Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Viewers
Related Articles: Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Viewers
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Viewers. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Viewers
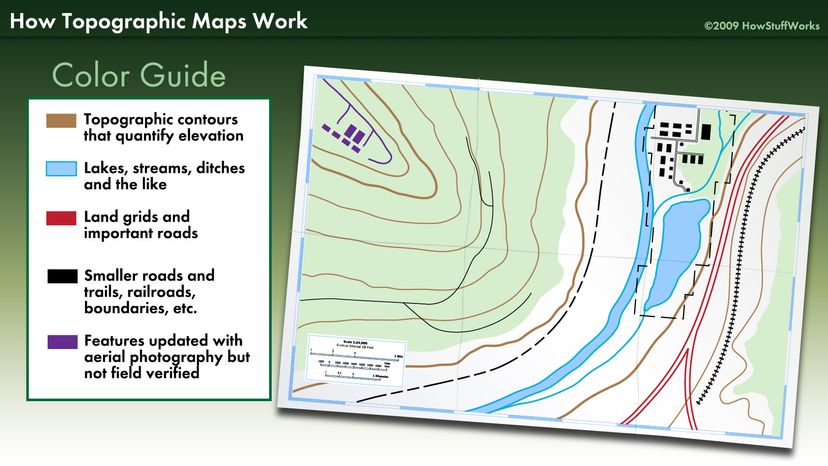
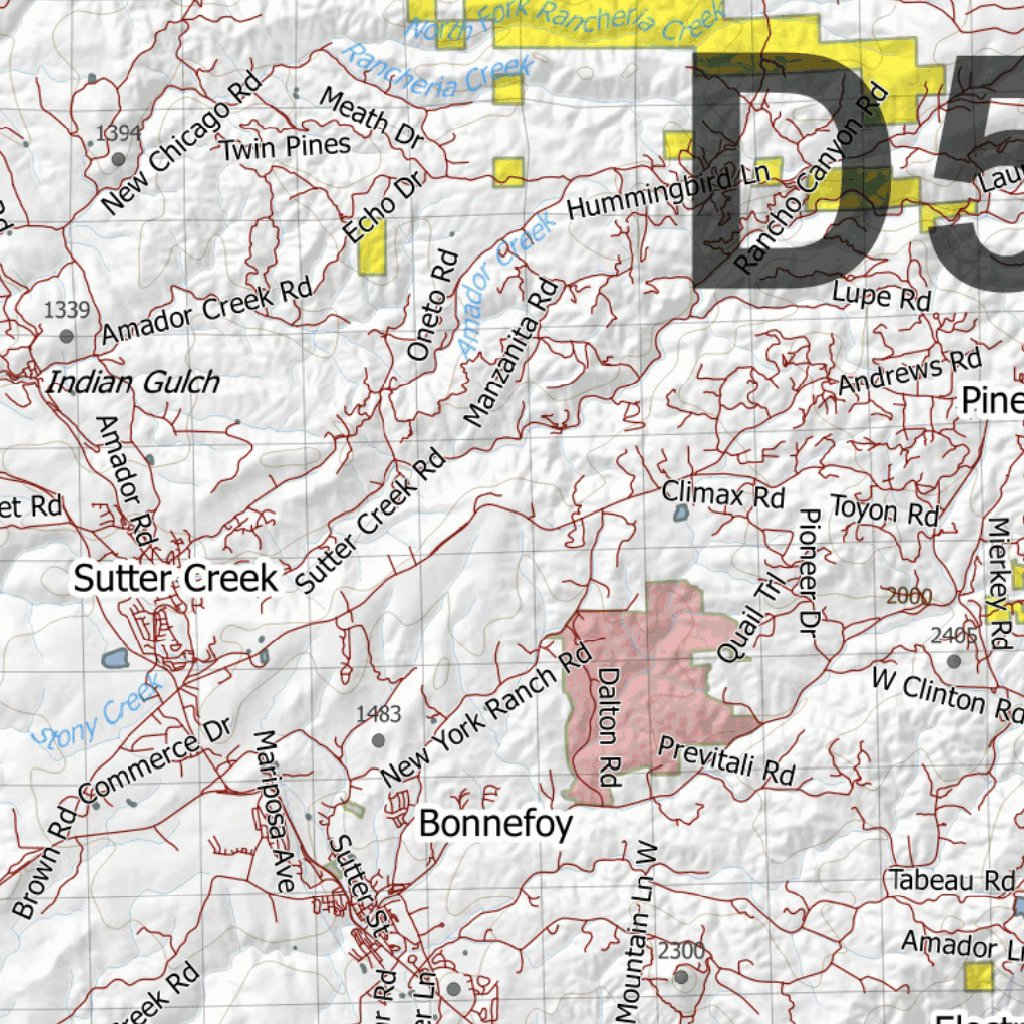
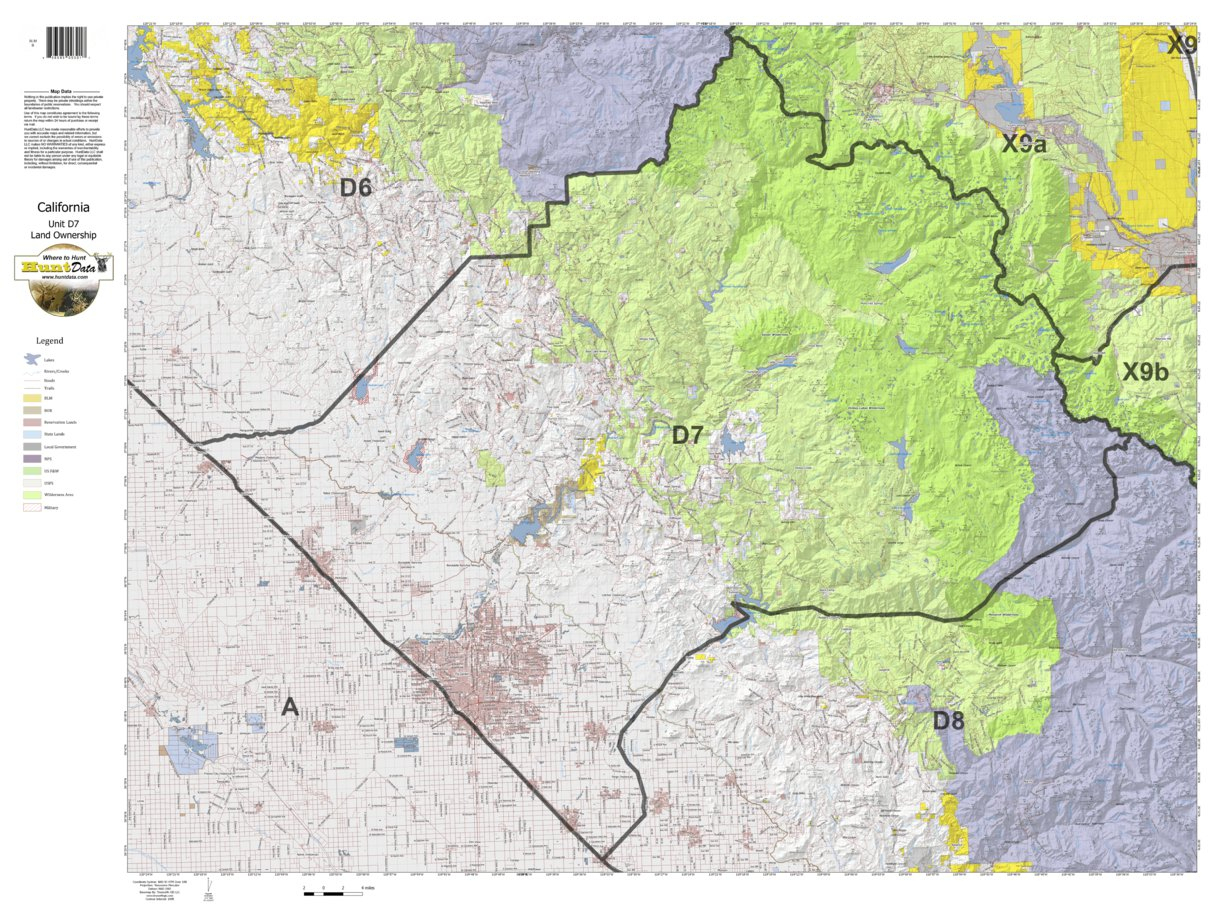
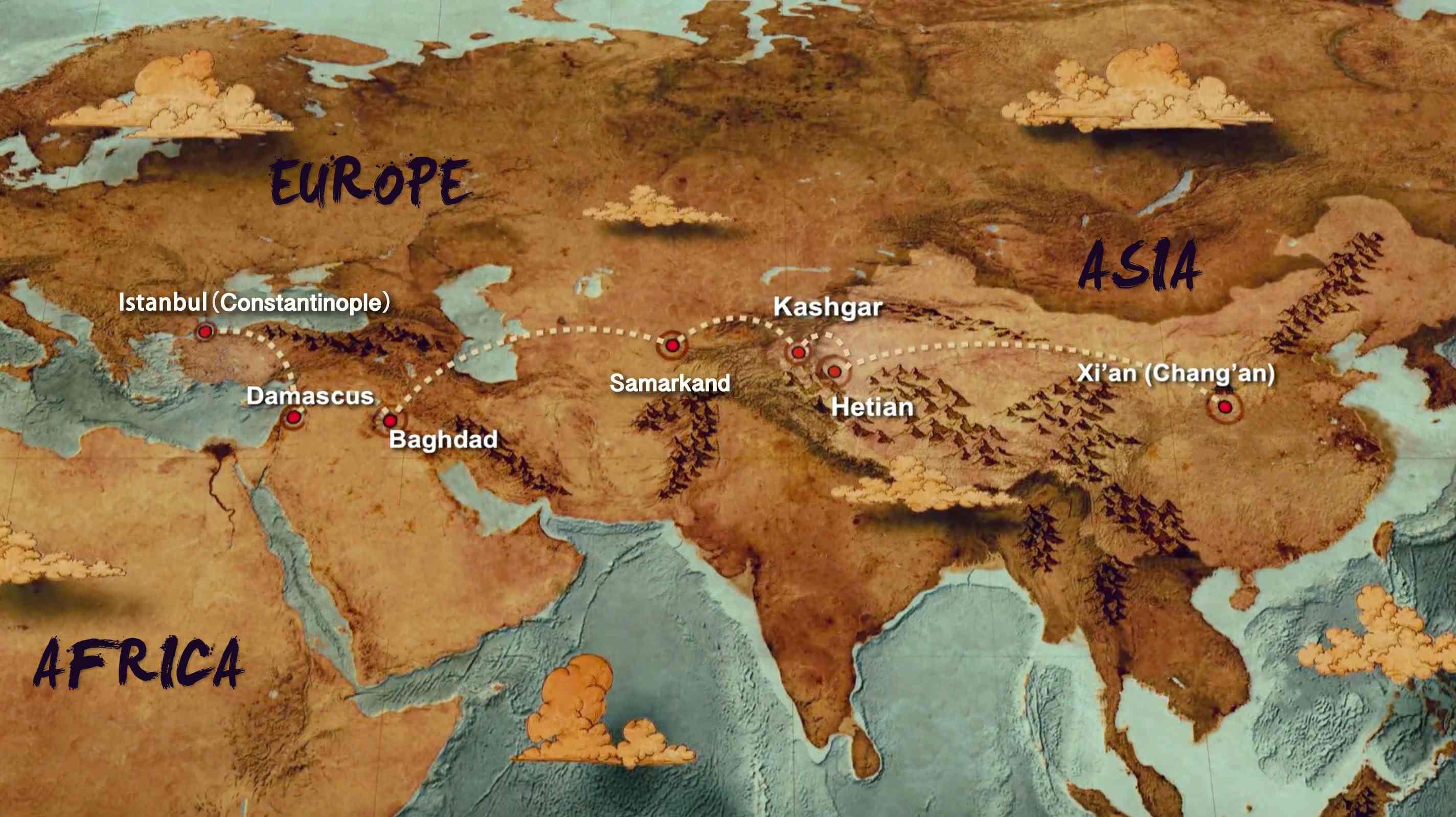
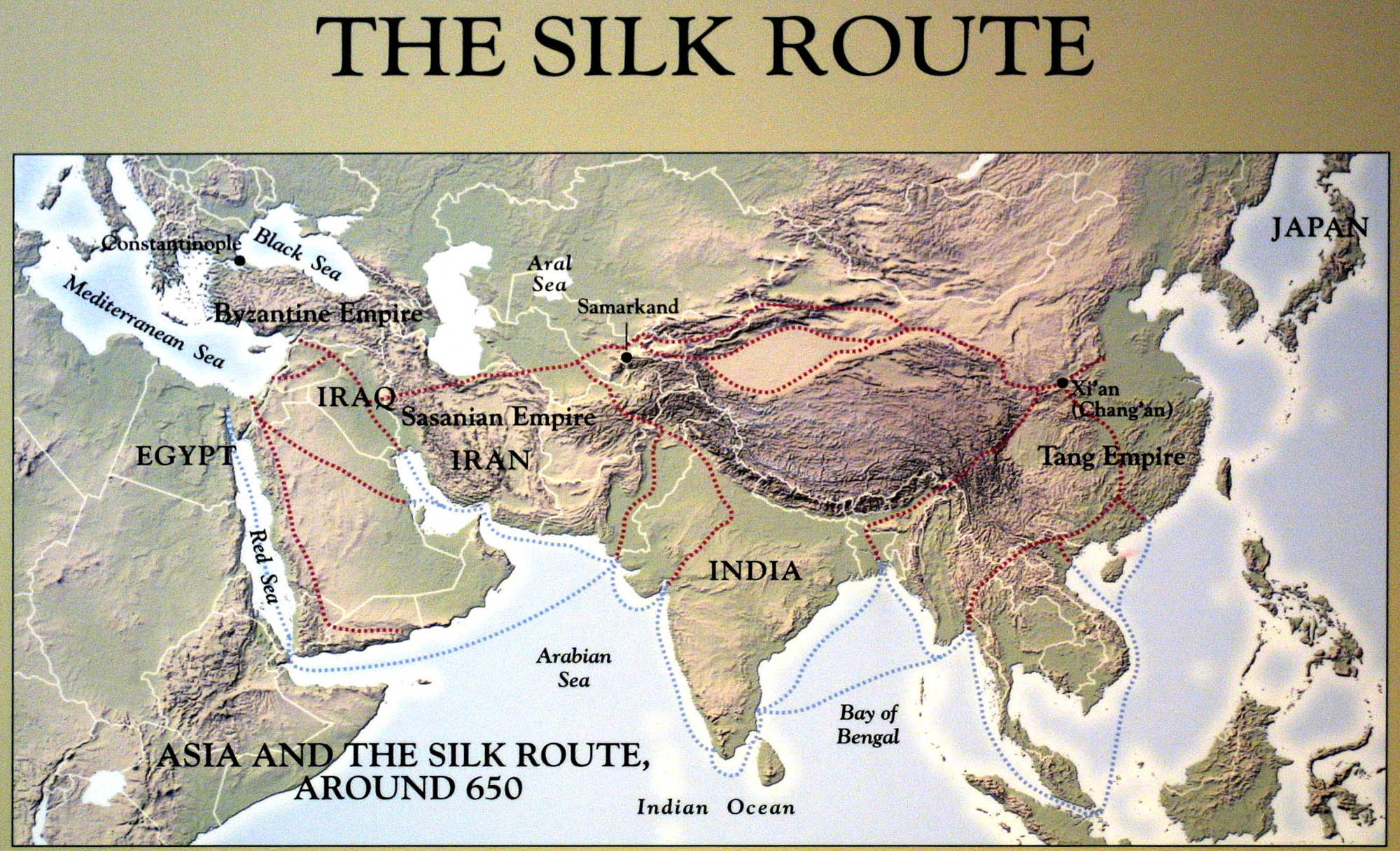
Topographic maps, with their intricate lines and symbols, hold a wealth of information about the Earth’s surface. They depict the terrain’s elevation, slopes, valleys, and other physical features, providing a detailed visual representation of the landscape. However, deciphering these maps can be challenging for the uninitiated. This is where topographic map viewers come into play, acting as user-friendly interfaces that unlock the hidden secrets of these maps.
Understanding Topographic Map Viewers
A topographic map viewer is a digital tool that allows users to interact with and analyze topographic maps. It typically combines a map interface with a range of features, enabling users to explore, measure, and gain insights from the data presented on the map. These viewers are essential for various applications, including:
- Outdoor Recreation: Hikers, campers, and outdoor enthusiasts rely on topographic map viewers to plan their routes, identify trails, and assess terrain difficulty.
