Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map for Georgia: A Guide to Successful Gardening
Related Articles: Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map for Georgia: A Guide to Successful Gardening
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map for Georgia: A Guide to Successful Gardening. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map for Georgia: A Guide to Successful Gardening

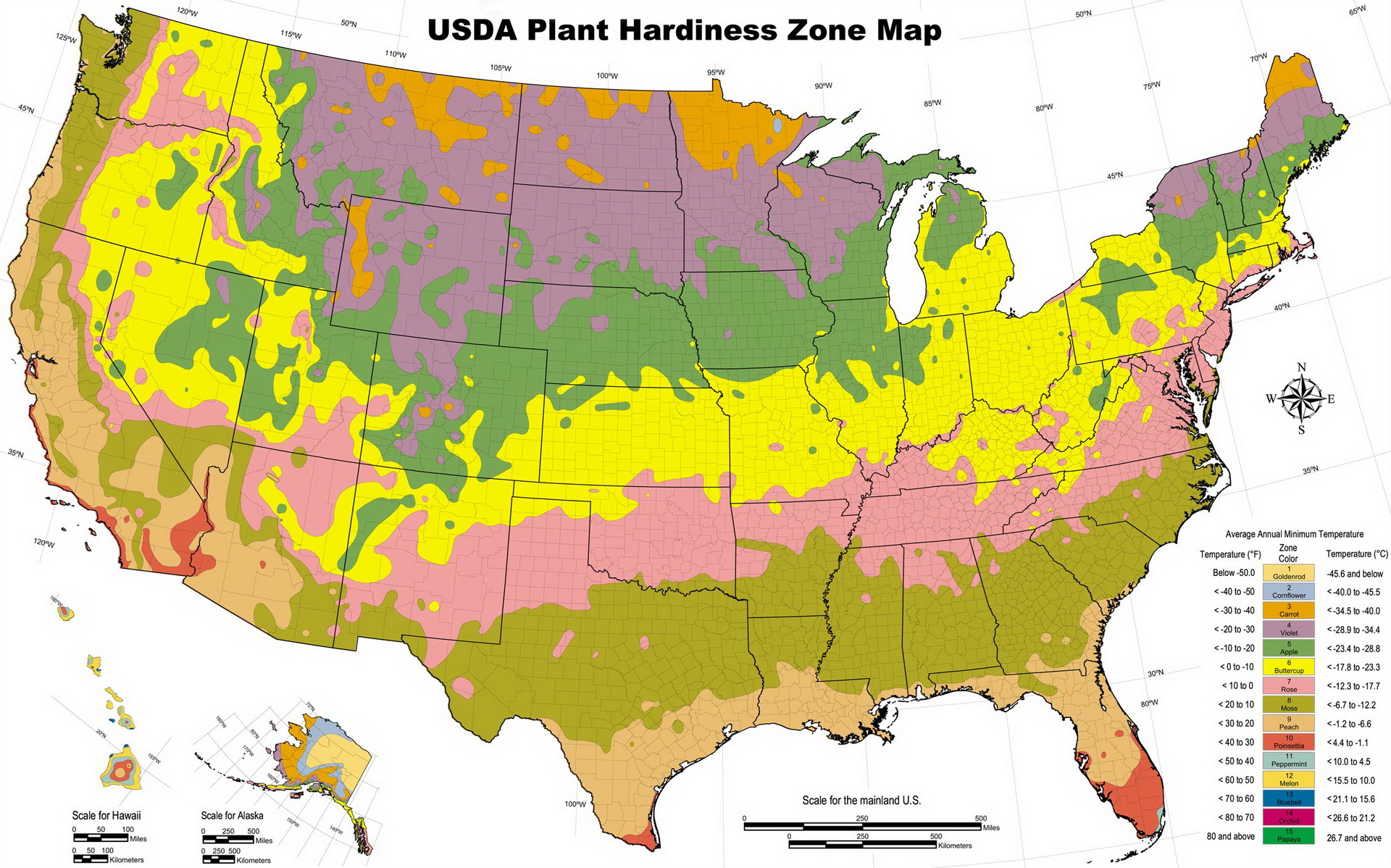
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Plant Hardiness Zone Map is an invaluable tool for gardeners, landscape architects, and anyone interested in growing plants successfully. This map divides the country into zones based on average annual minimum winter temperatures, offering a crucial guide for selecting plants that thrive in specific climates.
