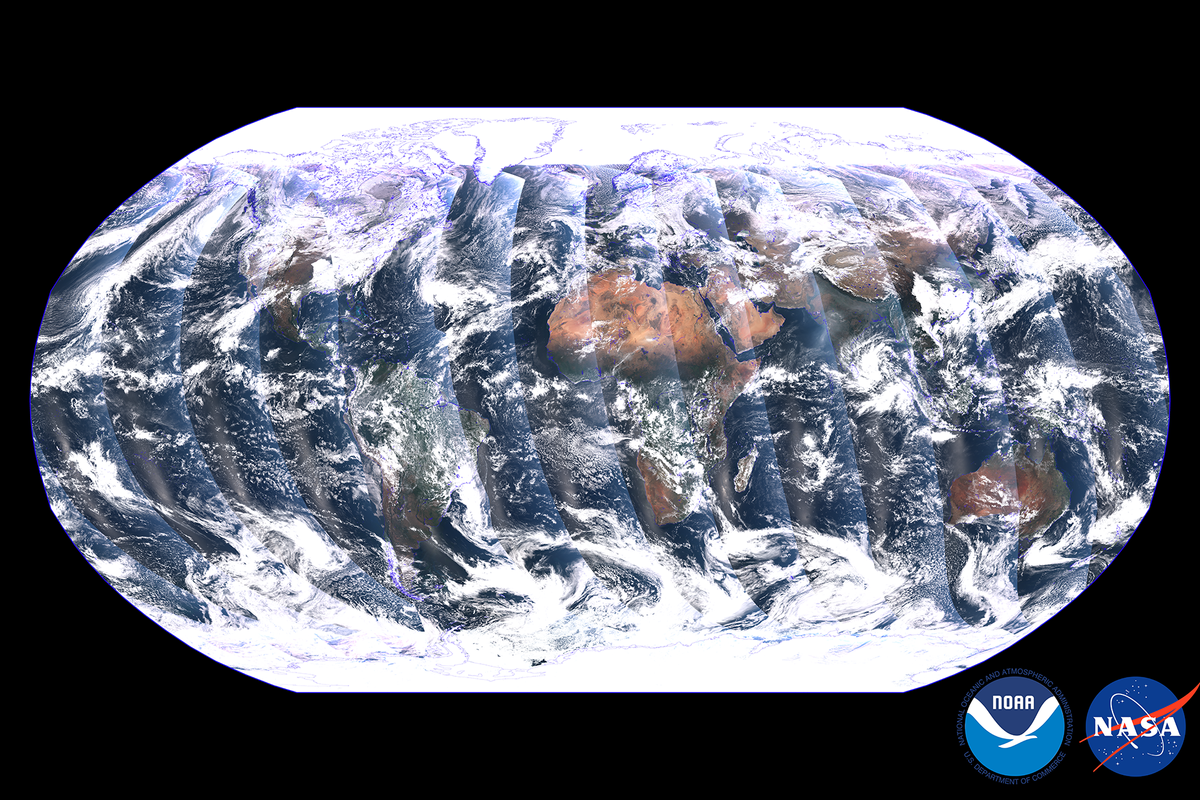
Satellite imagery, a powerful tool for observing and understanding our planet, has revolutionized various fields, from environmental monitoring to disaster response, and even everyday navigation. This technology allows us to capture detailed visual representations of the Earth’s surface from space, providing invaluable insights into our world’s complexities.