- Land Management: Environmental agencies, forestry departments, and land developers use topographic map viewers to analyze land use, monitor changes, and plan projects.
- Urban Planning: Planners utilize topographic map viewers to understand the city’s topography, analyze potential development sites, and assess flood risks.
- Construction and Engineering: Engineers and contractors use topographic map viewers to assess construction sites, plan infrastructure projects, and ensure proper drainage.
- Education: Students and educators use topographic map viewers to visualize geographical concepts, understand elevation changes, and explore different landscapes.
Key Features of Topographic Map Viewers
Topographic map viewers offer a diverse range of features designed to enhance map analysis and exploration. Some common features include:
- Map Navigation: Users can easily pan, zoom, and rotate the map to focus on specific areas of interest.
- Layer Control: Viewers allow users to toggle different map layers, such as elevation contours, roads, landmarks, and water bodies, to customize their view.
- Measurement Tools: Users can measure distances, areas, and elevations directly on the map, providing precise data for various applications.
- 3D Visualization: Many viewers offer 3D representations of the terrain, allowing users to visualize the landscape from different perspectives.
- Data Integration: Some viewers can integrate external data sources, such as weather information, satellite imagery, or aerial photographs, to enhance map analysis.
- Offline Access: Certain topographic map viewers allow users to download maps for offline use, enabling access in areas with limited internet connectivity.
Benefits of Using Topographic Map Viewers
The use of topographic map viewers offers numerous benefits, making them valuable tools for various sectors:
- Enhanced Visual Understanding: Topographic map viewers provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of the terrain, making it easier to analyze and interpret the data.
- Improved Decision-Making: By visualizing the landscape, users can make informed decisions regarding route planning, land management, project development, and more.
- Increased Efficiency: Topographic map viewers streamline map analysis, saving time and effort compared to traditional methods.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Sharing maps and data through topographic map viewers facilitates collaboration among teams, improving communication and decision-making.
- Accessibility and Affordability: Many topographic map viewers are available online or as mobile applications, making them accessible and affordable for a wide range of users.
Exploring Popular Topographic Map Viewers
Several popular topographic map viewers are available online and as mobile applications, each offering unique features and functionalities:
- Google Earth: A widely recognized platform that provides a 3D globe view with integrated topographic maps, satellite imagery, and street view.
- ArcGIS Online: A powerful web-based mapping platform that offers a wide range of tools for creating, analyzing, and sharing maps, including topographic maps.
- Mapbox: A leading platform for creating custom maps and map applications, providing access to various data sources, including topographic maps.
- OpenStreetMap: A collaborative project that creates and maintains a free and open-source map of the world, including topographic data.
- CalTopo: A specialized platform for outdoor enthusiasts, offering detailed topographic maps, route planning tools, and integration with GPS devices.
- Avenza Maps: A mobile application that allows users to download and view topographic maps offline, ideal for outdoor activities and areas with limited connectivity.
FAQs Regarding Topographic Map Viewers
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a regular map?