The Importance of Understanding Plant Hardiness Zones
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map serves as a fundamental resource for determining the suitability of plants for a particular location. Understanding these zones empowers individuals to make informed decisions about plant selection, ensuring optimal growth and survival. Selecting plants appropriate for the specific hardiness zone significantly increases their chances of flourishing, reducing the risk of frost damage and promoting healthy growth.
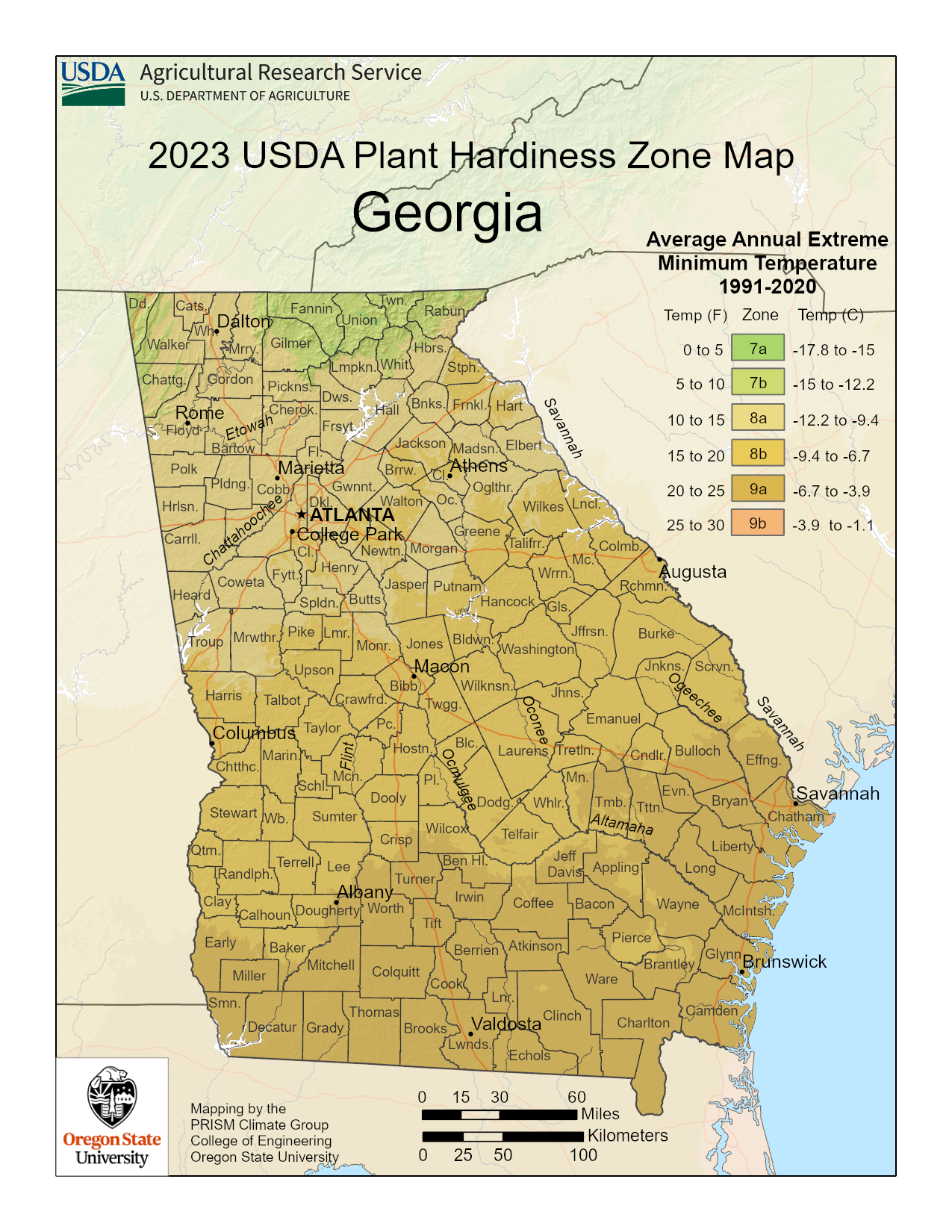
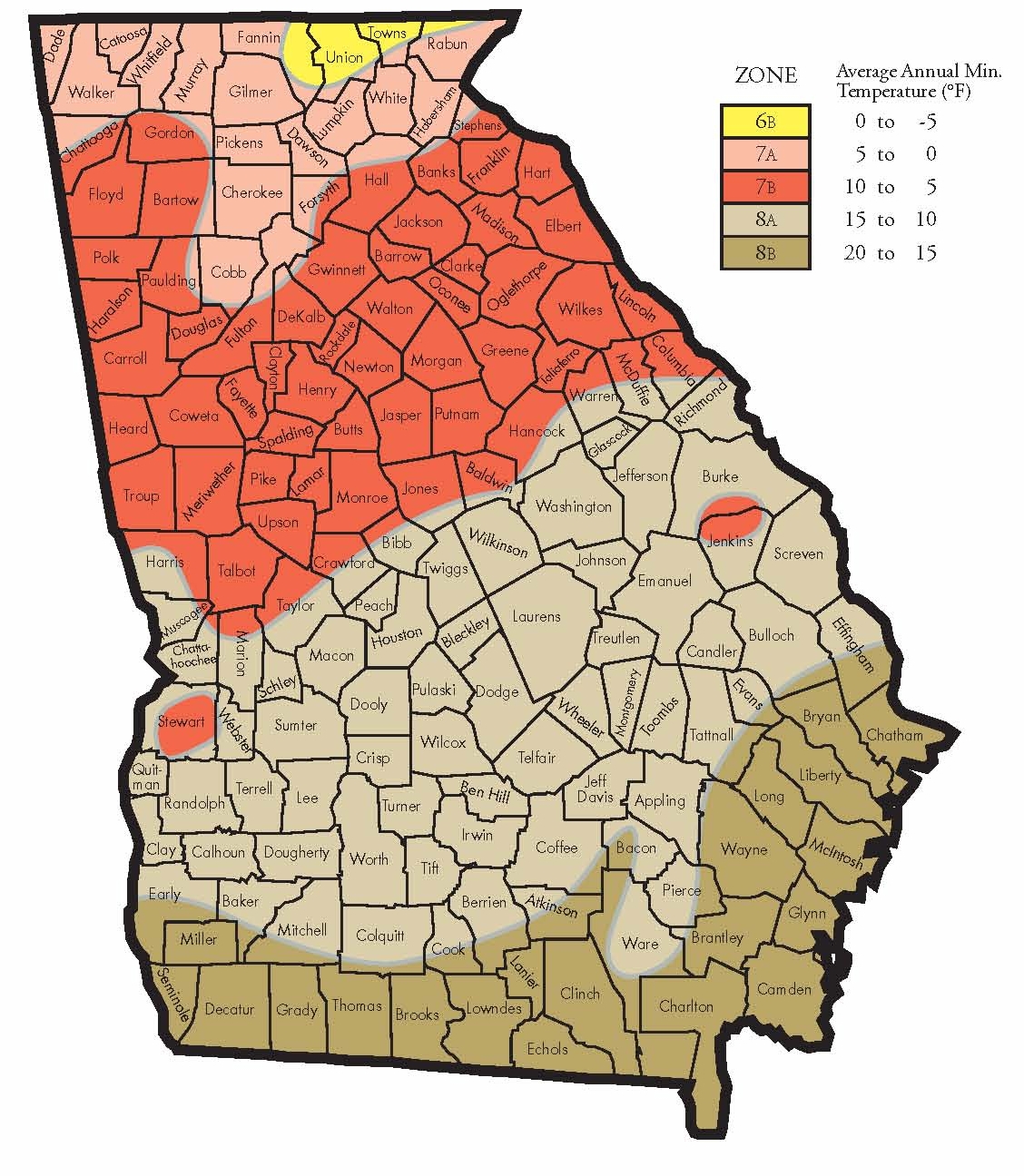
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map for Georgia: A Detailed Breakdown
Georgia, with its diverse topography and varying climates, encompasses a range of USDA plant hardiness zones. This variation allows for a wide selection of plants to thrive across the state.
-
Zone 7a: This zone, covering much of northern Georgia, experiences average minimum winter temperatures between 0°F and 10°F. This zone supports a diverse range of plants, including many popular flowering shrubs, trees, and perennials.
-
Zone 7b: This zone, encompassing a larger portion of northern Georgia, experiences average minimum winter temperatures between 5°F and 10°F. This zone offers similar growing conditions to Zone 7a, allowing for a wide selection of plants.
-
Zone 8a: This zone, spanning a significant portion of central and southern Georgia, experiences average minimum winter temperatures between 10°F and 15°F. This zone supports a broader range of plants, including many subtropical species, and offers a longer growing season.
-
Zone 8b: This zone, encompassing coastal areas of southern Georgia, experiences average minimum winter temperatures between 15°F and 20°F. This zone provides a warmer climate, allowing for the successful cultivation of a wider variety of heat-loving plants.