The Evolution of Satellite Imagery
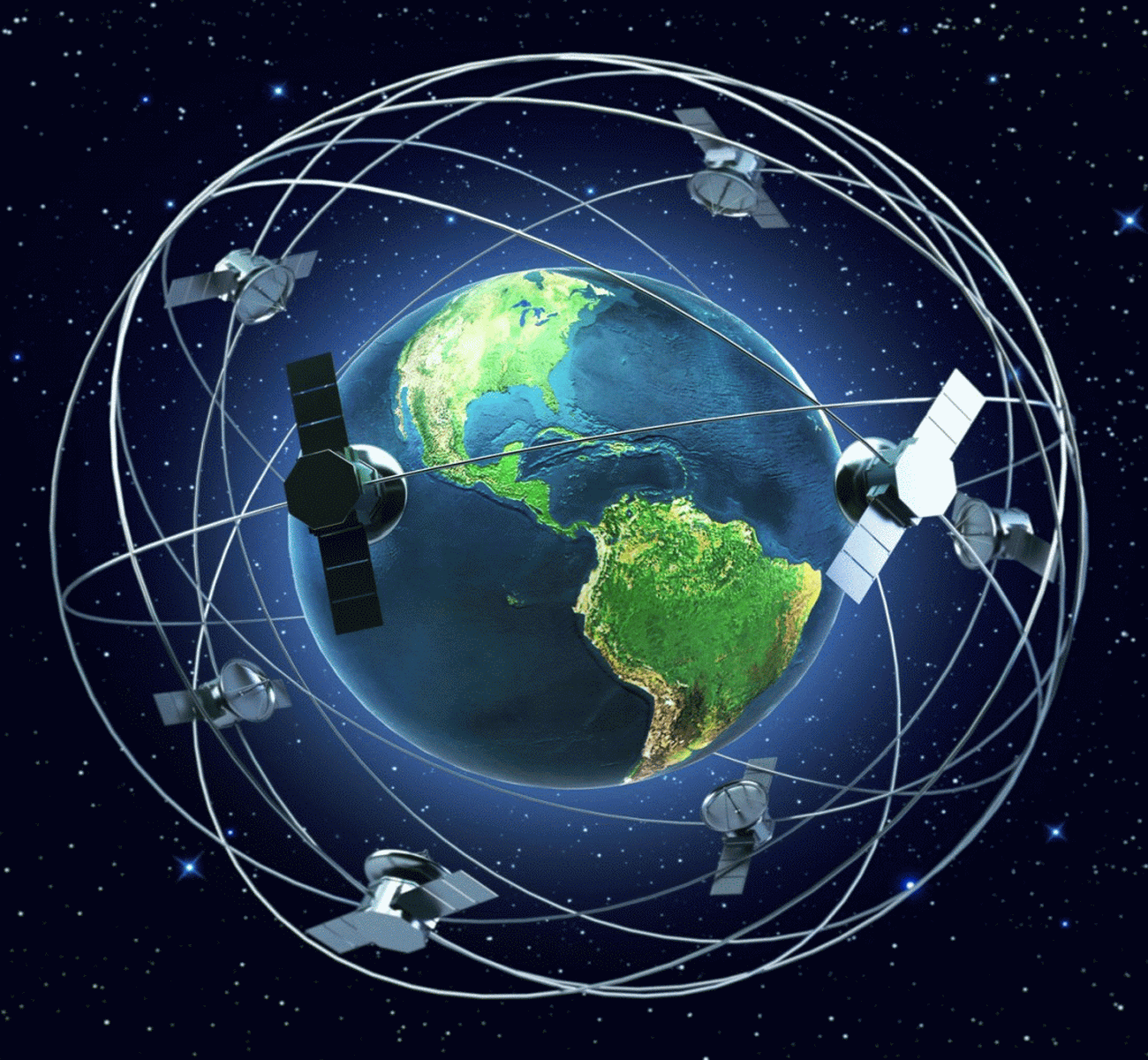
The journey of satellite imagery began in the 1960s with the launch of the first weather satellites. These early missions primarily focused on meteorological observations, providing crucial data for weather forecasting. As technology advanced, the capabilities of satellites expanded, leading to the development of specialized imaging systems for diverse applications.
Understanding the Technology Behind Satellite Imagery
Satellite imagery relies on sophisticated sensors that capture electromagnetic radiation reflected or emitted from the Earth’s surface. These sensors operate across various wavelengths, including visible light, infrared, and microwave, enabling them to detect different features and provide distinct information.
Types of Satellite Imagery
The world of satellite imagery encompasses a wide range of types, each with specific characteristics and applications:
-
Optical Imagery: Captured using visible and near-infrared light, optical imagery provides detailed visual representations of the Earth’s surface. It is particularly useful for mapping land use, identifying vegetation changes, and monitoring urban development.
-
Radar Imagery: Utilizing microwave radiation, radar imagery can penetrate clouds and vegetation, making it effective for mapping terrain, detecting floods, and monitoring agricultural activities.
-
Infrared Imagery: Sensitive to heat radiation, infrared imagery allows for the detection of temperature variations, making it crucial for monitoring wildfires, volcanic activity, and urban heat islands.
-
Hyperspectral Imagery: Capturing hundreds of narrow spectral bands, hyperspectral imagery offers detailed spectral information about different materials, enabling the identification of minerals, vegetation health, and environmental pollutants.
Applications of Satellite Imagery
The applications of satellite imagery are vast and continue to expand with technological advancements:
1. Environmental Monitoring: Satellite imagery plays a critical role in monitoring environmental changes, such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change. It enables scientists to track changes in vegetation cover, identify sources of pollution, and assess the impact of climate events.
2. Disaster Response: Satellite imagery is crucial for disaster response efforts, providing rapid assessments of damage caused by natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, and hurricanes. It helps coordinate rescue efforts, allocate resources, and prioritize relief efforts.
3. Agriculture: Satellite imagery provides valuable insights into agricultural practices, allowing farmers to monitor crop health, identify areas of stress, and optimize irrigation and fertilization. It also helps in assessing crop yields and monitoring agricultural land use.
4. Urban Planning: Satellite imagery is used for urban planning, providing insights into population density, infrastructure development, and transportation networks. It helps in identifying areas of growth, planning for future development, and managing urban sprawl.