A: A topographic map focuses on depicting the terrain’s elevation, slopes, and other physical features, while a regular map primarily shows geographical features like roads, cities, and boundaries.
Q: How can I find topographic maps for a specific area?
A: Many online map viewers offer access to topographic maps, or you can search for specific maps from government agencies or specialized mapping companies.
Q: What are the best topographic map viewers for outdoor recreation?
A: Popular choices for outdoor enthusiasts include CalTopo, Avenza Maps, and Gaia GPS, offering detailed maps, route planning tools, and integration with GPS devices.
Q: Can I create my own topographic maps?
A: Yes, specialized software like ArcGIS Pro or QGIS allows users to create and edit topographic maps using various data sources.
Q: Are topographic map viewers free to use?
A: Some viewers offer free basic functionalities, while others require subscriptions or paid plans for advanced features.
Tips for Using Topographic Map Viewers
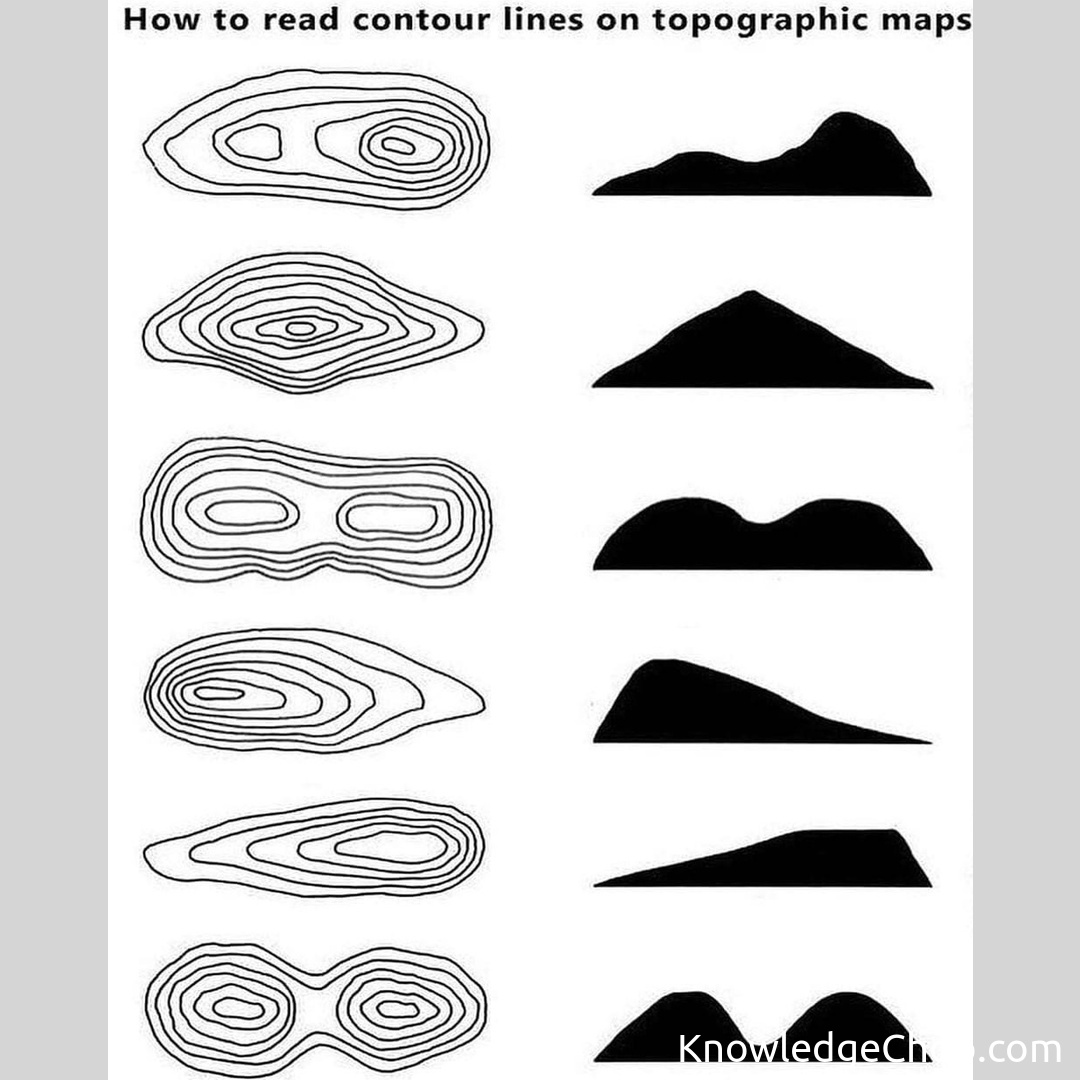
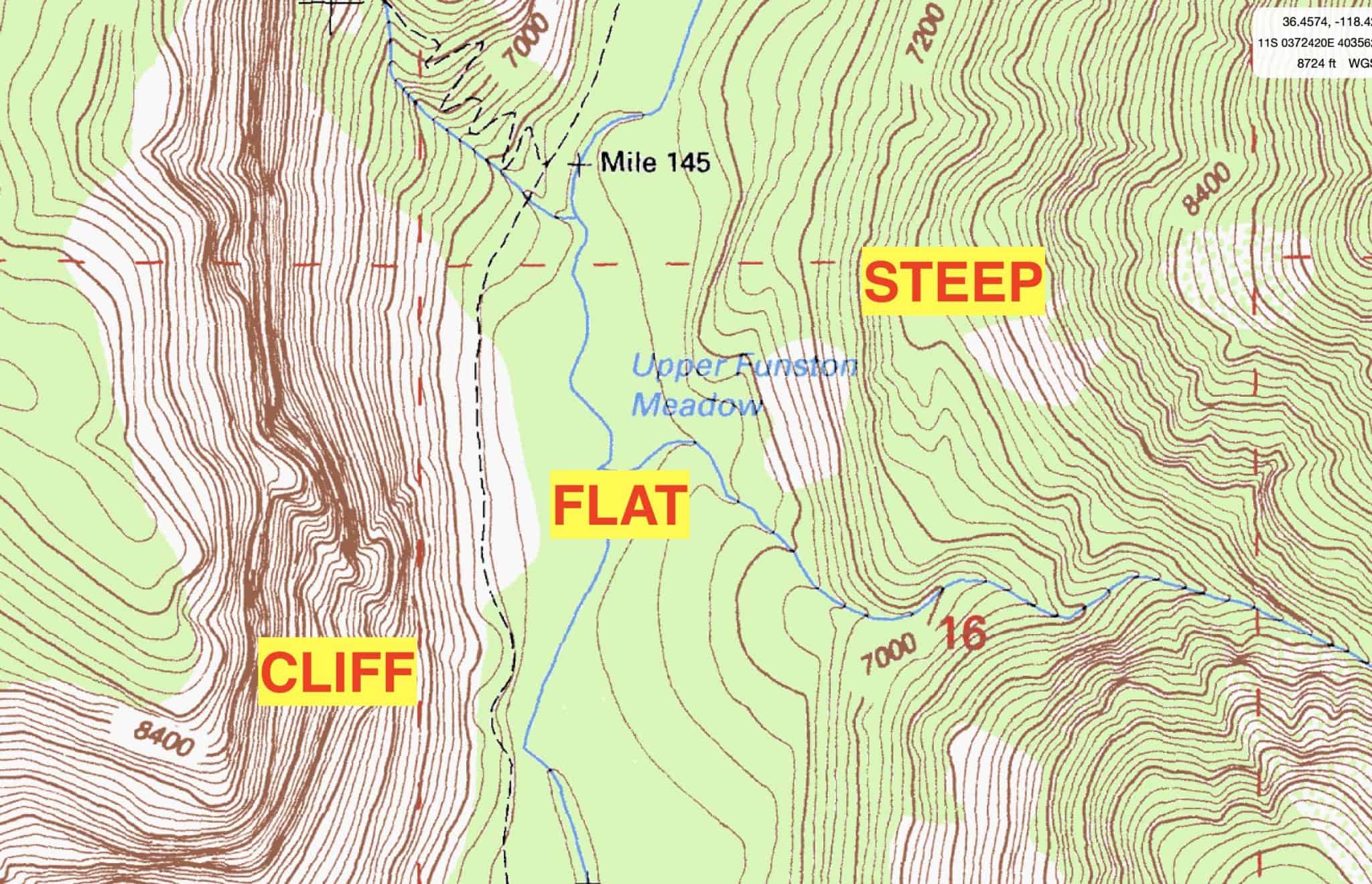
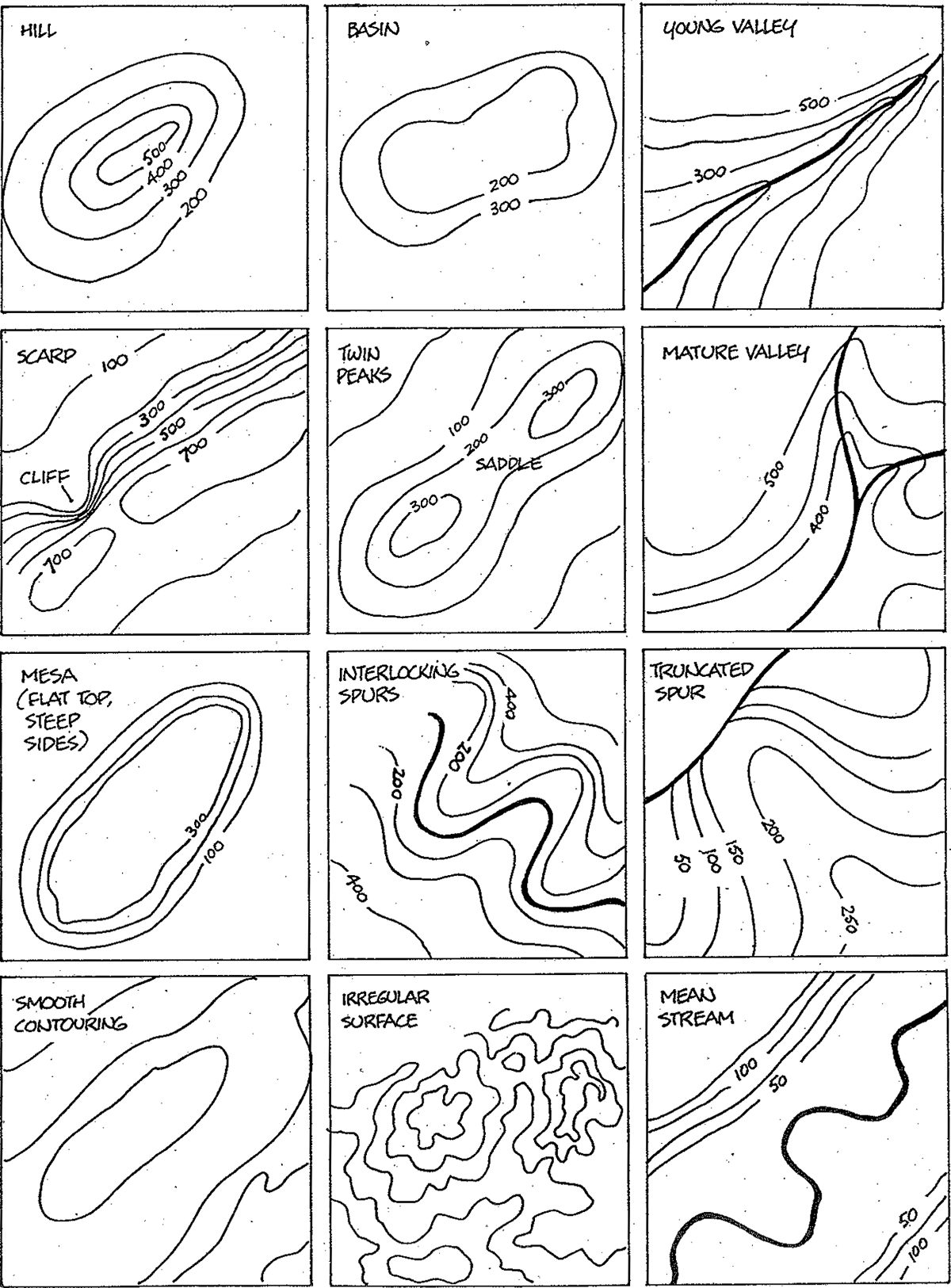
- Understand the map symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used on topographic maps to interpret elevation contours, water features, and other elements.
- Explore different map layers: Experiment with different map layers to find the best combination for your needs, such as elevation contours, roads, and landmarks.
- Utilize measurement tools: Take advantage of the measurement tools to calculate distances, areas, and elevations for accurate planning and analysis.
- Consider 3D visualization: Use 3D views to gain a better understanding of the terrain’s shape and elevation changes.
- Integrate external data: Explore options for integrating external data sources, such as weather information or satellite imagery, to enhance your analysis.