Factors Affecting Plant Hardiness Zones in Georgia
While the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map provides a general framework, several factors can influence the actual hardiness of a specific location within Georgia. These include:
-
Elevation: Higher elevations generally experience cooler temperatures, potentially shifting a location to a lower hardiness zone.
-
Microclimates: Specific areas within a larger zone can exhibit unique microclimates due to factors like proximity to water bodies, wind patterns, or urban heat islands. These microclimates can alter the actual hardiness of the location.
-
Soil Type: Soil composition and drainage can significantly impact plant growth and survival. Well-drained soils tend to be warmer and more hospitable to plants than poorly drained soils.
-
Urbanization: Urban areas often experience higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas due to the urban heat island effect. This can shift a location to a higher hardiness zone.
Benefits of Using the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
-
Reduced Risk of Frost Damage: Selecting plants appropriate for the specific hardiness zone minimizes the risk of frost damage, ensuring their survival and promoting healthy growth.
-
Increased Plant Success Rate: Knowing the appropriate hardiness zone for a location allows for the selection of plants that thrive in those conditions, significantly increasing their chances of success.
-
Enhanced Garden Diversity: Understanding plant hardiness zones allows for a wider selection of plants, enhancing garden diversity and creating a more vibrant and interesting landscape.
-
Cost-Effective Gardening: Choosing plants suited to the specific hardiness zone reduces the need for costly replacements due to frost damage, making gardening more cost-effective.
-
Environmental Sustainability: Selecting plants that thrive in the local climate reduces the need for supplemental watering and fertilization, promoting a more sustainable and environmentally conscious approach to gardening.
FAQs Regarding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map for Georgia
1. What is the difference between USDA Plant Hardiness Zones and Growing Zones?
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map focuses on average minimum winter temperatures, while growing zones consider various factors, including the length of the growing season, average precipitation, and soil type. While the hardiness zone map provides valuable information about plant survival, growing zones offer a more comprehensive understanding of plant suitability for a specific location.
2. Can I grow plants outside my hardiness zone?
While it is generally recommended to select plants within the designated hardiness zone, it is possible to grow plants outside their zone with careful planning and protection. This can include selecting specific varieties with increased cold tolerance, providing winter protection, and understanding the potential risks.
3. How can I find the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone for my specific location in Georgia?
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is readily available online. Several websites, including the USDA website and the National Gardening Association website, provide interactive maps and tools to identify the specific hardiness zone for any location.
4. What are some tips for selecting plants for a specific hardiness zone in Georgia?
- Research plant tags: Most plant tags include information about the plant’s hardiness zone, making it easy to select appropriate plants.
- Consult with local nurseries: Local nurseries have expertise in the specific climate and growing conditions of the area and can offer valuable guidance on plant selection.
- Consider microclimates: Take into account any microclimates within your property, such as areas sheltered from wind or those near water bodies, which can influence plant hardiness.
Tips for Successful Gardening in Georgia Using the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
- Start with a plan: Before purchasing any plants, consult the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map for your specific location and create a plan based on the suitable plants for your zone.
- Research plant varieties: Explore different varieties within a species, as some may have increased cold tolerance or other desirable characteristics.
- Consider microclimates: Utilize microclimates within your property to create diverse planting areas and expand the range of plants you can grow.
- Provide winter protection: For plants that are marginally hardy in your zone, consider providing winter protection, such as mulch or burlap wraps, to help them survive colder temperatures.
- Monitor plant health: Regularly observe your plants for signs of stress or damage, and take appropriate action to address any issues promptly.
Conclusion
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is an essential tool for anyone interested in successful gardening in Georgia. By understanding the specific hardiness zone for a location, individuals can make informed decisions about plant selection, ensuring optimal growth and survival. Utilizing this resource empowers gardeners to create vibrant, diverse, and thriving landscapes, contributing to the beauty and sustainability of Georgia’s horticultural landscape.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map for Georgia: A Guide to Successful Gardening. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!










![Free Blank Printable World Map Labeled Map of The World [PDF]](https://worldmapswithcountries.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/World-Map-Labeled-With-Countries-scaled.jpg?6bfec1u00266bfec1)






























![[C# MonoGame] Map Editor with Farseer Physics Integration (WIP) - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/hdK8ZU07ouY/maxresdefault.jpg)