5. Military and Intelligence: Satellite imagery plays a crucial role in military operations and intelligence gathering. It provides high-resolution images of enemy positions, infrastructure, and troop movements, aiding in planning and executing military strategies.
6. Navigation and Mapping: Satellite imagery is used to create accurate maps and navigation systems. It provides detailed visual representations of the Earth’s surface, enabling efficient navigation and location tracking.
7. Archaeology and Cultural Heritage: Satellite imagery has proven valuable in archaeology, enabling the discovery of ancient settlements, archaeological sites, and cultural heritage sites. It helps in mapping these sites, understanding their significance, and preserving them for future generations.
8. Resource Management: Satellite imagery is used to monitor and manage natural resources, including water resources, forests, and mineral deposits. It provides insights into resource availability, depletion rates, and potential environmental impacts.
9. Climate Change Research: Satellite imagery plays a crucial role in climate change research, providing long-term data on sea level rise, ice sheet melting, and changes in vegetation patterns. It helps scientists understand the impacts of climate change and develop mitigation strategies.
10. Public Safety: Satellite imagery is used for public safety purposes, such as monitoring traffic flow, identifying potential hazards, and assisting in search and rescue operations. It provides a wide-area view, enabling efficient response to emergencies.
Benefits of Satellite Imagery
-
Comprehensive Coverage: Satellite imagery provides a wide-area perspective, enabling the monitoring of vast regions and capturing data that may be inaccessible by ground-based methods.
-
Regular Monitoring: Satellites can capture images frequently, allowing for regular monitoring of changes over time. This is crucial for tracking environmental changes, disaster response, and resource management.
-
Objectivity and Accuracy: Satellite imagery provides objective and accurate data, reducing the risk of human bias or errors.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Satellite imagery can be more cost-effective than traditional methods of data collection, especially for large-scale projects.
-
Accessibility: Satellite imagery is increasingly accessible to researchers, policymakers, and the public, enabling a wider range of applications and informed decision-making.
Challenges and Considerations
-
Data Processing and Analysis: Processing and analyzing large volumes of satellite imagery can be computationally intensive and require specialized software and expertise.
-
Cloud Cover and Weather Conditions: Cloud cover and adverse weather conditions can obstruct satellite imagery, limiting data collection and analysis.
-
Data Resolution and Accuracy: The resolution and accuracy of satellite imagery can vary depending on the sensor type, satellite orbit, and other factors.
-
Privacy and Security: The use of satellite imagery raises concerns about privacy and security, particularly regarding the potential for surveillance and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
-
Ethical Considerations: The use of satellite imagery for military and intelligence purposes raises ethical considerations regarding the potential for misuse and the impact on human rights.
FAQs about Satellite Imagery
1. How does satellite imagery work?
Satellite imagery relies on sophisticated sensors that capture electromagnetic radiation reflected or emitted from the Earth’s surface. These sensors operate across various wavelengths, enabling them to detect different features and provide distinct information.
2. What are the different types of satellite imagery?
Satellite imagery encompasses a wide range of types, including optical, radar, infrared, and hyperspectral imagery, each with specific characteristics and applications.
3. What are the applications of satellite imagery?
Satellite imagery has numerous applications, including environmental monitoring, disaster response, agriculture, urban planning, military and intelligence, navigation and mapping, archaeology and cultural heritage, resource management, climate change research, and public safety.
4. What are the benefits of using satellite imagery?
Satellite imagery offers several benefits, including comprehensive coverage, regular monitoring, objectivity and accuracy, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility.
5. What are the challenges and considerations associated with satellite imagery?
Challenges and considerations include data processing and analysis, cloud cover and weather conditions, data resolution and accuracy, privacy and security, and ethical considerations.
Tips for Using Satellite Imagery Effectively
-
Identify your specific needs and objectives: Clearly define the purpose and goals of your project to select the most appropriate type of satellite imagery and data analysis techniques.
-
Choose the right satellite and sensor: Consider the required spatial resolution, spectral range, and temporal frequency to ensure the imagery meets your needs.
-
Utilize specialized software and tools: Employ software and tools specifically designed for processing, analyzing, and visualizing satellite imagery.
-
Validate and calibrate your data: Ensure the accuracy and reliability of the imagery by validating and calibrating it against ground truth data or other reliable sources.
-
Collaborate with experts: Consult with experts in remote sensing, GIS, and data analysis to leverage their knowledge and expertise.
Conclusion
Satellite imagery has become an indispensable tool for understanding our planet and addressing various global challenges. Its wide-ranging applications, from environmental monitoring to disaster response, highlight its importance in shaping our world. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of satellite imagery will continue to evolve, providing even more comprehensive and insightful data to inform decision-making and drive progress towards a sustainable future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Look at Satellite Imagery and its Impact. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!