Conclusion
Topographic map viewers have become indispensable tools for navigating and understanding the Earth’s landscape. They offer a user-friendly interface for interacting with topographic maps, unlocking valuable insights for various applications, from outdoor recreation and land management to urban planning and scientific research. With their wide range of features and accessibility, topographic map viewers continue to empower users to explore, analyze, and interpret the world around them with unprecedented detail and clarity. As technology advances, we can expect further innovations in topographic map viewers, enhancing their capabilities and expanding their applications even further.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Viewers. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
























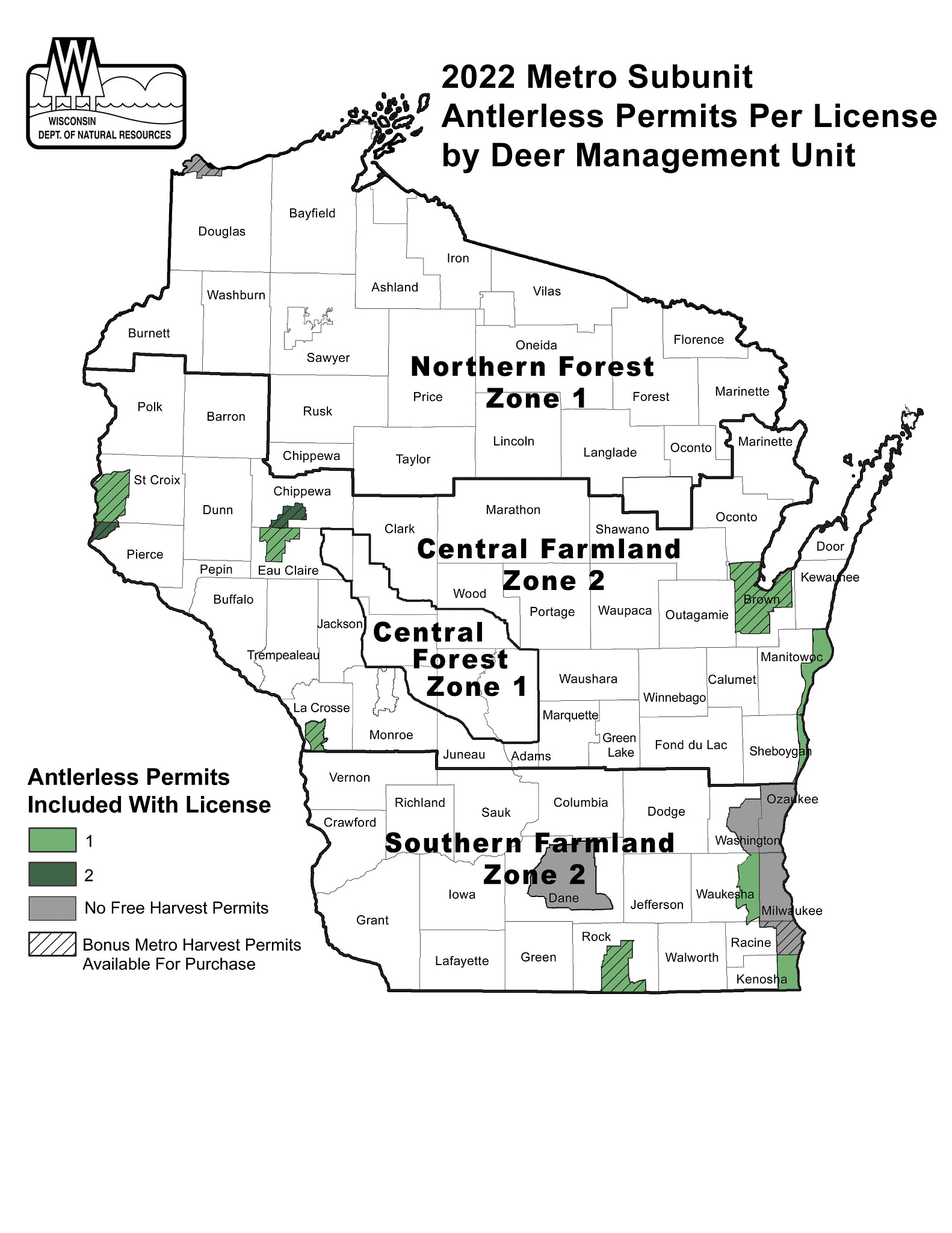
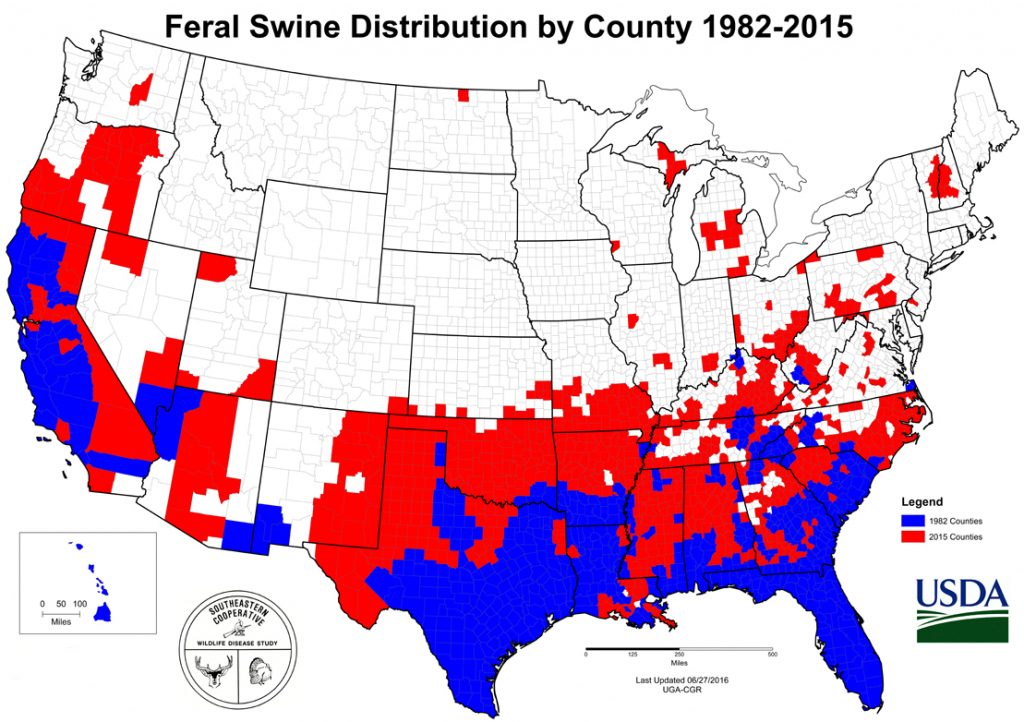
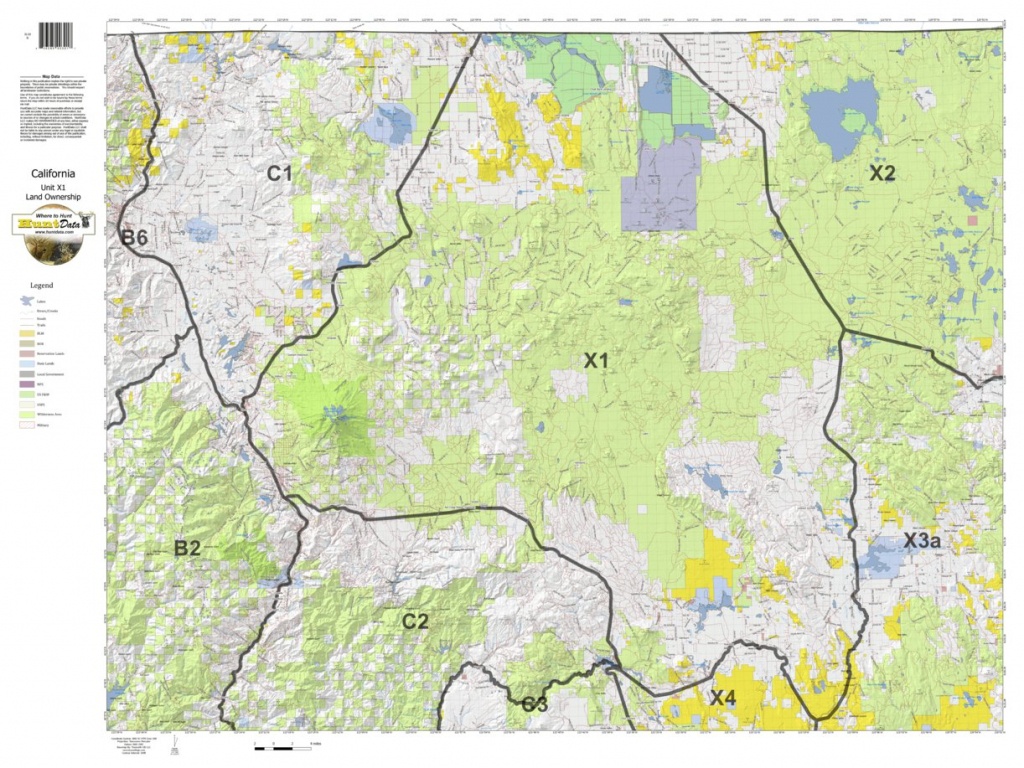

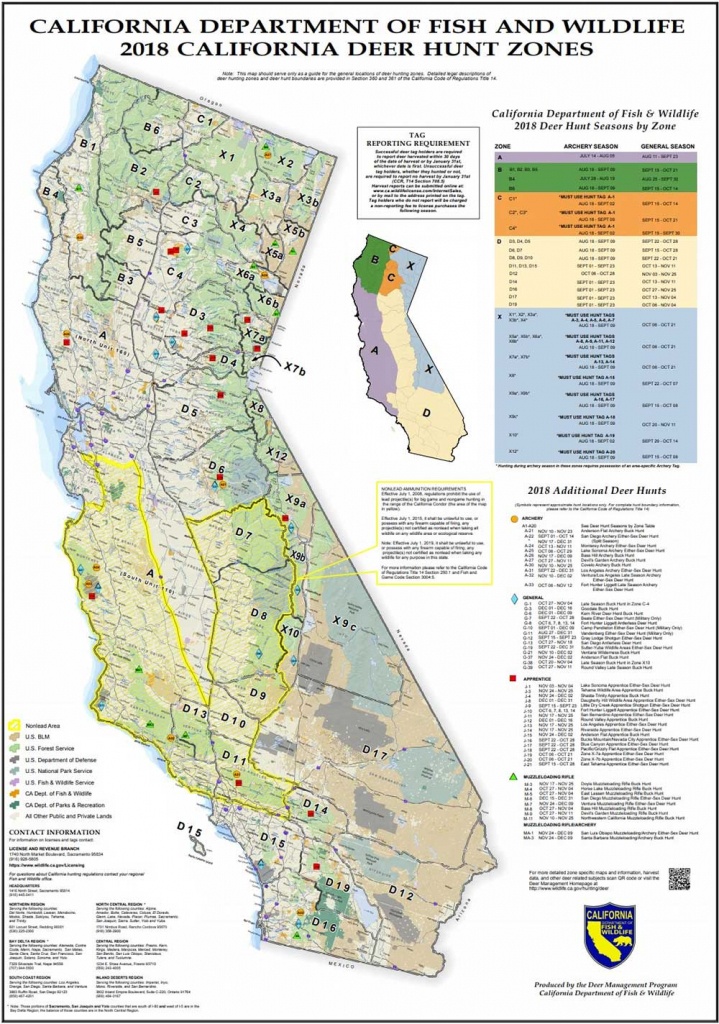
































+03-12-20-3.jpg)